Buffer Solution Material: Principles, Types, Example Problems
Loading...
One of the materials discussed in Chemistry is a buffer solution which plays an important role in stabilizing pH, both in the body and in certain chemical reactions. This solution is also called a buffer or buffer solution.
Buffer solutions are often incorporated into products used in everyday life. A simple example is eye drops that do not cause a stinging sensation when they are dropped into the eye. How did it happen? The following is a detailed description of the buffer solution.
List of contents
Definition of Buffer Solution

A buffer solution is a solution that does not change the pH level at all when added water and undergoes little change when mixed with acids or bases in high concentrations low.
In other words, this solution called a buffer has a pH level that tends to be stable even though other liquids are added to it. For example, a buffer with a pH of 5 will remain at the same level after being mixed with water.
The buffer with a pH of 5 will usually only change to a level of 5.1 or 4.9 after the addition of a small amount of acid or base solution. So, there is no change in pH levels to be too high or too low.
Properties of Buffer Solution

An easy way to identify and distinguish buffers from other types of solutions is to know their properties. Some of the characteristics of buffers include:
- Has the ability to maintain the initial pH despite the addition of other solutions such as water, strong bases or strong acids with certain levels;
- Can maintain the initial pH even though the solution undergoes a dilution process;
- The power to maintain pH will be greater if it has a large number of moles;
- Able to maintain the value of Ka, both at a temperature that changes frequently or at a constant temperature.
Read: Liquid
Buffer Solution Principle

Please note that buffers are categorized into 2 types, namely acidic and basic solutions. What does it mean?
- Acid buffer is a type of solution made from a mixture of weak acid and its conjugate base so that it is effective in maintaining the initial pH in acidic conditions;
An example of an acid buffer is CH3COOH and CH3COO– or CH3COOH and CH3COONa, HF and NaF as well as NaH2PO4 and NaHPO4. - Base buffer is a type of solution that comes from a weak base and its conjugate acid which is mixed so that it is able to maintain the initial pH in alkaline conditions.
An example of a base buffer is N2H4 and N2H5+ as well as NH3 and NH4+.
Acids and bases mixed with their respective conjugates will give rise to ionic equilibrium in water. As a result, the buffer solution is able to keep the pH within a certain range without changing much.
Then, how does it work? Here's a simple illustration to clarify:
- If the mixture of weak bases (NH4OH) and its conjugate acid are added to a small amount of base, a reaction will occur by the OH ion.– and positive ions from the conjugate acid (NH4+);
- If the mixture of weak acids (CH3COOH) and its conjugate base (CH3COO–) is added to a relatively small amount of acid solution, a reaction will occur between H. ions+ and negative ions from the conjugate base (CH3COO–).
Read: Stoichiometry
Buffer Solution Function

In everyday life, buffers have very important uses for humans and plants. What are the intended functions?
- For plants, buffers are used to balance pH levels in plants that are cultivated using a hydroponic system. Balanced pH levels will have a good effect on plant development;
- For humans, buffers play a role in keeping blood pH unchanged. The pH level in the blood is maintained properly so that metabolic processes in the body run smoothly. The types are hemoglobin buffer, phosphate buffer and carbonate buffer;
- For humans, buffers still have another function, namely maintaining a consistent pH level in the mouth so that it does not cause tooth decay. The solution to maintain the pH is released by saliva so that the acid from food that enters the mouth can be neutralized.
Buffer Solution Capacity

In fact, the buffer solution has a capacity which is also known as the buffer intensity or buffer index. Buffer capacity is a measure that shows the ability of the buffer to maintain a consistent pH level when mixed with a strong base or strong acid.
The intensity of the buffer is greatly influenced by the amount of content of the bases or acids in each solution. The buffer solution that has the largest capacity is the solution that contains large amounts of acids or salts.
For example, CH3COOH and CH3COONa amounted to 2 moles greater capacity than the combination of CH3COOH and CH3COONa which only amounts to 1 mole.
Meanwhile, if the content is small, then the buffer capacity is also small. A buffer index with a high level will work more effectively to neutralize acids or bases before a significant change in pH occurs.
In addition, the buffer capacity is also influenced by the ratio of the number of moles of acid-salt or base-salt. A large comparison, of course, produces a buffer whose intensity is also large.
For example, CH3COOH and CH3COONa whose ratio is 1:1 (the value is equal to 1) is greater than CH3COOH and CH3COONa whose ratio is 1:2 (the value becomes 0.5).
Read: Density Formula
Buffer Solution Formula

Advertisement
How are buffers calculated? There is a formula that must be applied to perform these calculations. The formula is divided into two namely special acid buffer and alkaline buffer.
First, the formula for the acid buffer solution is as follows:

Ka refers to the constant of the acid equilibrium
V is the valence which is the amount of the weak conjugate base or ion content
Second, the formula for an alkaline buffer solution is:
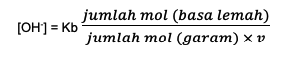
Kb is a constant of base equilibrium
V is the valence which is the amount of conjugate acid or weak ion content
Examples of Buffer Solution Problems and their Discussion

Here's an example question to further hone your understanding of buffers:
1. CH solution3COOH 0.1 M, Ka (10-5) as much as 200 ml was added to the CH. solution3Also 200 ml of 0.1 M COONa, then what is the pH of the mixture?
The first step is to calculate the moles of each solution first:
mole CH3COOH = m v = 0.1 200 = 20 mmol
mole CH3COONa = m v = 0.1 200 = 20 mmol
Then, straight into the buffer formula for an acid buffer:

Based on these calculations, the concentration of H. ions+ already known that is. Next, enter the calculation to find the pH, namely:
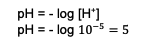
So, the pH of the resulting mixture is 5.
2. NH. solution3 0.1 M Kb (10-5) as much as 400 ml mixed with a solution of NH4Cl 0.1 M as much as 200 ml. Determine the pH of the mixture that appears because of the mixture!
The first step is to find out the moles of the solution, namely:
moles of NH3 = m v = 0.1 400 = 40 mmol
moles of NH4Cl = m v = 0.1 200 = 20 mmol
After that, use the base buffer formula to determine the concentration of OH. ions– which will be used to calculate the pH later.

Then, enter into the calculation of the pH of the mixture, namely:
pOH = – log [OH–] = 5 – log 4
pH = 14 – pOH
pH = 14 – (5 – log 4) = 9 + log 4
Conclusion
Buffer is a solution that is able to maintain the initial pH level in a certain range after being added with a small amount of acid or base solution. There are 2 types, namely an acid buffer from a weak acid and its salt and an alkaline buffer from a weak base and its salt.
Learning about buffer solutions that have a function in life is important. Not only understand the working principle, but also know the pH of the mixture of the buffer that has been formed and the acid-base reaction to form a buffer.
X CLOSE
Advertisements
ADVERTISEMENT
X CLOSE
