Statement of Financial Position
The statement of financial position or also commonly referred to as a balance sheet is a form of report that is very important for a company, MSME, or other type of agency.
Quoted from one of the people at klc.kemenkeu.go.id named Bp. Moh. Luthfi Mahrus as PKN STAN Lecturer majoring in Accounting, explained the statement of financial position.
For more information regarding this information, see the reviews below carefully.
Table of contents
Definition of LFinancial Position report
1. Generally
The statement of financial position in general is one type of financial statement prepared by a company entity or company to provide information related to the position of liabilities, assets, and capital at the end of period.
For accountants, it may be very familiar with the report which can also be called an extension of the basis of accounting.
The source of data for making this type of financial report comes from the work sheet.
This type of financial report will provide information relating to the nature and amount of investment in company resources.
Or in this case, the company's assets, obligations to creditors, and the company's owner's capital.
Therefore, the balance sheet can also help to predict the timing, amount, and uncertainty of future cash flows.
2. According to experts
The following are some definitions of the statement of financial position according to the experts that we get from MastahBisnis.com:
a. Mr. Moh. Luthfi Mahrus (PKN STAN Lecturer)
"A report showing the company's assets, liabilities, and equity for a certain period with the aim of facilitating analysis, evaluation, and predicting future cash flows".
b. Sofyan S. Harahap (2006:107)
"A report that describes the position of assets, liabilities, and capital at a certain time".
c. Mahmud M Hanafi and Abdul Halim (2002:63)
“A report that summarizes the financial position of a company as of a certain date.
This one report will later show economic resources (assets or assets), economic liabilities (debt), capital, and the relationship between these items.
d. Weygandt, Jerry. J, Kieso Donald, Kimmel Paul
"A report related to assets, liabilities, and owner's equity for a certain period".
e. Munawir (2007:13)
It is a systematic report of the assets, liabilities, and also the capital of a company at a certain time.
So that it can be seen that the purpose of this type of report is to show the financial position of a company at the date of certain time, which is usually the time at which the books are closed and the remainder is determined at the end of a fiscal year or calendar".
f. Soemarso
"It is a report that contains liabilities, a list of assets, and the company's capital at a certain time, such as at the end of the month".
g. Harahap (2006:107)
"The balance sheet is a report that describes the position of assets, liabilities, and capital at a certain time".
Functions of the Statement of Financial Position

There are three main functions in the balance sheet, including:
- When viewed from the contents, this type of report functions as a basic tool for calculating the rate of return and the basis for evaluating the structure of the company's capital.
- To assess the company's risk and future cash flows.
- To analyze liquidity, solvency, and financial flexibility within a company.
Well The following are three benefits of the statement of financial position in terms of liquidity, solvency, and flexibility, among others:
1. Liquidity
Liquidity can be referred to as a benchmark / benchmark in reflecting the amount of time it takes for the obligation to be paid / paid.
This ratio can help investors and creditors to assess how big the ability of a company to pay off short-term debt.
As for shareholders, this liquidity ratio is used to evaluate the possibility of future cash dividends / to determine whether to buy more shares of the company / not.
Therefore, it can be concluded that the greater the liquidity ratio in a company, the smaller the risk faced by a company, and vice versa.
2. Solvency
Solvency is a ratio that has a reference to a company's ability to pay all of its debts at maturity.
In other words, a company is said to be at risk if the company that has debt and the debt is repaid with the assets owned by the company.
Actually, the assets owned by the company should be used to expand and develop the company, not to cover the company's debts.
Therefore, the risk faced is not only the company's assets are reduced, but the worse thing is in the form of exhausted assets but the debt has not been repaid.
3. Flexibility
Flexibility is a ratio used to measure the company's ability to make effective decisions.
Effective decisions can be in terms of company development related to the company's financial situation.
If the financial situation in a company is called unhealthy, then the variety of decisions that can be taken will be very limited.
This could be due to the limited assets owned at that time.
Therefore, it can be said that the higher the level of flexibility of a company, the smaller the risk that will be faced by the company.
Elements of the Statement of Financial Position

The balance sheet has three elements that report the financial position, including the following:
1. Assets
An asset or asset is a resource controlled by an agency or company with the hope of providing economic benefits in the future.
The next asset classification divides assets into two more specific groups, namely non-current assets and current assets.
a. Non-current Assetsr
Non-current assets / non-current assets are assets that are very difficult to convert / convert into other forms.
Examples: Trademarks, land, patents, machines, tools, and buildings only.
b. Current assets
Current assets are assets that are not difficult to convert into other forms.
This type of asset has many names, such as liquid assets & current assets.
Examples: Deposits, stocks, securities, accounts receivable, cash, and merchandise.
2. Liabilities / Debts / Liabilities
This obligation will generally arise from past events so that the company must work on settlements in the future or in the future.
It will also create an outflow of corporate resources that contains economic benefits.
This further classification of liabilities divides liabilities into three, namely:
a. Current Liability
Current liabilities / short-term debt is a type of debt that generally must be paid with very fast maturities (less than one year).
The nature of this debt is that it is used for things that are not too important in business. This short-term debt is also not repaid in an urgent situation.
Example:
- Interest payable
- Bills payable
- Accounts payable
- Income tax payable.
b. Noncurrent liabilities
This type of debt is inversely related to current liabilities.
The type of long-term debt is debt that usually must be repaid after making payments more than 12 months.
Companies often take policies to take on long-term debt when they want to expand their business and develop their business more quickly
Example:
- Mortgage debt
- Bonds payable
- Capital lease.
c. Contingent Liability
Contingencies are often referred to as outstanding liabilities that will continue in the future. However, this does not always happen to all business people.
Example:
- Product warranty
- lawsuit
3. Capital / Equity
Capital or equity is a residual right to a company's assets after deducting all liabilities.
So that you understand better, in general, the balance sheet will represent the following basic accounting equations:
Assets = Liabilities + Capital
Contents of the Statement of Financial Position

A complete and clear balance sheet or statement of financial position generally includes the following points:
- balance sheet.
- Income statement.
- Statement of Changes in Equity.
- Statements of changes in financial position that can be presented in the form of cash flow statements or fund flow statements.
- Notes and other reports and informational materials that form an integral part of the financial statements.
Classification of Statement of Financial Position

In the balance sheet, assets and liabilities occur in the form of classification based on the characteristics or characteristics of the company's operations.
The following are the classifications, among others:
1. Current asset (Current Assets)
Current assets are assets that can normally be converted / converted into cash within a maximum period of 1 year / in the normal company activity cycle.
This type of current asset occurs in the balance sheet based on the order of its liquidity, starting with very liquid accounts.
The following are examples of current assets:
- Cash.
- Petty cash.
- Notes receivable.
- Accounts receivable.
- Merchandise inventory.
- Accumulated depreciation of fixed assets.
- Insurance premium.
- Equipment.
- Short term investment.
- Prepaid lease.
- And others.
2. Fixed assets (Fixed Assets)
Fixed assets are assets that are used in a company and have a function that exceeds a bookkeeping period / exceeds 1 year. Usually used in the company's operational activities not for sale, and has a high material value.
The following are examples of fixed assets:
- Building.
- Equipment.
- Soil.
- Goodwill.
- Vehicle.
- Trademark.
- Copyright.
- Patent.
- franchise.
- And others.
3. Other assets (Other Assets)
Other assets are assets that are not included in the category of current assets or fixed assets.
An example is a machine that has not been used in the company's operations.
4. Current Liabilities (Current Liability)
Current debt / short term debt is an obligation that is expected to be repaid in the normal operating cycle / max within 1 year.
The following are examples of current liabilities:
- Accounts payable.
- Tax debt.
- Notes payable.
- Prepaid income.
- Long term debt maturing soon.
- Accrued expenses (expenses payable).
- And others.
5. Long-term obligation (Long Term Liability)
Long-term liabilities are debts where the maturity / repayment is in a period of more than 1 year.
The following are examples of long-term liabilities:
- Mortgage debt.
- Bond debt.
- And others.
6. Capital (Equity)
In the balance sheet of a company in the form of a Limited Liability Company (PT), there is an equity category which includes 2 main components, including:
a. Paid-up capital.
Paid-in capital is capital that is obtained when the owner/shareholder deposits money and/or other assets in a company.
Components of paid-in capital consist of:
- Share capital, is a part of shares launched to explain an ownership.
- Share premium is an excess of the amount deposited by the shareholders.
b. Retained earnings / retained earnings / reserves.
Retained earnings is a component that comes from capital which explains the excess profit that reinvested in the company after the payment of dividends to shareholders stock.
In a company whose form is an individual, the capital only consists of the capital of the owner of the company. Meanwhile, taking capital by the owner owned by a company is referred to as private.
And for a company that is a partnership, the capital consists of the partner's capital.
As well as in companies that are cooperatives, capital consists of other deposits, members' principal savings, and reserves.
Weaknesses of Statement of Financial Position

It turns out that it can not only help to see the financial condition of a company, but this report also has several weaknesses of its own.
If on several matters relating to the measurement / assessment of the elements of the company's assets and liabilities.
The following are some of the weaknesses of the financial position or balance sheet, including:
- This report when viewed from some of the assets (assets) which are measured and presented at cost / amortized cost not at present value. Present value cannot reflect fair value.
- Assets / assets that are not tangible have economic benefits. However, it is very difficult to measure its value objectively because it is produced internally and cannot be recognized in a balance sheet. Tangible assets, for example, trademarks that are generated internally.
- Then there is the matter of the liability element, which in each balance sheet may have data that is not reported as a liability. This is because some of the obligations are intentional, indeed there are those that are deliberately hidden through accounting engineering known as the term off-balance sheet financing.
- The next weakness is in measuring the value of some elements of the balance sheet. This may involve the use of judgments and estimates, such as estimating the useful lives of property, plant and equipment and estimating warranty obligations.
Forms & Examples of Statements of Financial Position

The form of the statement of financial position is the same as the balance sheet in general which can be formed according to the company's needs.
In fact, there is also no financial accounting standard that regulates the form of the balance sheet should be what it should look like.
There is a company that presents assets first, then only equity and finally liabilities (this kind of practice is very common in many European countries).
Not only that, there are also companies that present current assets in the first order in the asset category, and current liabilities in the first order in the liability group.
All of this depends on the policies of each company.
WellIn general, there are two types of balance sheet reports, namely:
1. Balance Sheet Account Form (Account Form)
This form of report generally presents various elements of the balance sheet side by side:
The content on the left presents assets while on the right presents liabilities and equity.
Example of an account balance sheet:
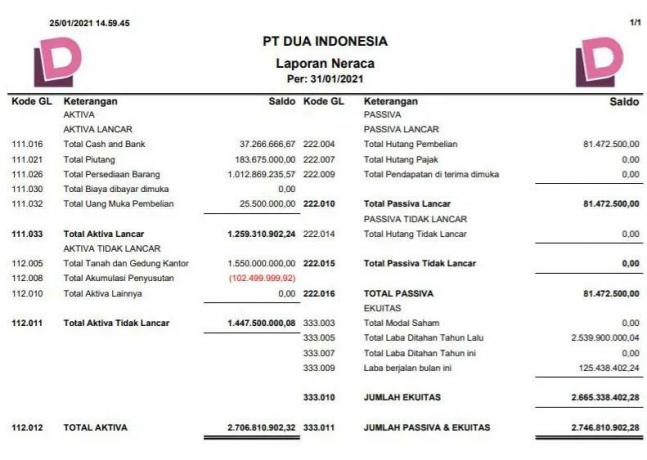
Example of a balance sheet in pdf/word form:
2. Balance Sheet Report Form (Report Form)
The balance sheet in the form of this one report generally presents various elements of assets, liabilities, and equity sequentially extending down or in portrait.
The sequence starts from assets, then proceeds to debt and finally capital.
Example of a balance sheet in the form of a report:

Example of a balance sheet in pdf/word form:
Conclusion
The statement of financial position or also known as the balance sheet is a very important financial report to find out the financial condition of a company or agency.
The balance sheet has three important elements, namely assets, liabilities, and capital.
