Translate JAVA to Indonesian (Ngoko & Krama)
Loading...
As we know, Indonesia is a country that is very rich in various cultures in it.
Not only local arts, language has become one of the nation's invaluable wealth.
The Javanese themselves are one of the largest tribes who are residents of this archipelago. So not if many are curious and want to learn the language through Javanese translation or Javanese language dictionaries or even directly converse with native Javanese.
Some words in Javanese are also easy to understand because they are absorption from Indonesian.
Javanese language has different levels ranging from subtle manners, inggil krama, and ngoko.
For those of you who want to learn Javanese, we present a translation service or translate Javanese to Indonesian below.
The Javanese translator above makes it easier for you to interpret words or translate from Indonesian to Javanese.
The variations of the Java language supported in the Java translation program above include several krama (levels) in Javanese, such as:
- Javanese Krama: It is a polite level of Javanese
- Javanese Kramantara: It is a level of Javanese language in the form of manners but mixed with English.
- Wredha-Krama Javanese: Is a language of manners for people who are old.
- Javanese market manners: It is the language of manners in spoken form.
list of contents
Javanese language

Javanese is an Austronesian language that is very widely used by residents of the Javanese tribe in the central and eastern parts of Java.
Not only that, Javanese is also spoken by the Javanese diaspora residing in other parts of Indonesia. Examples are in Sumatra and Kalimantan, and outside Indonesia such as the Netherlands, Suriname and Malaysia.
The total number of Javanese speakers is estimated at up to 75.5 million people in 2006.
History of Java

Broadly speaking, the development of the Javanese language is divided into two different language phases, namely Old Javanese and New Javanese.
Here's the explanation:
1. Old Javanese
The earliest form in the Old Javanese language that is preserved in writing is in the Sukabumi Inscription, which dates from 804 AD.
Since the 9th to 15th centuries, this one language variety is commonly used in the area of the island of Java.
Old Javanese language is usually written in the form of stanza poetry, so it is often also referred to as kawi (literary language).
The writing system used in Old Javanese is an adaptation of the Pallawa script, which originated in India.
Almost as much as 50% of the total vocabulary in Old Javanese writing is rooted in the language of Sanskrit, although the Old Javanese language also has several borrowed words from several other languages in Indonesia Archipelago.
The variety of Old Javanese language used in several manuscripts from the 14th century onwards is also often referred to as "Middle Javanese".
Although the variety of Old Javanese and Middle Javanese languages is no longer widely used in the Java area after 15th century, but both varieties are still commonly used in Bali for religious rituals.
2. New Javanese
Advertisement
The New Javanese language grew into the main literary variety of the Javanese language since the 16th century.
This language shift took place simultaneously with the arrival of Islamic influence.
At first, the standard variety of the New Javanese language was based on the variety of languages in the northern coast of Java, where the people at that time had converted to Islam.
The written works in this variety of languages have many Islamic nuances and some are in the form of Malay translations.
The New Javanese language also adopted Arabic letters and adapted them into Pegon letters.
The revival of Mataram gave rise to a variety of standard Javanese writings which shifted from the coastal areas to the interior.
It was this variety of writing that was preserved by the writers of Surakarta and Yogyakarta so that it became the basis for the standard variety of the Javanese language today.
Writing System
Recently, language Modern Javanese is written using four types of script, namely the Javanese script, the Pegon alphabet, the Latin alphabet, and other scripts.
Here's a brief explanation:
1. Javanese alphabet
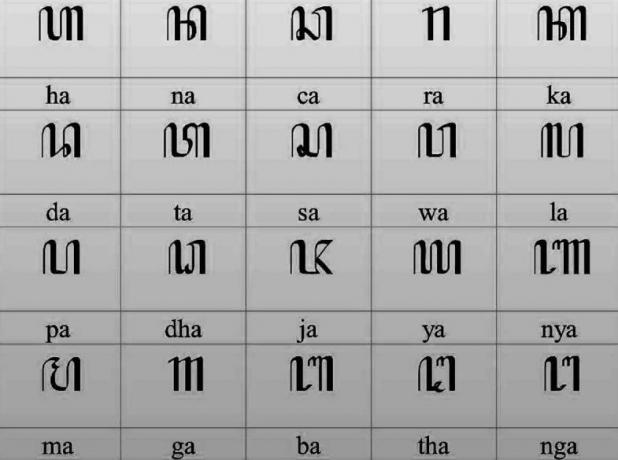
The Javanese script is a script belonging to the Brahmi family, which is derived from the Pallawa script through the Kawi script.
The script appeared in the 16th century, precisely in the golden age until the end of the Majapahit Kingdom.
At this time, Javanese script has been widely used in public spaces, especially in the Surakarta and Yogyakarta areas.
Javanese script is installed to accompany the Latin alphabet on street signboards, agency names, or in public places.
The Javanese script is also the Balinese script and the Cirebon script, both of which are descended from early versions of the Javanese script in the 16th century.
2. Pegon alphabet
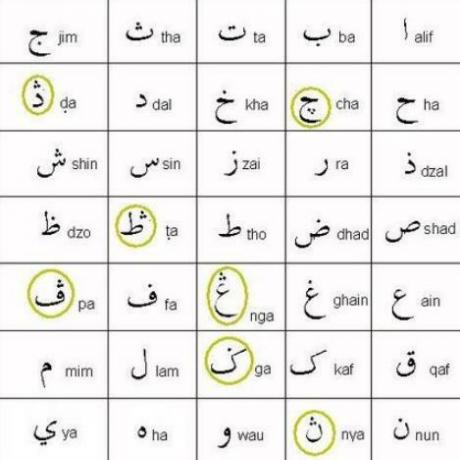
The word pegon has the meaning of "deviating", meaning that if the Javanese language written using the Arabic alphabet is something unusual.
The Pegon alphabet appeared simultaneously with the entry of Islam in Java and developed during the golden ages of the Demak Kingdom to the Pajang Kingdom.
This Pegon alphabet is related to the Jawi (Arabic – Malay) alphabet by adopting some standard Arabic letters which are added with new letters that have absolutely nothing to do with Arabic.
Even though it smells of Arabic, Arabs will not be able to understand this alphabet.
If in the Jawi alphabet there are always no vowels / vowel markers, then in the Pegon alphabet there are those with vowels and those without.
3. Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet began to be intensified to transcribe various works written using Javanese and Pegon scripts in the 19th century.
4. Other characters
In ancient times, this ancient Javanese language was written using the Kawi script and the Nagari script.
This script is often found in various inscriptions from the 8th to 16th centuries, this script continues to experience changes both in terms of form and typography.
Javanese dialect

Based on the narrative by J. J. Ras who is a professor of Javanese language and literature at Leiden University, as for several Javanese dialects which are grouped based on their distribution.
Among them are:
1. Middle Dialect
For the areas of Madiun-Kediri-Blitar, Surakarta-Yogyakarta, Blora-Rembang-Pati, Semarang-Demak-Kudus-Jepara.
2. Western dialect
For the areas of Indramayu-Cirebon, Banyumas-Bagelen, Banten, Tegal-Brebes-Pekalongan.
3. Eastern dialect
For the Banyuwangi, Surabaya-Malang-Pasurusan area.
X CLOSE
Advertisements
X CLOSE
Advertisements
