Stoichiometry Chemistry: Concepts, Types, Example Problems
Loading...
The notion of stoichiometry is a science in the field of chemistry which is the basis for calculating the quantitative relationship of reactants and products that occur in chemical reactions. It is based on the equation of the reaction and the basic laws.
The characteristic of stoichiometric reactions is that there is no residue from the reactants or reactions because they have all been used up. Generally, this material has been taught in high school grade 10 and often comes out in various school exams. Here's a full explanation.
List of contents
Stoichiometric Chemistry Materi
Studying stoichiometry means having to understand several related things. Some of these things include the basic laws of chemistry, concepts in chemistry that are related and their types. Practice questions are also needed so that the understanding they have is more mature.
Basic Laws of Chemistry for Stoichiometry
There are 5 basic laws in chemistry that are important to know to understand stoichiometry, including:
1. Law of Conservation of Mass

In 1789, a chemist named Lavoisier formulated the law of conservation of mass. The essence of the law of conservation of mass is that the total weight possessed by a substance will remain the same, both before and after a chemical reaction.
For example, the mass of wood before being burned with the mass of the result of burning wood does not change. In other words, the mass of a substance or object possessed before and after a reaction occurs is conserved.
2. Law of Fixed Comparison

Joseph Proust was an expert who created the law of fixed proportions in 1799. This law states that the ratio of the total weight of the elements that make up a particular compound will not change or remain constant.
As an illustration, the ratio of the masses of substance A and substance B contained in a solution is always constant and is not affected at all by the volume of the solution.
3. Law of Multiple Comparison

Furthermore, the basic law of stoichiometry that needs to be understood is the law of multiple ratios made by John Dalton in 1803. Multiple comparisons are an extension of the law of constant comparison.
The law of multiple proportions states that when 2 elements form more than 2 compounds, their total weight is one of the constituent elements is constant, then the total weight of the other constituent elements is an integer simple.
4. Gay Lussac's Law
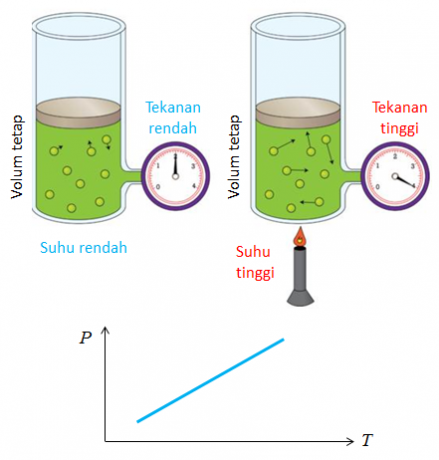
Another name for the law discovered by Joseph Gay Lussac is the law of the ratio of volumes. The conclusion obtained from the law of volume comparison is that temperature and pressure affect the change in gas volume.
5. Avogadro .'s Hypothesis
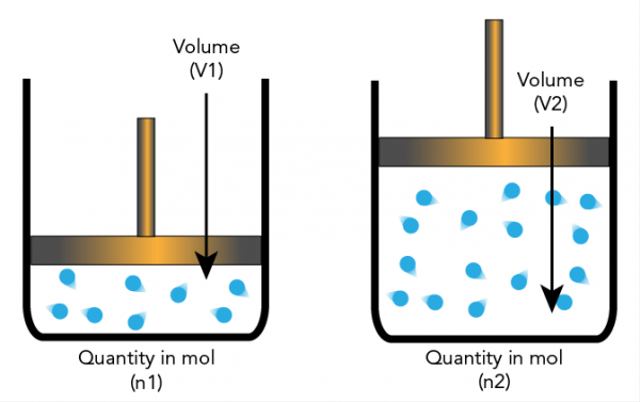
Amadeo Avogadro put forward a hypothesis that elemental particles can be molecules and elements so that they are not always atoms. This leads to further explanations on which stoichiometry is based.
Avogadro's hypothesis states that if temperature and pressure have the same number, then the ratio of gases with the same volume will have the same number of molecules.
Read: Colloidal Material
Chemical Concepts to Understand in Stoichiometry
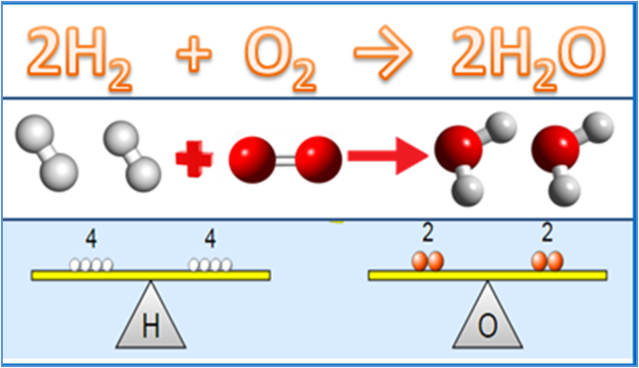
Not only basic laws, other important things that are closely related to stoichiometric material are concepts in chemistry. At least, there are 4 concepts that need to be understood, namely relative atomic mass, relative molecular mass, molarity and the concept of moles.
1. Relative Atomic Mass (Ar)
In chemistry, the abbreviation for relative atomic mass is Ar. This concept refers to the total atomic weight which is determined by comparing it with the standard atomic total weight. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry uses the carbon atom as the standard of determination.
The carbon atom or the C-12 isotope was chosen because it has a stable nucleus which is more inert than other types of atoms. Inert refers to the resistance to chemical reactions that occur.
2. Relative Molecular Mass (Mr)
Furthermore, there is the concept of relative molecular mass which is abbreviated as Mr. The concept of stoichiometry Mr is the total weight of a molecule whose measurement is using atomic mass units.
Advertisement
Based on this concept, different molecules with the same compound have the possibility of differences in molecular mass because the isotopes they contain are from different elements.
3. Mol Concept
Chemistry has a unit of account to simplify the calculation process, namely the mole. The mole concept is based on Avogadro's number to represent the number of molecules, atoms or ions. According to this concept, 1 mole is equivalent to 6.022 x 1023 the particles of the substance.
The mass of one mole can be said to be equivalent to Ar and Mr in grams. For example, the total weight of the molar mass of carbon 12 g/mol is equal to Ar of carbon 12 amu.
4. Molarity
Molarity is a concept in chemistry that states the number of moles of solute present in 1 liter of solvent. In other words, molarity refers to the concentration possessed by the amount of solute per unit volume.
Read: Molarity Formula
Types of Chemical Stoichiometry

Please note that there are 3 types of stoichiometry namely reactions, gases and compounds or compositions. Here's a full explanation:
1. Reaction Stoichiometry
The definition of reaction stoichiometry is a type of concept that emphasizes the quantitative relationship between substances present in a particular chemical reaction. This concept is used to balance the chemical equations that occur.
Based on this explanation, it can be said that the substances that participate in a chemical reaction affect the quantitative relationship between these substances.
2. Gas Stoichiometry
Next, gas stoichiometry refers to the concept of chemical reactions in which gases are present. A gas at a certain pressure, temperature and volume is considered an ideal gas. The gas consists of only one set of particles whose motion is random and does not interact.
The ideal gas equation is expressed by P.V = n. R.T. In the formula, P is the pressure in atm, V is the volume of the gas in liters, n is the number of moles, T is the temperature of 273 K and R is the gas 0.082 L atm/mol K.
3. Compound Stoichiometry
The definition of stoichiometry of a compound or composition is a concept that expresses the quantitative relationship of the total weight or the amount of substance that the elements in a particular compound have.
This concept is often used to explain the total weight of hydrogen and nitrogen which have combined to form complex ammonia.
Read: Density Formula
Examples of Stoichiometry Problems and Discussion

How to solve problems related to stoichiometry. The following is an example of a question and its discussion to make it easier to understand:
1. Find the number of each atom contained in 2 moles of H2O!
It should be noted that H2O has 2 H atoms and 1 O atoms. Then the solution becomes:
The number of H atoms = 2 2 mol 6.02. 1023 atoms/mole = 24.08. 1023 atom. So, the number of atoms contained in 2 moles of H is 24.08. 1023.
Now, just count the number of atoms owned by the O atom, namely:
The number of O atoms = 1 2 mol 6.02. 1023 atoms/mole = 12.04. 1023 atom. Based on these calculations, it can be seen that the number of atoms in 2 moles of O is 12.04. 1023.
2. Calculate the total weight or mass possessed by 2 moles of C6H12O6 (glucose)! It is also known that the sum of Ar C = 12, O = 16 and H = 1.
The solution:
From the question, it can be seen the following information:
n = 2 mol
Mr C6H12O6 = (6 Ar C) + (12 1) + (6 16)
= 180
Next, the calculation becomes:
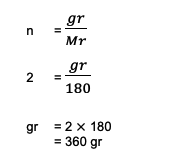
So, the total weight of 2 moles of glucose or C6H12O6 as much as 360 grams based on these calculations.
One of the important topics in chemistry is stoichiometry which is the basic concept of calculation to find out the quantitative relationship between chemical equations and formulas. Several other concepts in chemistry also need to be understood because they are related to stoichiometry.
X CLOSE
Advertisements
ADVERTISEMENT
X CLOSE
