Scientific Approach: Definition, Objectives, Stages, Examples
X
Advertisements
Loading...
The existence of a scientific approach during teaching and learning activities has the aim that students can have capabilities in critical, scientific and analytical thinking skills.
This scientific approach is also a learning model that uses the scientific method during its learning activities.
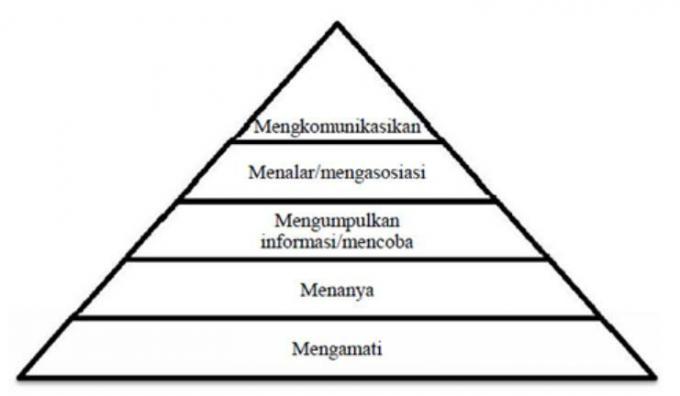
The way that can be taken so that this capability can be achieved is by implementing 5M, namely observing, asking, trying, processing and communicating.
In the following, we will discuss the scientific approach in more detail, please read carefully.
list of contents
Understanding Scientific Approach

Advertisement
The following is the understanding of the scientific approach according to several experts, including:
a. Ministry of Education and Culture
The scientific approach is a learning model which in the process includes various scientific principles. Starting from collecting data by asking questions, observing, doing experiments, processing information and data, to communicating.
b. Wikipedia
The scientific approach is an approach that must be used in learning in schools, be it in elementary schools or schools Intermediate, based on the rules of the 2013 Curriculum or commonly referred to as the scientific framework of learning that is applied in the Curriculum 2013.
c. Rusman
The scientific approach is a learning approach that provides broad space for students to explore and elaborate on learning materials. And able to actualize abilities through various learning activities that have been designed by the teacher.
The Purpose of the Scientific Approach
The learning model using a scientific approach has several objectives, such as:
1. Creating a Conducive Learning Environment
Advertisement
By applying this one approach, every educator hopes to be able to create a conducive learning environment through a series of activities that have been systematically designed.
With learner-centered learning, it is also hoped that an active and productive learning environment will be formed.
2. Improving Thinking Skills at Higher Levels
One of the goals of this approach is to improve and develop higher-order thinking skills for students.
The expected high-level thinking skills are as follows:
- Critical thinking,
- analytical,
- synthesis,
- and able to make innovations or original ideas related to the material being studied.
3. Improve Concept Understanding
In practice, the scientific approach will lead to learning activities in order to find and develop concepts independently.
Students can also gain meaningful concepts and understanding through this one approach.
Students or students will not only receive the concept in the form of rote memorization, but will also gain an in-depth understanding of the concept.
4. Improve Systematic Thinking Ability
This one approach also has the main characteristic in the form of stages of learning that take place in a coherent and systematic manner.
This will encourage an increase in the ability to think systematically in students.
Be it the ability to understand a problem or the ability to solve problems.
5. Improve Communication Skills
This type of approach is also expected to be able to create a learning process that can provide a stimulus to students so that they tend to be more active in learning in communicating through problem solving discussions, conveying ideas, discussing data processing, to how to communicate learning outcomes verbally or verbally writing.
6. Increase Learning Motivation
As a form of learning activities with the center being students, it is hoped that this one approach can increase learning motivation.
Advertisement
This series of lessons that require students to be more active and innovative can also create a learning atmosphere that is not monotonous. So that students will not feel bored.
Steps of Scientific Approach
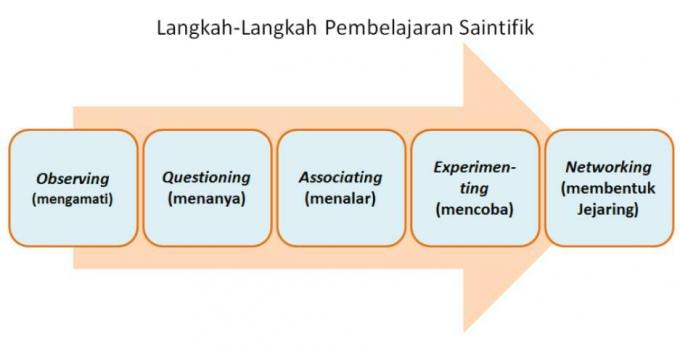
The following are some of the steps of a scientific approach that you need to know, including:
1. Observing (Observing)
The first step in this approach is the observing process.
Through observation, each student is able to find a fact if there is a relationship between the object of observation and the learning material being studied with the teacher.
This observation activity can also be done by using a tool or not.
Observations using tools can be done by using tools for practical activities such as microscopes or others.
Meanwhile, if you don't use tools, you can do direct observations by:
- Listen to the explanation by the teacher.
- Watch a variety of relevant videos and images.
- Until listening to information from the radio and other sources of information.
The learning outcomes obtained in this stage can be in the form of the attention of students at the time of learning make observations on an object, hear an explanation, or read a source writing.
You can also see the learning outcomes of students from some notes made during the observation process.
Timeliness used in observation activities can also be used as a form of achieving their learning outcomes.
2. Asking (Questioning)
The questioning activity is one of the activities carried out by students when creating and asking questions that are relevant to the material being studied.
This activity is directly related to discussions regarding information that is not yet understood, additional information to be obtained, as well as a form of clarification of information that is not yet clear.
You must also have mature readiness in determining the method and selection of media or facilities that are in accordance with the characteristics of each student and relevant to the material. So that students or students will be interested and well stimulated in the process of this activity.
Advertisement
This will also encourage the number of questions that will be asked from the students.
And in this activity, the learning outcomes that you can observe from students are related to the types and quality of questions that arise.
The types of questions can be in the form of conceptual, factual, procedural, or hypothetical questions.
Preferably, you also have the ability to analyze the type and quality of questions so that you can carry out an assessment of the questions asked comprehensively.
3. Gathering Information/ Trying (Experimenting)
This activity is a continuation of the questioning activity in the previous stage.
In practice, this activity can be done by digging or collecting information from various sources in various ways.
The various activities at this stage include:
- Explore activities
- Discuss
- Try
- Demonstrating
- Doing experiments
- Imitate
- Read sources other than textbooks
- Interview with sources
- Collecting data through a questionnaire
- And others.
The learning outcomes that you can observe at this stage are the number and quality of information sources that have been studied by students. the completeness of the information that has been collected, the validity of the information obtained, and also the instruments used at the time of data collection or information.
4. Reasoning (Associating)
The reasoning stage is a logical and systematic thought process on various observable facts to get conclusions in the form of knowledge.
Activities that can be carried out at this stage include:
- Processing the information that has been collected.
- Analyze data by creating categories or groupings.
- Linking phenomena/information into a pattern.
- And finally, make conclusions.
Educators can later direct students when working on discussions related to the topic being discussed.
Furthermore, an educator can also carry out an assessment at this stage in the form of: the process of developing interpretations, arguments and conclusions regarding information from two facts or draft.
In the next stage, educators must also be able to provide an assessment of the ability of students in learning synthesizing arguments and making conclusions related to the types of facts, concepts, and opinion.
Not only that, other learning outcomes can also take the form of new structures, arguments, development of interpretations, and so on drawing conclusions that show the relationship of facts or concepts from two or more sources that are not contradictory.
5. Communicating (Communicating)
In the final stage, an educator will also provide opportunities for students to communicate the results of the learning process that has been done.
Students will be able to communicate it in the form of reports/ paper which contains diagrams, charts, and graphs.
At a further level, students can also compile learning outcomes in the form of written reports and present it systematically starting from the results, process, to conclusions verbally by presenting it on in front of the class.
The learning outcomes that can be seen from this stage are the ability to present the results of the analysis in the form of graphics, writing, electronic media, or other creative forms.
There are physical forms that teachers can assess directly, such as scientific papers, written reports, and videos uploaded on social media.
