Redox Reaction Material: Concepts, Equalizations, Examples
Loading...
Examples of redox reactions we may often hear when we were in high school. A redox reaction is a chemical reaction that occurs due to a combination of reduction and oxidation reactions. That's why the term becomes redox (reduction-oxidation)
This reaction includes all chemical processes from atoms to changes in state of oxidation number or oxidation state. In a complete chemical reaction, this oxidation reaction is always followed by a reduction reaction, so it is known as a redox reaction.
List of contents
Reduction and Oxidation

As mentioned earlier, redox reactions are an abbreviation of reduction and oxidation reactions that occur when an electrochemical process occurs.
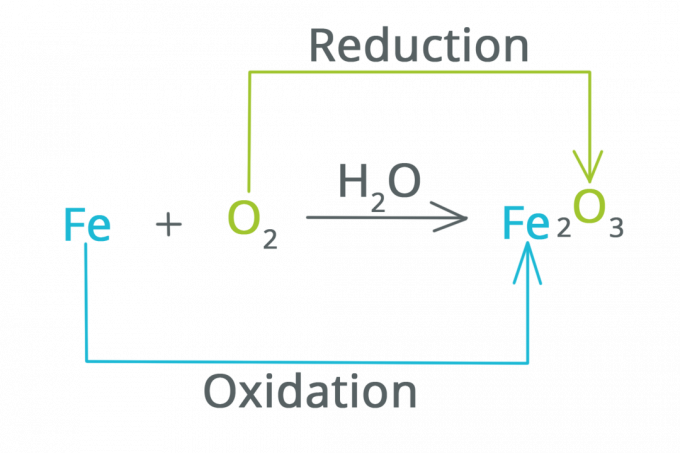
Reduction is a reaction in which the oxidation number decreases and electrons increase. It can be said that reduction is a reaction that causes a substance to lose oxygen.
Oxidation is a reaction in which the oxidation number increases and electrons decrease. It can be said that oxidation is a reaction in which a substance binds to oxygen.
Read: Liquid
Oxidation Number (Oilox)

The concept of a redox reaction involving the transfer of electrons can only occur in ionic compounds, while for covalent compounds it does not. Therefore, a third redox concept emerged, namely based on changes in oxidation numbers.
The oxidation number is the positive and negative charge on an atom. Elements with positive oxidation states are generally atoms with metallic elements, while for elements with negative oxidation states, non-metal atoms are generally used.
Based on the concept of changing the oxidation number, there are eight rules for determining this number, namely:
- The oxidation number of free elements with atomic and molecular shape is 0
- The oxidation number of monatomic and polyatomic ions according to the type of charge on the ion
- The oxidation number of elements in groups IA, IIA, IIIA according to the group they belong to
- The oxidation number of the transition group elements is more than one
- The sum of the oxidation numbers of the elements that make up an ion = the amount of charge it has
- The oxidation number of hydrogen when bonded to a metal = -1, whereas if H is bonded to a non-metal it is +1
- Number of oxygen in peroxide compounds = -1, oxidation number of O in non-peroxide compounds = -2
Reducing and Oxidizing

Before discussing examples of redox reactions, it never hurts to know the reducing agents and oxidizing agents first. In a reaction that involves an oxidation reaction and a reduction accompanied by a change in the oxidation number.
Oxidizing agents are substances that can oxidize other substances or substances that are reduced when they react. While the reducing agent is a substance that can reduce other substances or substances that undergo oxidation when reacting.
Read: Solid
Redox Reaction Characteristics
In addition to examples of redox reactions, other things we should know are the characteristics of this reaction, the following characteristics, among others:
- There are reducing agents and oxidizing agents
- There is a change in oxidation state
- There are free elements such as chlorine, oxygen, cuprum, and others.
Redox Reaction Function

There are various functions of redox reactions in everyday life, namely:
- In order to understand the process of metal corrosion and how to prevent it
- Application of activated sludge as a sewage treatment
- Plant photosynthesis process
- Seeing the oxidation of food in cells
- Bolts and nuts are given a zinc coating, in this layer there is a zinc oxidation process and cation reduction
- Making kitchen utensils from stainless steel so they don't rust
- Making sulfuric acid and processing ore for industrial needs.
Redox Reaction Equalization

Actually, this redox reaction occurs in aqueous solvents, so the equation he has will involve H+ and OH- ions. There are 2 methods used to teach it, namely by means of oxidation numbers and half reactions.
Balancing of redox reactions can be done by balancing the oxidation numbers or oxidation states, both molecular and ionic reactions. This oxidation method is based on “The sum of all e-oxidized equals the total amount of e-reduced”
Examples of Redox Reactions in Daily Life

In examples of redox reaction problems, we often find questions to mention redox reactions in everyday life. The following are examples of redox reactions in everyday life, namely:
1. Clothes Bleach
Bleach is a compound that can remove color from objects. For example, textiles. The loss of color caused by bleach is due to an oxidation reaction.
Oxidizing agents that are often used in bleaching agents are hydrogen peroxide and sodium hypochlorite.
2. Plant Photosynthesis Process
Photosynthesis is a natural biological oxidation-reduction reaction process. Photosynthesis itself is a very complex process.
Organisms from the process of photosynthesis can use the energy in sunlight to produce sugar and oxygen from redox reactions.
3. Propane Burning
Another example is combustion. In propane combustion, the air contains O2, while the carbon atoms will be oxidized and form CO2, while oxygen will become H2O.
Read: Gas Substance
Examples of Redox Reaction Problems

Advertisement
1. Determine the oxidation state of the element in the compound SO42- and NaNO3
Answer:
SO42– = polyatomic ion
Oxx of a polyatomic ion = total charge = -2
Oxox of O in the compound = -2
The block S + 4. oxidation state = -2
-6 + 4. (-2) = -2
So, the oxidation number of S = -6 and the oxidation number of O = -2.
NaNO3 = compound without charge
Total oxidation state = 0
Oxox of O in the compound = -2
Oxx of Na (metal) = number of valence electrons = +1
The oxidation state is Na + the oxidation number is N + 3. oxidation state = 0
+1 + (+5) + 3. (-2) = 0
So, the oxidation state of Na = +1, the oxidation state of N = +5, and the oxidation state of O = -2
2. Which of the following is the oxidizing agent, the reducing agent, the reducing agent, and the product of the following chemical reaction.
Fe + HCl → FeCl3 + H2
Answer:
Oxidizing agent (reduced) = HCl
Reducing agent (experiencing oxidation) = Fe
Oxidation product = FeCl3
Reduction result = H2
3. Balance the following redox equations
Bi2O3 + ClO– → 2BiO3– + Cl– (language atmosphere).
Answer:
How to oxidation number
Equalized left and right charge: 2OH– + Bi2O3 + ClO– → 2BiO3– + Cl–
The same number of atoms: 2OH– + Bi2O3 + 2ClO– → 2BiO3– + 2Cl– + H2O
So Equivalent Reaction: 2OH– + Bi2O3 + 2ClO– → 2BiO3– + 2Cl– + H2O
Half Reaction Way
Redox: Bi2O3 + 2ClO– → 2BiO3– + 2Cl–
Balance the charge by adding OH– (base).
2OH– + Bi2O3 + 2ClO– → 2BiO3– + 2Cl–
Balance the number of atoms by adding H2O.
2OH– + Bi2O3 + 2ClO– → 2BiO3– + 2Cl– + H2O
So Equivalent Reaction: 2OH– + Bi2O3 + 2ClO– → 2BiO3– + 2Cl– + H2O
Studying examples of redox reactions and even their complete discussion is not easy, moreover there are so many compounds that must be memorized in this material. Therefore, don't hesitate to keep practicing in order to understand it well.
ADVERTISEMENT
X CLOSE
