Flat Plane Geometry: Various Angles, Flat Shapes, Formulas
Flat Plane Geometry is a term for various two-dimensional shapes. A flat shape is a flat area bounded by straight lines or curved lines. –sc: wikipedia
Flat Plane Geometry also discusses the concept of the distance between two points and the distance from a point to a line. In addition, it also discusses the midpoint between two points.
Table of contents
Flat Plane Geometry
A. Corner
The angle in geometry is a quantity of rotation on a line segment from one starting point to another position.
Not only that, in a regular two-dimensional form, an angle can also be defined as the space between two intersecting straight line segments.
The total measure of the angles on a circle is 360°. The total measure of the angles in a right triangle is 180°. The measure of an angle in a square or quadrilateral is 360°. To measure angles, we can use a protractor or ruler.
Various Angles
1. Acute angle
An acute angle is an angle that is less than 900 and greater than 00 (00< a < 900 )
2. Right angle
A right angle is an angle whose measure is 90 .0
3. Obtuse angle
Support angle; is an angle that is less than 1800 and greater than 900 (900 0 )
4. Straight Angle
A straight angle is an angle whose measure is 180 .0
5. Full Circle Angle
An angle in a full circle is an angle whose measure is 360 .0
Two-dimentional figure
Flat Build Parts
1. dot (.)
A dot is a dot, so it has no length. Point is the simplest form of geometry. This is because the dot is only used to indicate the position.
Point A
2. Line.
A line (straight line) we can think of as a collection of points that extends infinitely in both directions.
If two points are connected, a line will be obtained.
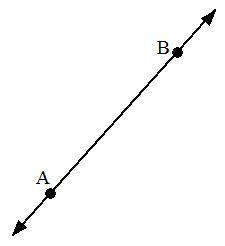
3. Field
We can think of a plane as an infinite number of points that will form a flat surface that extends in all directions to infinity.
Perimeter and Area of Flat Shape Bangun
1. Square (Equilateral Square)
A quadrilateral in which all four sides are the same length and all four angles are right angles.
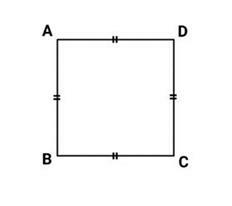
Length :
AB = BC = CD = DA
Since the sides are the same length, the perimeter of a square is given by:
K = AB + BC + CD + DA'
Commonly used formulas are:
K = 4s
L = s x s
L = s2
Problems example:
Find the perimeter and area of a square that has a side of 5 cm!
Answer:
K = 4s
= 4.5
= 20 cm
L = s x s
= 5 x 5
= 25 cm2
2. Rectangle
A rectangle as the name implies is a quadrilateral whose two opposite sides are the same length and all four angles are right angles.
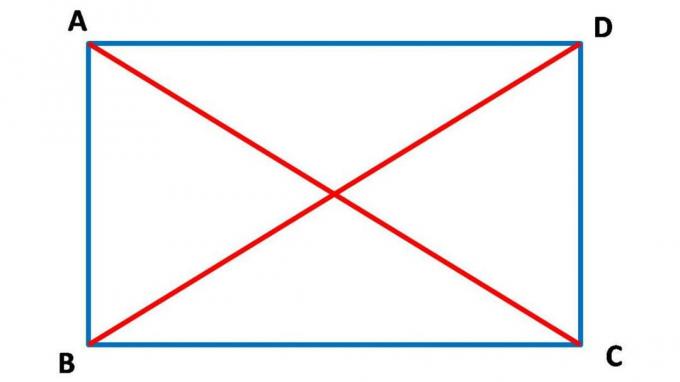
Long:
AB = CD (p)
BC = DA (l)
Commonly used formulas are:
K = 2p +2l
K = 2(p + l)
L = p x l
Problems example:
Find the perimeter and area of a rectangle whose length is 8 cm and width is 4 cm!
Answer:
K = 2(p + l)
= 2(8 + 4)
= 2(12)
= 24 cm
L = p x l
= 8 x 4
= 32 cm2
3. Triangle
A triangle is a flat shape whose sum of angles is 180 .0 and formed by connecting three non-linear points in one plane.
There are several types of triangles, including:
1. Equilateral triangle
An equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides are the same or the same length.
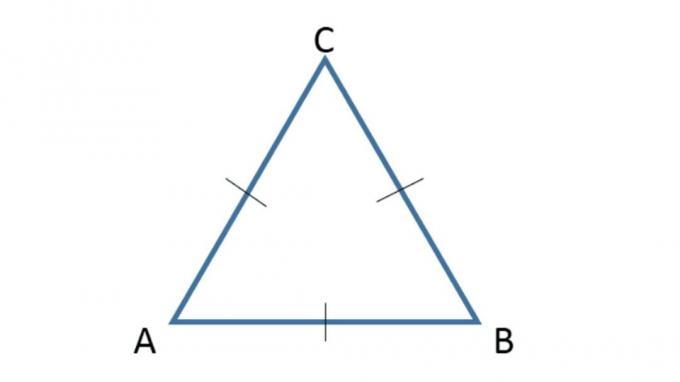
Length AB = BC = CA
A = B = C = 600
A + B + C = 1800
K = AB + BC + AC
Commonly used formulas are:
K = 3s
Area = 1/2. pedestal. high
2. Isosceles triangle
An isosceles triangle is a triangle that has two equal angles and two equal sides.
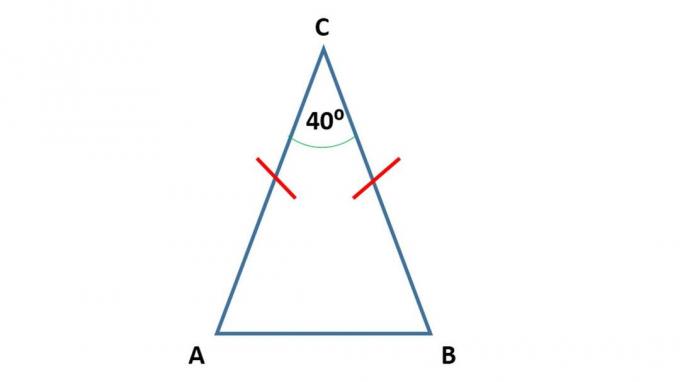
AC length = CB
Angle A = B
A + B + C = 1800
K = AB + BC + AC
3. Right triangle
A right triangle is a triangle in which one of the angles is 900
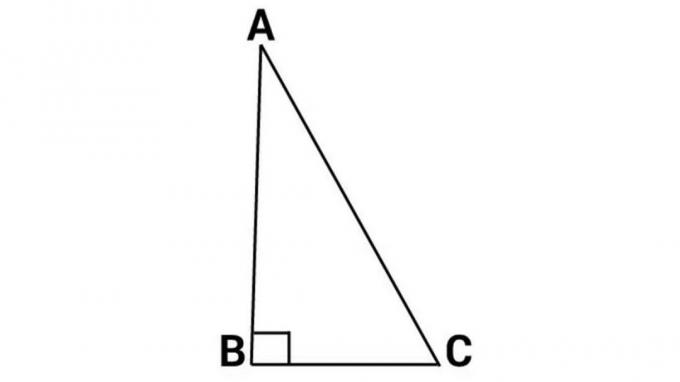
A = 900
K = AB + BC + AC
3. Any Triangle
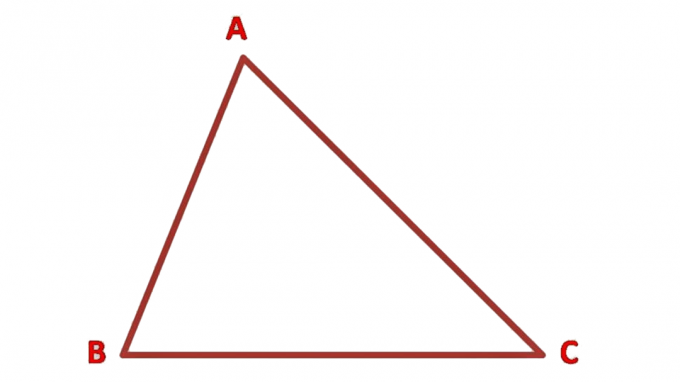
– The three sides are not the same length ( AB BC AC )
– The three angles are not equal (∠A B C )
– A +∠B +∠C = 1800
K = AB + BC + AC
Commonly used formulas are:
L = 1/2.(AB). (CD)
L = 1/2.a.t
Problems example:
1. Find the perimeter of a triangle whose side is 6 cm.
2. Find the area of a triangle with a base of 8 cm and a height of 4 cm.
Answer:
- K = 3s
= 3.6
= 18 cm
- L = .a.t
= .8.4
=16 cm2
4. Parallelogram
A parallelogram is a shape that has two pairs of parallel sides.
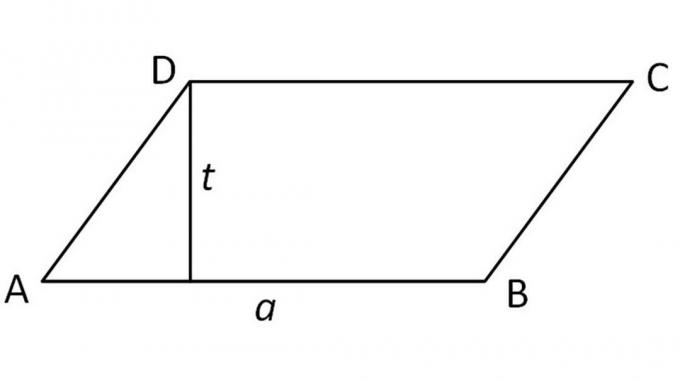
K = AB + BC + CD + DA
Commonly used formulas are:
K = 2(p + l)
L = pedestal . high
Problems example:
Find the perimeter and area of a parallelogram whose base is 6 cm, width 4 cm and height 3 cm!
Answer:
K = 2(p + l)
= 2(6 + 4)
= 2(10)
= 20 cm
L = a.t
= 6 x 3
= 18 cm2
5. Kite
A kite is a shape with two pairs of sides that are the same length.
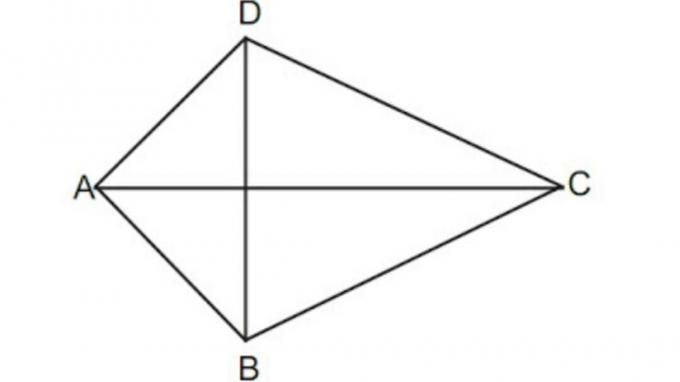
Commonly used formulas are:
K (Kll) = AB + BC + CD + DA
L = 1/2.d1.d2
Diagonal 1 (d1) = d1 = 2 × L d2
Diagonal 2 (d2) = d2 = 2 × L d1
a or b = a = (½ × Kll) – c
c or d = c = (½ × Kll) – a
Problems example:
Find the area of a kite whose diagonal is 9 cm long and 8 cm wide.
Answer:
L = 1/2.d1.d2
=. 8. 9
= 36 cm2
6. Trapezoid
A trapezoid has only one pair of parallel sides.
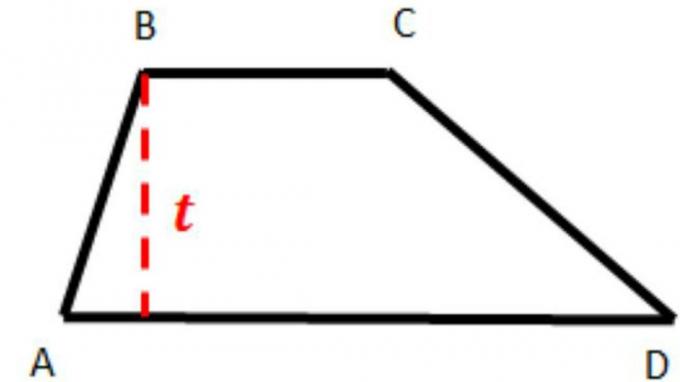
Commonly used formulas are:
K = AB + BC + CD + DA
L = 1/2.t.(AB + CD)
Problems example:
Find the area of a trapezoid having P1 = 8 cm, P2 = 13 cm and 6 cm high!
Answer:
L = 1/2.t.(P1 + P2)
= 1/2. 6. (8 + 13)
= 63 cm2
7. Circle
The shape of a circle is obtained by determining the locus or the set of all points that are a fixed distance from a point.
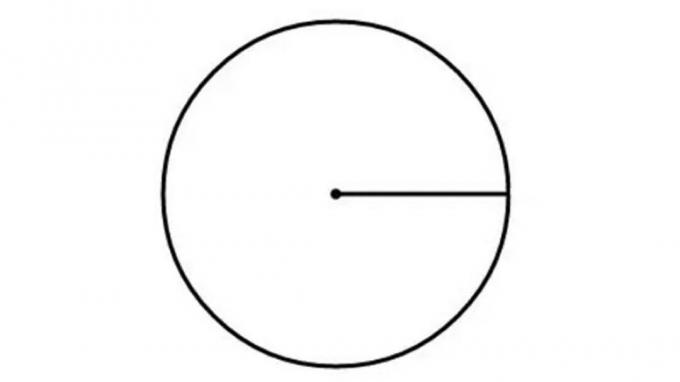
Commonly used formulas are:
K = 2πr
L = πr2
Example: Find the circumference and area of a circle whose diameter is 60 cm.
Answer:
K = 2.π .r
= 2. π. 30
= 60p cm2
L = πr2
= π .302
= 900π cm2
Thus a brief review of Flat Plane Geometry that we can convey. Hopefully the above review of Flat Plane Geometry can be used as your study material.
