Digestive System: Pictures of Organs & Their Functions
When we eat, food that enters our body through the mouth will then be reprocessed by other organs of the digestive system.
Through this process, the food will be converted into a substance or energy that is useful for the body and then disposed of as waste.
A study says, if the human digestive system is stretched from the mouth to the process of disposal through the anx, then it reaches about 30 feet in length. Amazing isn't it?
Table of contents
Definition
Digestive system in humans is a system in the body that helps humans to process food and drinks that enter the body through the mouth to become substances that can be consumed it is easier to be processed by the body and then the content in it is taken which is beneficial for internal organs and body parts as a whole whole.
Or, there is also a mention if digestive system is the process of changing food and absorption of food essence in the form of nutrients needed for the body through the help of enzymes that break down complex food molecules into simple parts that are easy to digest body.
There are several organs that also work to process food and drink. These organs start from the outermost organs to the core organs.
External organs start from the mouth - esophagus - stomach - pancreas - liver - intestines - anus.
Or if we draw conclusions, then the digestive system in humans includes:
- Injection: The process of putting drinks and food into the mouth
- Mechanical Digestion: The process of converting food into smaller pieces that are softer by the teeth.
- Chemical Digestion: The process of converting complex food molecules into simpler ones by acids, enzymes, water and bile.
- Removal Process: The process of removing waste and absorption of nutrients.
Food Digestion Process

1. Process injection
The first process of digestion of food is the process of entering food and drinks into the mouth using the help of hands and also food utensils such as spoons and forks.
This initial process aims to convert crude food molecules into simpler molecules. So that the food can be continued into the throat.
2. Mechanical Digestion
The mechanical process is a process that changes small food to be softer by using the help of teeth and other aids in the mouth.
The purpose of mechanical digestion is actually to facilitate or assist in the next process. And this process is done consciously and according to our wishes.
3. Chemical Digestion
Chemical digestion is a process which converts food that is still in a complex form into a simpler form. And then made into various simpler molecules to make it easier for the digestive system to process them.
In the process of digestion is assisted by sam, enzymes, water and also 'bile'. This process is done unconsciously because it uses the help of these elements.
4. Absorption process
The absorption process is the movement of nutrients from the digestive system to the circulatory system and lymphatic capallaries through osmosis, active transport and diffusion.
5. Removal process Proses
The process of elimination is the last process in a series of processes in the human digestive system.
In this process all undigested material from the digestive tract will then be excreted by the body through the defecation section.
That way, humans will experience the disposal of waste substances through defecation through the anus.
All organs of the digestive system will work one after another and play their role well. However, if the body does not have enough fiber, it will make the digestive system work it will be hard to digest hard foods and has the potential to make the organs experience problem.
The application of a healthy diet by regularly eating fruits and vegetables will help launch the digestive system.
Digestive System
There is an arrangement of organs in the human digestive system that are arranged in sequence. Starting from the outermost part, to the inner part.
Part of the external digestive process will be felt by humans, or it can also be done consciously. But if it has entered into a deeper process, then it will be digested by this organ in the body.
In the process, enzymes then take over, so that the digestive process cannot be realized.
The following are some parts of the human digestive system, including:
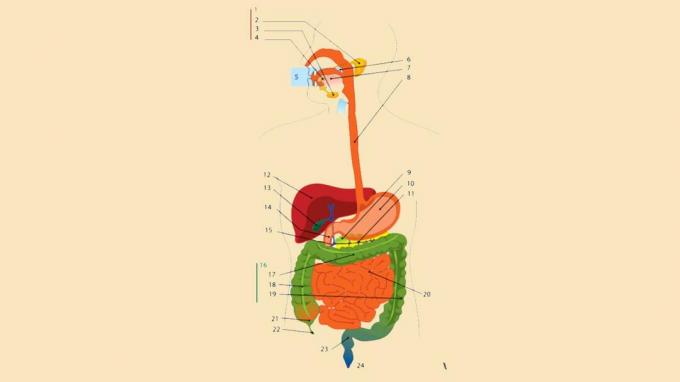
Information:
- Salivary glands (the outermost part of the human digestive system as well as the accessory digestive tract)
- parotid
- Submandibular (position under the jaw)
- Sublingualis (position under the tongue)
- Oral cavity (contains teeth and tongue)
- Tonsils (Tonsils)
- Tongue
- Esophagus
- Pancreas (a part of the digestive system)
- stomach
- Pancreatic duct
- Heart
- Gall bladder
- Duodenum
- Bile duct
- Colon
- Transverse colon
- ascending colon
- descending colon
- Ileum
- cecum
- Appendix or Appendix
- Rectum or intestinal axis
- Anus (is the last part of the human digestive system)
Organ Group
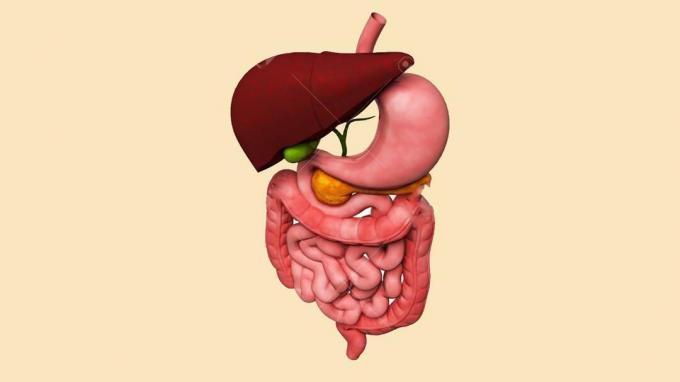
There are various organs involved in the human digestive system, including the digestive system which is divided into two groups, including:
1. Digestive tract
The digestive tract is a tube-like part of the canal that is surrounded by stretched muscles.
The digestive tract works continuously or continuously.
The functions of the performance of the digestive tract are:
- Digest food.
- Breaking food into smaller pieces.
- Absorbs it into the blood vessels.
Organs included in the digestive tract include:
- Mouth
- Pharynx
- Esophagus
- stomach
- Small intestine
- Colon.
Starting from the large intestine, the food will then be expelled out of the body through the anus which is the outermost organ of the digestive system.
Food waste that has been expelled through the anus is a material that is no longer needed by the body.
2. Additional digestive organs
The function of this additional digestive organ is to work to assist the digestive tract in carrying out its functions.
Some additional digestive organs include:
- Tooth
- The tongue in the oral cavity
- Gall bladder
- And the part of the digestive gland that will be connected directly to the digestive tract through a channel.
Additional digestive glands will produce secretions that work together to break down food ingredients that enter the human body.
Teeth, gallbladder, tongue, as well as various digestive glands as well as salivary glands, liver and parts of the pancreas.
Human Digestive Tool
Basically, the digestive system is a combination of various specific organs in the body.
Of course, these organs include the digestive system which has their respective roles.
For more details, the following is a brief explanation of the organs in the human digestive system starting from the outermost part, including:
1. Tooth
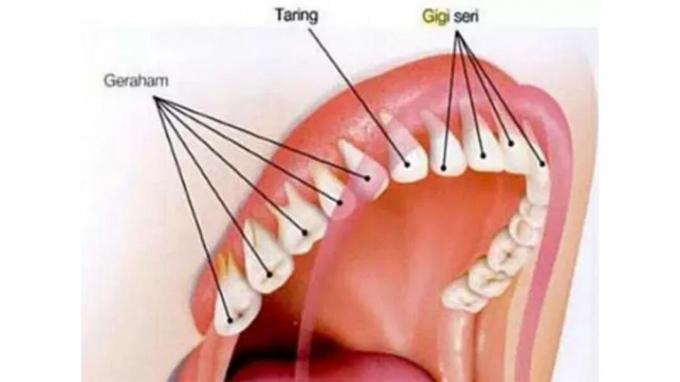
Teeth have a function as a mechanical digestive process.
The main function of teeth is to break down coarse food into softer molecules.
In the world of health, we are advised to chew every food that enters our mouth 20 to 30 times.
Because it is good for stomach health. Because, the finer the food we swallow, then it will reduce the performance of the stomach.
According to its function, teeth are divided into 3 parts, each part of the human tooth has its own shape and role. Here's a full explanation:
- incisors
The normal number of incisors that grow in the human mouth is 8 pieces. These incisors have an ax-shaped surface.
The main function of incisors is to chop food.
- Canine tooth
The normal number of incisors that grow in the human mouth is 4 pieces. These canine teeth have a pointed shape resembling a spear.
Because of their pointed shape, the main function of canine teeth is to tear food.
- Molars
Molars are one type of teeth that have a function in chewing food.
The molars have a wide and wavy surface.
The normal number of incisors that grow in the human mouth is as many as 8 molars on the right and left sides of the mouth.
2. Tongue
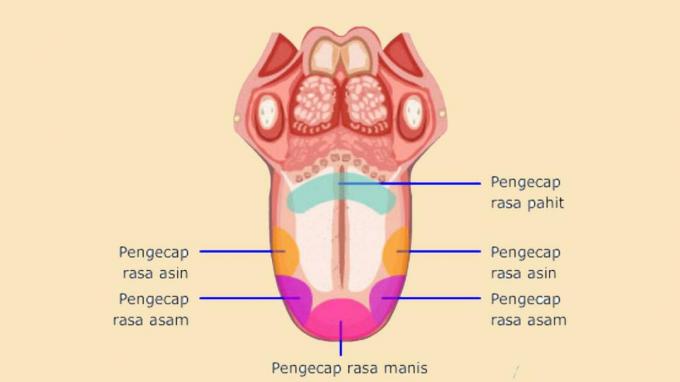
The tongue is one of the organs that fall into the category of the human senses, precisely in the position of the sense of taste. Therefore, all food that enters our mouths can be recognized and does not taste bland.
In the digestive system, the tongue has function as a regulator of the position of food at the time in the mouth. As well as to help the process of swallowing as well as mixing food that takes place in the mouth.
The tongue is what will direct the food to be between the teeth, so that the incoming food can be crushed and become a softer form of food.
This form of food is also commonly referred to as a bolus.
You need to know, basically the tongue is divided into 4 groups, because each part of the tongue has its own role.
The following is a brief description of the parts of the tongue and their functions:
- Part end tongue
Its function is to feel something that feels sweet. - The edges front tongue
Its function is to feel something that feels salty. - Part side tongue
Its function is to feel something that feels acid. - Part back tongue
Its function is to feel something that feels bitter.
3. Salivary gland
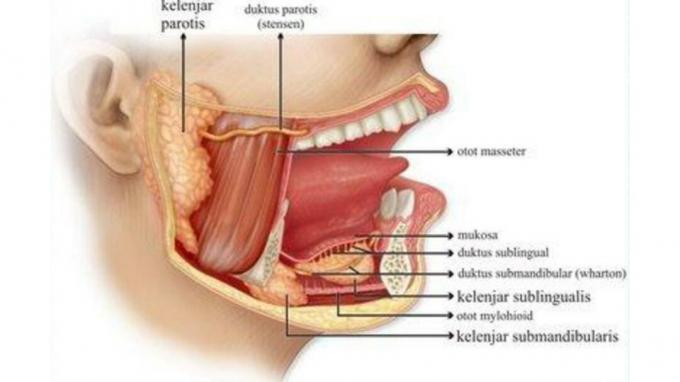
The salivary gland is one of the human digestive systems that has a very vital function.
The salivary glands are one of the organs in the mouth, in addition to the teeth and tongue.
The salivary gland is an organ that has the function of producing saliva.
It functions as a food lubricant. Not only that, saliva also has a function as a guard to keep it wet.
Within a day, the salivary glands are able to produce as much as 1-2.5 liters of saliva.
The saliva produced by the salivary glands in it contains several substances. Among others, such as: mucus, water, amylating enzymes and ptyalin enzymes.
4. Esophagus
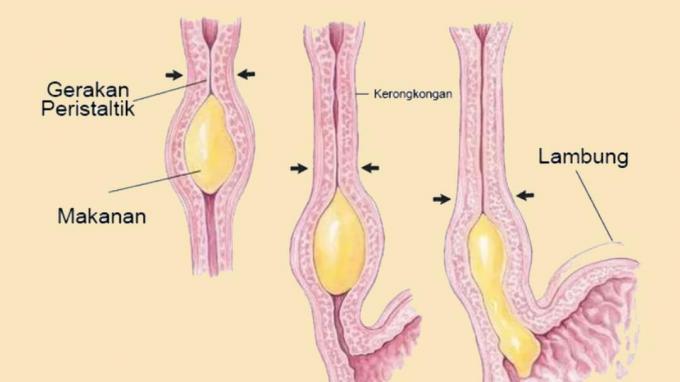
The esophagus is an organ that acts as a conduit for food from the mouth to the stomach.
The esophagus is divided into two types, namely the pharynx and the esophagus.
- Pharynx
Pharynx or also known as pharynx is the part of the esophagus that is a long tube that connects the mouth to the stomach.
Inside the pharynx there is an important part of the digestive system, namely: epiglottis valve.
This section has a role to regulate the passage of food between these foods so that they remain in the esophagus. So that the food does not enter into other channels such as the respiratory tract or larynx.
- Esophagus
While the esophagus is an organ that has a shape resembling a straight tube, and has muscles and thick walls.
In the esophagus there is also a squeezing motion that occurs due to the construction of the esophageal muscles.
5. stomach
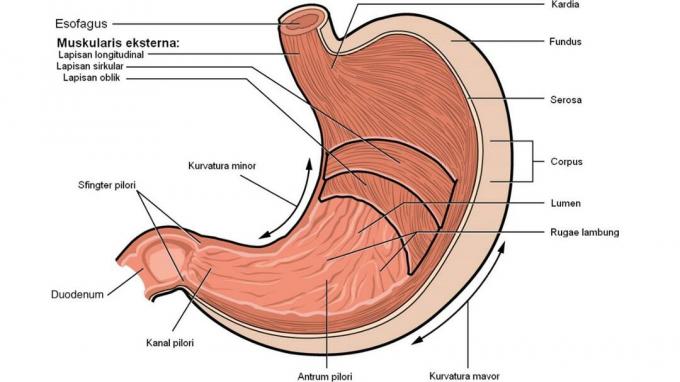
According to one source, the stomach can accommodate 1 to 2 liters of food.
The stomach has a wall formed from the presence of smooth muscles that have a function as a food grinder.
It is these muscles that will later break down food, so that food can mix with gastric juices.
The process of breaking down food will be carried out by mechanical contractions of the stomach muscles.
Not only that, the digestive process in the stomach is also assisted by various enzymes produced by the stomach.
6. Small intestine
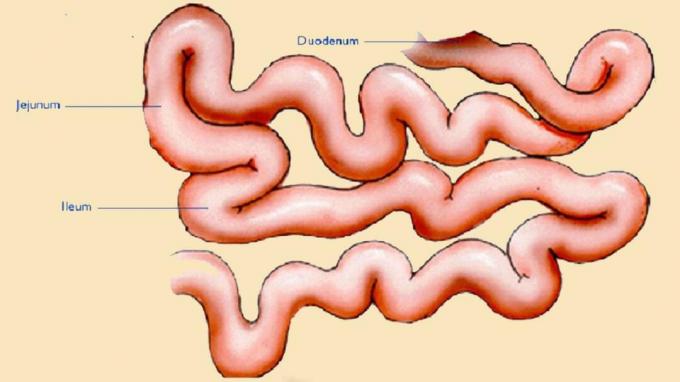
After the food is mashed in the stomach, then the food will be forwarded to the small intestine.
According to experts, the small intestine is approximately 6 to 8 meters long. The small intestine itself is essentially divided into 3 parts, namely the duodenum, jejunum and ileum.
- Duodenum or also commonly referred to as the 12 finger intestine is an intestine that has a length of about 25 cm.
- Jejunum or also known as the middle intestine has a length of up to 250 cm or about 2.5 meters.
- Ileum or also referred to as the absorption intestine has a length of about 3.6 meters.
The small intestine in the digestive system has the main function as a place of digestion and absorption of food nutrients.
Digestion of food occurs in the duodenum and the middle intestine and then continues to the process of absorption of food nutrients that occurs in the absorption intestine.
When food is in the small intestine, the digestive process that takes place is a chemical process.
Chemical processes that occur in the small intestine are assisted by enzymes produced by the pancreas gland and the small intestine itself.
The inner wall of the small intestine is covered by millions of villi and microvilli. The combination of the two increases the surface area of the small intestine massively, allowing absorption of nutrients to occur.
7. Colon

After the food is absorbed nutrients in the small intestine, then the food will be forwarded to the large intestine.
The large intestine itself is divided into 3 groups, namely the ascending colon, the transverse colon and the descending colon.
The large intestine has a role as a place for decomposition of food debris that has previously been absorbed by the small intestine.
The process of decay that takes place in the large intestine is assisted by bacteria called Escheichia coli (E-Coli).
For the rest of the food such as water, minerals and salt will then be re-absorbed by the intestines.
After the nutritional content contained in the food is completely exhausted, the food will then be expelled through the anus.
8. Anus
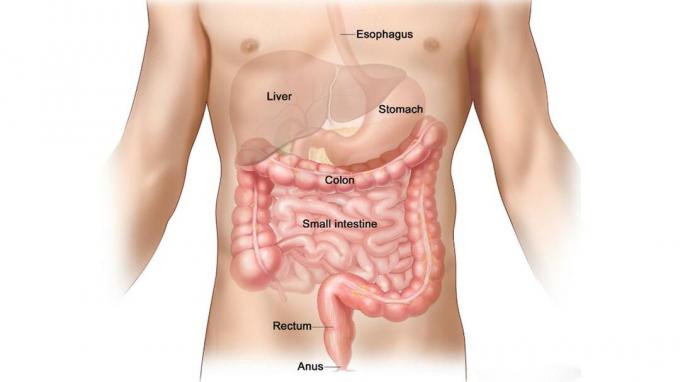
After the nutrients in the food are completely absorbed or used up, the rest of the food will then rot and be expelled by the anus.
In the digestive system, the anus is the last organ or door of the digestive process. The anus has a function as a place for the disposal of feces or feces.
Digestive Enzymes
After discussing at length about the digestive system in humans, it would be nice if we also learned about digestive enzymes. Here are some explanations about digestive enzymes.
1. Enzymes in the Mouth
- Ptyalin enzyme functions to convert starch into maltose, this enzyme is produced by the salivary glands.
2. Enzymes in the Stomach
- Pepsin enzyme functions to convert protein into peptones.
- Renin enzyme is a type of enzyme that functions as an enzyme to convert caseinogen into milk protein as well as having a function to precipitate milk casein.
- Sastic lipase enzyme functions to convert triglycerides into fatty acids.
3. Enzymes in the Pancreas
- Amylase enzyme functions to convert starch into glucose or maltose.
- Trypsin is an enzyme that converts proteins into amino acids.
- Lipase enzymes function to convert fats into glycerol or fatty acids.
Enzymes in the Intestinal Gland
- Disaccharase enzymes function to convert disaccharides into monosaccharides.
- Erepsin enzyme or also dipatidase functions to convert dipeptide substances into amino acids.
- Intestinal lipase enzymes function to convert fats into glycerol or fatty acids.
- Paptidase enzyme functions to convert polypeptides into amino acids.
- Sucrase enzyme functions to convert sucrose into glucose and also galactose.
- Lactase enzyme functions to convert lactose into glucose and also galactose.
- Maltase enzyme is a type of enzyme that functions to convert lactose into glucose and also galactose.
- Enterokinase enzyme functions to convert trypsinogen into trypsi which is useful for the pancreatic duct.
Diseases & Disorders
The following are some diseases or disorders that can attack the human digestive system, including:
1. Diarrhea
Diarrhea is one of the most common digestive system disorders. The symptoms will make the patient feel heartburn and the stool becomes watery.
Cause:
- The lining of the large intestine is irritated.
- Consumption of unhygienic or germ-laden food.
If the patient's stool is mixed with blood or pus, then these symptoms indicate that the patient has experienced dysentery.
Where dysentery is caused by Shigella bacterial infection that occurs in the wall of the large intestine.
2. Gastritis
Gastritis is a disease in which the lining of the stomach becomes inflamed.
Origin:
- The level of hydrochloric acid or Hcl is too high
- Patients consume foods that contain lots of germs.
Symptoms:
- Feel full quickly when eating
- Gastrointestinal disorders
- Pain and heat in the stomach
- CHAPTER with dark black stools
- Loss of appetite
- Vomiting blood
- Bloated
- Stomach ache
- Hiccup
- Gag
- Nausea
See a doctor immediately if you feel:
- stomach ulcer symptoms for more than a week
- CHAPTER with dark black stool texture
- vomiting blood.
Cause:
- Bacterial infection H. pylori
- Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages
- Side effects of taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (eg ibuprofen and aspirin) on a regular basis
- Stress
- Drug abuse
- Autoimmune reaction
- Pernicious anemia
- bile reflux
- Chronic vomiting
- Increasing age
- Bacterial and viral infections
- Crohn's disease
- HIV/AIDS Penyakit
3. Ulcer
Ulcer is a disorder of the digestive system which is characterized by a burning feeling in the stomach wall, as well as feelings of nausea and bloating.
This ulcer is caused by the bacteria from Helicobacter pylori.
Cause:
- High levels of stomach acid
- Poor or irregular eating patterns
- Stress
- And others.
4. Constipation or Constipation
Constipation is a disorder of the digestive system in which the stools that are passed become hard.
Cause:
- Absorb too much water
- Less consumption of fibrous foods
- The habit of delaying defecation.
5. Hemorrhoids or Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids, also known as hemorrhoids, are swellings that contain enlarged blood vessels.
These blood vessels are in the area or in the buttocks, whether it is in the anus or in the rectum.
In general, this disease does not cause any symptoms. If a person is affected by hemorrhoid symptoms, then the things that often happen are:
- Bleeding after defecation, which is a bright red color.
- There is a lump hanging outside the anus. Usually the lump must be pushed back into the anus after defecating.
- Itching in the anal area.
Often experienced by people who sit too long and women who are pregnant.
6. appendicitis
Appendicitis is a digestive system disorder in which the appendix or appendix becomes inflamed.
If the tuft of worms is not removed immediately, then over time it will break.
If the inflammation of the appendix is marked by the presence of pus, then you should immediately go to the doctor. because if this disease is not treated properly it will cause death.
7. Stomach Ulcer
Peptic ulcer is a condition in which the lining of the stomach is injured.
This disorder is generally caused by erosion of the lining of the stomach itself.
This disease can affect anyone regardless of age. However, people over the age of 60 years have a higher risk of suffering from this disease.
Symptoms:
- Pain or tenderness in the abdomen
- Pain then appears and spreads to the neck.
- Feels more sore on an empty stomach, appears at night, will disappear and recur again in the following week.
8. Appendicitis
This disease occurs because the appendix is infected by bacteria. Appendicitis occurs due to a hole between the appendix and the large intestine that is blocked by mucus or chili seeds.
9. Sprue
Thrush is a digestive system disorder that generally appears in the mouth area.
When we experience this disorder, when we eat our mouth will feel sore.
Canker sores occur because of heat in the cavity of the tongue or oral cavity. The most basic cause is a lack of vitamin C.
10. Colic
Symptoms:
Pain that arises because the channels in the abdominal cavity are blocked, such as the intestines, urinary tract, bile and female oviducts.
One of the causes of this disorder is because sufferers consume foods that are too spicy, sour or eat too much.
11. Malnutrition or Malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs because the formation of enzymes is impaired. Malnutrition is due to atrophic pancreatic cells having lost too much endoplasmic reticulum.
12. Poisoning
Poisoning is generally due to wrong consumption of food.
Which usually occurs because of the influence of the Salmonella bacteria, which will cause typhoid and paratyphoid disease.
13. Worms
Almost 80% of Indonesians suffer from intestinal worms.
Worms are diseases that attack the human digestive system. This disease is generally experienced by children, however that does not mean that adults will not get worms either.
May be useful.
