Definition of FPB and KPK and Examples
Loading...
Mathematics subject matter which discusses the KPK and FPB was first introduced in the fourth grade of elementary school. Maybe many still remember this lesson, including how to calculate it. Even so, not a few have forgotten the material.
If you are one of those who forgot the KPK and FPB materials, there is no need to worry because the following review will discuss in full about these materials. For more details, let's see the discussion below.
List of contents
Definition of KPK

What are KPK and FPB? KPK stands for Least Common Multiple, which is the smallest multiple of a number that is equal to a certain number. Multiples can be defined as the product of a number by a natural number.
For example, it is as follows:
Multiples of 2 = 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, …
Multiples of 3 = 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, …
Multiples of 4 = 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, …
Multiples of 5 = 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, …
In English, KPK is known as LCM or Least Common Multiple. Where the LCM of two or more numbers is the least common of the two or more numbers.
Or it can be said that the LCM of two or more numbers is the smallest positive integer that can be divided by 2 or more numbers. For more details, you can listen to how to find the KPK and GCF values below.
Read: Fractions
How to Find the KPK Value

There are two methods that can be used to get the KPK value, namely the simple method and the factorial method. The following is an explanation of the two methods.
1. Simple Method
The first way you can try to find the value of the LCM is a simple method. For example, suppose you want to find the LCM value of 4 and 18, then the method is as follows:
Multiples of 4 = 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36, …
Multiples of 18 = 18, 36, 54, 72, …
Based on the multiples of 4 and 18 above, the smallest multiple of the same number is 36. Thus, the LCM of 4 and 18 is 36.
2. Factorial Method
Another method that can be used to find the LCM value of two numbers is the factorial method. For example, for example, you want to find the LCM of the numbers 30 and 45, then the method is as follows:
Describe the factors of the number for which the LCM value is 30 and 45.
30 = 2 x 3 x 5
45 = 32 x 5
LCM = 2 x 32 x 5
= 18 x 5
= 90
Thus, the LCM of 30 and 45 is 90.
Read: Integers
Understanding FPB

The next material and discussion regarding the KPK and FPB is about the meaning of FPB. GCD stands for Greatest Common Divisor which in English is known as GCD or Great Common Divisor.
The GCF of two or more numbers is the largest positive integer and can divide the two or more numbers until it runs out.
Read: ABC formula
How to Find the GCF Value
Advertisement
To find the GCF value of two numbers, there are two ways that can be done, namely using the simple method and the factorial method. The following is an explanation of each method of calculating the GCF.
1. Simple Method
The first method you can try to find the GCF value is a simple method, for example, if you want to find the GCF from numbers 18 and 4, the method is as follows:
Factor 18 = 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18
Factor 4 = 1, 2, 4
Based on the simple method above, it can be seen that the largest and the same factor of the numbers 18 and 4 is 2. Thus, the GCF of 18 and 4 is 2.
2. Factorial Method
In this factorial method, there are two alternative ways that can be used to find the GCF of a number. One way is to use a factor tree. Factor trees are usually used to find numbers whose factorization is large, such as above 100.
To make this factor tree the method is quite easy, you just write the numbers and then make two branches that are consists of the left branch which is a prime number and the right branch which is the result of the division.
Then the branch is continued down with the prime numbers and the result of the division until it runs out. For example, suppose you want to find the prime factorization of the number 100, then the factor tree looks like this:
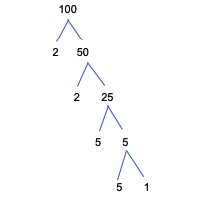
Based on the factor tree image above, it can be seen that the factorization of the number 100 is 2 x 2 x 5 x 5 or 22 x 52.
Read: Algebra
Examples of KPK and FPB Questions

If previously we have discussed the meaning and some simple examples to find the value of KPK and FPB separately, the following are some examples of questions that can be studied to better understand the KPK material and FPB.
1. Ali owns two motorbikes that must be serviced regularly at the workshop. The first motorbike must be serviced every 25 days, while the second motorbike must be serviced every 30 days. How many days does Ali have to bring his two motorbikes for service?
Discussion:
From the problem above, we will look for the KPK of two numbers, namely 25 and 30, as for the method as follows:
- Simple Method
The LCM of 25 and 30 is:
25, 50, 75, 100, 125, 150, 175, 200.
30, 60, 90, 120, 150, 180, 210.
Based on the simple method with multiples of the numbers above, it is known that the LCM of 25 and 30 is 150. So Ali had to bring his two motorbikes for service every 150 days.
- Factorial Method
Factorial of 25 = 52
Factorial of 30 = 2 x 3 x 5
Thus, the LCM of 25 and 30 is 2 x 3 x 52 = 150. So every 150 days Ali has to take his two motorbikes to a repair shop for service.
2. Siska has 15 cheese buns and 20 peanut buns. Siska will put the bread into a food bag with the same composition to share. How many bags can Siska make?
Discussion:
From the questions above, we will find the GCF of the numbers 15 and 20 using the following method:
The factors of 15 are 1, 3, 5, 15.
The factors of 20 are 1, 2, 4, 5, 10, 20.
Thus, the GCF of the two numbers is 5. So the number of bags containing bread with the same composition is 5.
3. Find the LCM and GCF of the numbers 25 and 100.
Discussion:
Number factorization result:
25 = 1, 5, 25
100 = 1, 2, 4, 5, 10, 20, 25, 50, 100
The same factor is 25, so the GCF is 25.
Using the prime number method, namely:
25 = 5 x 5
100 = 2 x 2 x 5 x 5
LCM = 22 x 55 = 100
So the LCM of 25 and 100 is 100, while the GCF of 25 and 100 is 25.
Based on the above review, it can be concluded that the calculation of the KPK and GCF can use simple or factorial methods. You can use both methods because the resulting KPK and GCF values will be the same. How, already understand better how to calculate it?
X CLOSE
Advertisements
ADVERTISEMENT
X CLOSE
