COMPOUNDS: Definition, Types, Examples
Loading...
Without realizing it, humans often come into contact with various types of compounds in everyday life. Although maybe not everyone realizes let alone understands what compound means. In fact, there are many examples of compounds that are often found, such as salt, sugar, water, and so on.
In general, compounds are classified into several types based on the constituent elements. While the process of decomposition of compounds is carried out through a chemical reaction. It also distinguishes the form, texture, taste, and smell of each type of compound.
List of contents
Naming Compound Formulas
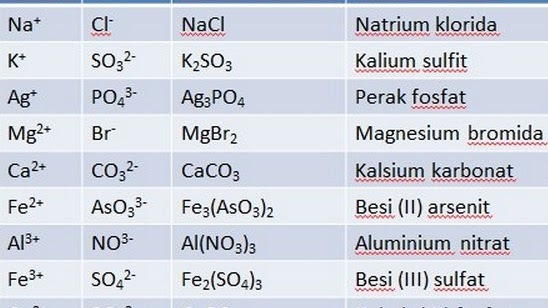
A compound is a single substance that can be broken down into two or more substances through a chemical reaction. An example of a compound that is often found in everyday life is water. In the process, water is a combination of the elements oxygen (O) and hydrogen (H) with the chemical formula H20.
Reporting from the official website of the Ministry of Education and Culture of the Republic of Indonesia, it is stated that the smallest part of an element is an atom. If two atoms combine through a chemical reaction, it will form a molecule or the smallest part of a compound.
Meanwhile, the process of forming compounds through chemical mixing and thermal or electrical decomposition. Compounds have different properties from their constituent elements.
For example, the properties of water are different from the properties of the elements that make it up, namely oxygen and hydrogen gas. The difference in appearance is also very real. Because water is a liquid, hydrogen is a gas. In addition, water can be used to extinguish fires.
However, hydrogen is a flammable substance. While oxygen is a substance needed in the combustion process. So, it can be seen that the constituent elements and the resulting compounds have very opposite properties, forms, and functions.
So, what is the difference between a compound and a mixture and an element? Although compounds and elements are single substances. However, there are differences between compounds and elements as well as mixtures.
This is because the element is a single substance that cannot be converted into simpler substances, and the element will still maintain its original properties or characteristics.
Example of elements:
- Gold
- Lead
- Iron
- Copper
- Zinc
- Nickel
A mixture is a material composed of two or more substances, but still has the properties of the original substance. Examples of mixtures include:
- Air
- River water
- Rock
- Chocolate milk
- Iodine salt
- Coffee
- Sweet tea
Read: Liquid
Types of Compounds
Before discussing further about absolute examples of compounds in everyday life. It's good if you can also distinguish the types of compounds.
Based on the constituent elements, compounds are categorized into several types, namely as follows:
1. Organic Compound

Comes from living things and the process of photosynthesis. Organic compounds contain the element carbon (C) as the main chain. This type of organic compound has the characteristic properties of being insoluble in water, and only soluble if mixed with organic solvents.
Because it is formed from the element carbon (C), it causes organic compounds to tend to be more flammable. An example of an organic compound is sugar (C12H22011)
2. Inorganic Compound
Advertisement

This type of compound comes from mineral resources. Inorganic compounds have relatively higher boiling points than organic compounds. However, inorganic compounds tend to be non-flammable and easily soluble in water. For example, silicon dioxide (SiO2).
3. Sour

Molecules that can donate hydrogen ions H+ and forms a covalent bond with Lewis acid. In chemistry, acid compounds consist of three definitions, namely Arrhenius, Bronsted-Lowry, and Lewis.
In general, acids have the following properties:
- Sour when dissolved in water.
- Reacts violently when mixed with metals.
- It stings to the touch and has the potential to damage the skin.
- Have a pH less than 7.
- Acids are liquid electrolytes although they are not necessarily ionic.
- Can turn blue litmus paper into red.
Acids have a variety of uses, including removing rust from metal objects through pickling or pickling. In addition, acid can also be used as an electrolyte in wet cell batteries. Sulfuric acid can be used as a catalyst to make gasoline.
Read: Acid Base
4. Ionic Compounds

This term refers to chemical compounds consisting of ions held together electrostatically (ionic bonds). Although this compound is neutral overall, it is composed of positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions), both in the form of sodium, chloride, to carbonate.
Properties of ionic compounds:
- It has a very high boiling point with a low vapor pressure.
- Alkalinity or similarity to acidic compounds.
- Most types of ionic compounds are very brittle.
- The compressibility of ionic compounds is determined by the structure.
- Easily soluble in polar liquids, such as water. However, it tends to be difficult to dissolve in gasoline.
- Low conductivity and generally do not conduct significant electricity.
Ionic compounds have a variety of uses and are commonly used by people in everyday life. Examples of ionic compounds include milk of magnesia, borax, to slaked lime.
5. Salt

In chemistry, salt is categorized into ionic compounds consisting of negative ions (anions) and positive ions (cations), thus forming compounds without a charge or neutral. Salt is formed from the reaction of bases and acids, such as chloride, acetate, fluoride, sulfate, to sodium chloride.
Of all the types of salt that exist, each salt has a different taste, namely:
- Sweet (lead & acetate)
- Salty (sodium chloride)
- Acid (potassium bitartrate)
- Savory (monosodium glutamate)
- Bitter (magnesium sulfate).
6. Oxide
Oxide compounds contain oxygen atoms and other elements. Did you know that most of the earth's crust is made up of oxides? These compounds are formed when elements are oxidized by oxygen. Oxides tend to have ionic structures with high boiling points.
7. language

Compounds that absorb hydronium ions (H3O) when dissolved in water. A base is a dual of an acid or chemical element that has a pH greater than 7. In general, bases are divided into two types, namely weak bases and strong bases. Depends on its ability to release OH ions.
Bases have some common characteristics, which are as follows:
- Has a bitter taste.
- Smooth base texture like soap.
- Can change the color of red litmus to blue.
- Able to conduct electric current.
- Can neutralize acids.
- Causes weathering.
- The pH value exceeds the number 7.
Read: Solid
Examples of Compounds in Daily Life

In everyday life, living things cannot be separated from compounds. Moreover, there are so many compounds that humans consume to survive.
The following are examples of compounds that are often used by humans:
| Compound Example | Chemical Formula |
| Carbon Monoxide Gas | CO |
| Carbon Dioxide Gas | CO2 |
| Nitrogen Monoxide Gas | NO |
| Water | H2O |
| Kitchen Salt | Sodium Chloride / NaCl |
| Hydrochloric Acid | HCI |
| Sulfuric acid | H2SO4 |
| Acetic Acid (Vinegar) | CH3COOH |
| Ammonia Gas | NH3 |
| Sodium hydroxide | NaOH |
| Sugar | C12H22011 |
| Urea | CO(NH2)2 |
| Alcohol | C2H3OH |
| Calcium | CaCo3 |
By knowing examples of compounds and their types. Now you can better understand what kind of compounds are contained in foods, drinks, and objects that are used every day. So, you can also be more careful in choosing what to consume and use.
X CLOSE
Advertisements
ADVERTISEMENT
X CLOSE
