Food Chain: Components, Types, Examples in 10 Habitats
Of course, every living thing needs some energy to live. They get energy from what they eat. In this regard, this time we will discuss thoroughly about the food chain. Come on read carefully the following reviews.
Table of contents
1. Food chain
The food chain is a process of eating eaten between living things in which there are objects that act as producers, consumers, and also decomposers.
This has no other purpose, namely to maintain the survival of each of these living things.
2.Components in the Food Chain
In the food chain pyramid, you will find words such as producers, consumers and decomposers.
So, in the following, we will provide an explanation of each of these words, including:
1. Producers (autotrophic organisms) are living things that can produce their own food.
An example is plants.
Plants can produce their own food which can be used as a source of energy for consumers. And the process in making food we know as the process of photosynthesis.
As a provider, producers will not eat other living things, but are eaten.
- Producers, land ecosystems are green plants.
- Producers in lake or marine aquatic ecosystems are blue green algae, and also chlorophyll bacteria.
The two groups of organisms will form phytoplankton. In addition to phytoplankton, producers in the aquatic ecosystem can be algae or green plants.
2. Consumer are living things that cannot make their own food. Therefore, to obtain energy, consumers will depend on producers or other creatures.
These consumers are divided into three parts, namely: primary consumers, secondary consumers and tertiary consumers. Here's the explanation:
-
Primary consumers (level 1 consumers) is the first consumer where it obtains energy directly from producers.
For example: living things that include herbivores such as cows, buffalo, rabbits and others. -
Secondary consumers (level 2 consumers) is the second consumer who obtains energy or food sources from the first consumer.
For example, animals that eat meat or are also often referred to as carnivores.
Examples are cats, dogs, snakes and others. -
Tertiary consumers (level 3 consumers) are consumers who obtain energy sources by eating second consumers.
For example, eagles, peregrines, tigers, lions and others.
3. Decomposer is an organism that has the task of breaking down the carcasses of living things.
These decomposers will eat all living things around the world trophic. These organisms have the task of converting organic substances into inorganic substances.
Feeding and feeding pathways in organisms from one trophic level to the next that form a sequence in a certain direction is a food chain.
The food chain initiated by the producer is called the grass food chain.
For example: grass → grasshopper → small bird → eagle.
trophic level is a level in the food chain where an organism obtains energy.
The food chain can also be started not from direct producers. However, it can also be started from detritus.
Detritus are organic particles that are the result of decomposition of various dead organisms and the remains of organisms.
Remains of organisms such as fallen twigs or leaves that are broken down by decomposers, animal waste.
This detritus is food for various organisms such as worms, termites, keluwing, and also cockroaches.
Detritus can form a food chain known as detritivore.
An example for a detritus food chain is:
destruction of animal dung → nematodes → acarina fleas → scorpions. Another example is: decomposed leaf → earthworm → chicken → human.
3. Food Chain Type
Judging from the originating organisms, food chains can be divided into several types.
Types or types such as: grazing chains, detritus chains, parasitic chains, and also saprophytic chains. Here are the differences between each type.
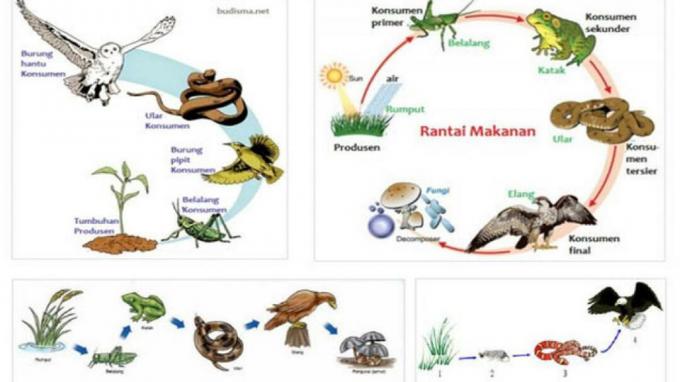
a. Grazing food chain
The first food chain is the most frequently encountered and we recognize.
This type of food chain begins with plants as producers in the first trophic level.
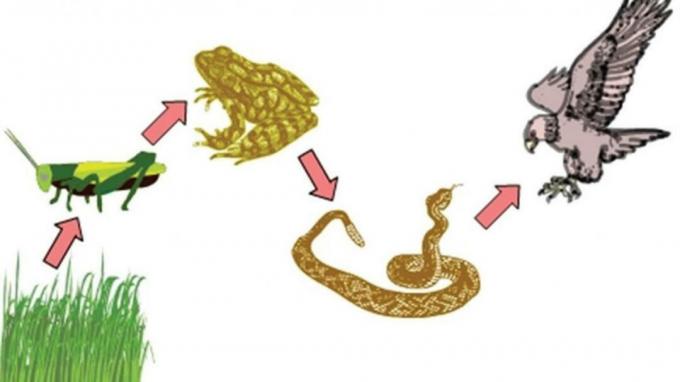
An example of a grazing food chain cycle is: grass → grasshopper → bird → snake.
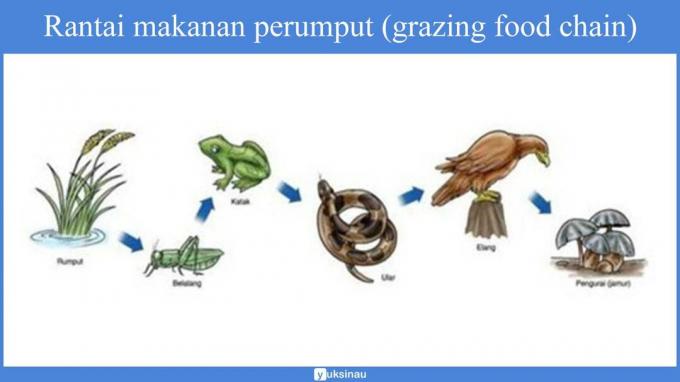
Another example:
From the picture above, we can see that autotrophic grass has a role as a producer. Then the grasshoppers eat the grasshoppers, then the lizards eat the grasshoppers. And ended up the lizard being eaten by the eagle.
In the picture above, grass as a producer is eaten by grasshoppers who act as the first consumers, grasshoppers are eaten by frogs who act as second consumers.
Then the katana is eaten by the snake as the third consumer, and the snake is eaten by the eagle which acts as the fourth consumer.
Then, when the eagle dies, the carcass will be eaten by other organisms and will be broken down by decomposing bacteria.
b. detritus food chain
The detritus food chain does not start with a plant, but begins with detritivore.
Detritivoreis a heterotroph organism that obtains energy by eating the remains of living things.
An example of this detritus food chain cycle is: leaf debris (garbage) → earthworms → chicken → humans.
Detritus is a fragment (destroyed) of organisms (animals and plants) that die and the remains of organisms such as: animal waste, leaves, fallen twigs that are broken down by decomposers (decomposer).
Then, what is included in this detritus-eating organism is referred to as detritivore.
Examples of detritivores are: worms, termites, keluwing and so on.
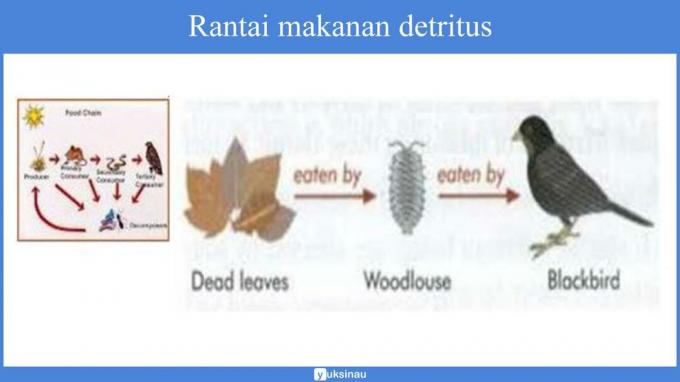
The flow of the detritus food chain can be seen from the picture above.
In the picture above, we can see that detritus can be in the form of crushed animal or plant tissue.
In the picture above, detritus is the remains of animal tissue that is eaten by caterpillars and then rats, snakes and birds.
But, in the end, the whole organism can become detritus as well.
While in other images, detritus can be in the form of crushed plants that are eaten by woodlice which are then eaten by birds.
c. Parasite food chain
Parasite is a term for organisms that live by harming other organisms (as hosts).
The hallmark or characteristics of this type of food chain is the presence of small organisms that prey on large organisms.
Consider the following example of a parasitic food chain. buffalo (blood) → fleas → starling → eagle
- d. Saprophyte food chain
As a characteristic of the saprophytic chain, it begins with the decomposition of the dead bodies of living things by saprophytic organisms.
Those that act as saprophytic organisms include bacteria, fungi, and lichens.
Saprophyteis a term for organisms that are able to decompose the remains of dead organisms.
Saprophytic organisms are different from detritivores.
Saprophytes will break down organic matter left over from dead bodies which will become inorganic materials (minerals) which are reabsorbed by plants.
Pay attention an example of a saprophyte food chain below:
Weathered wood → mushrooms → chicken → fox.
4. Types of Ecological Pyramids
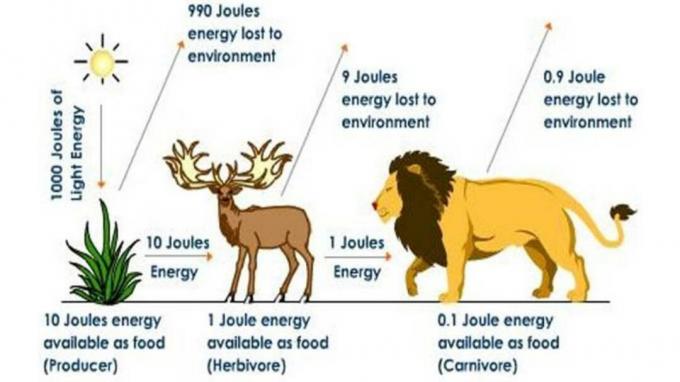
1. Energy Pyramid
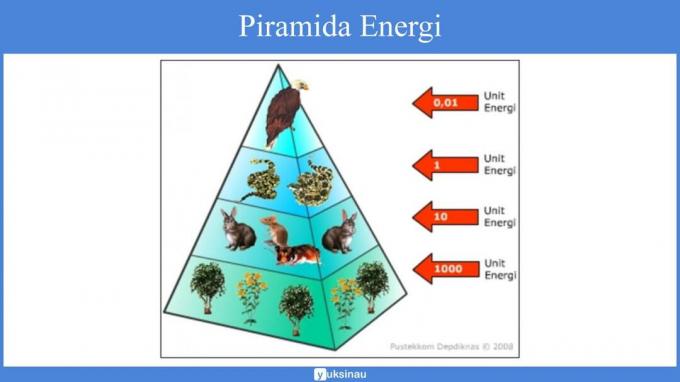
The energy pyramid is a pyramid that shows the loss of energy during the transfer of food energy in each trophic level in an ecosystem.
Inside the energy pyramid is not only the total amount of energy used by the organisms in each one the trophic level of the food chain but also involves the role of various other organisms in the transfer of food energy .
In energy use, the higher the trophic level, the more efficient it will be.
But the heat released in the energy transfer process will be much greater.
Heat loss in the respiration process will also increase from organisms with low trophic levels to organisms with higher trophic levels.
Meanwhile, in productivity, the higher the trophic level, the less. Thus, the energy stored will be less as well.
The energy in the energy pyramid is expressed in calories per unit area per unit time.
2. Biomass Pyramid

The pyramid of biomass is a pyramid showing the reduced energy transfer within each trophic level in an ecosystem.
In the pyramid the biomass at each trophic level will describe the dry weight of all organisms at the trophic level stated in grams/m2.
In general, the shape of the biomass pyramid gets smaller towards the top, because energy transfer between trophic levels is inefficient.
However, the pyramid of biomass can be inverted.
For example: in the open ocean, the producers are microscopic phytoplankton.
Meanwhile, consumers are microscopic creatures to large creatures such as blue whales, where the blue whale's biomass exceeds the producers.
The peak of the biomass pyramid has the lowest biomass, which means the number of individuals is small, and generally carnivorous individuals at the top of the pyramid will be large.
3. Pyramid of Numbers

The pyramid of numbers is a pyramid that shows the number of individuals in each trophic level in an ecosystem.
Pyramids of numbers generally have a narrow upward shape.
These pyramidal organisms have the same number from the lowest trophic level to the top Like the other pyramids, namely producers, primary and secondary consumers, and consumers tertiary.
Which means the number of plants at the first trophic level will be more than animals (primary consumers) at the second trophic level. There are fewer secondary consumer organisms than primary consumers, and there are fewer tertiary consumer organisms than consumer organisms secondary.
5. Examples of Food Chains in Various Habitats
The following are some examples of food chains found in various types of habitats. You can get to know him more in some of the food chains and the living things that play a role in them. Take a good look at the reviews below...
1. Rantai Food in the Rice Fields
The ecosystem in rice fields is one of the categories included in the artificial ecosystem with low biodiversity.
In the fields there are lots of plants that are dominated by plants, and rice is one of them.
Therefore, there will be many rice-eating organisms such as crickets, emprit birds and others.
Rice is one of the most widely grown food crops by most farmers.
This is because rice is the staple food in Indonesia. In the rice field ecosystem, rice has a role as a producer.
In addition to rice, producers in the fields include grass.
Example The food chain in rice fields, among others, is as follows:
- Rice → Bird → Snake → Eagle → Decomposer
- Grass → Insect → Rat → Snake → Decomposer
- Rice → Insect → Frog → Snake → Eagle → Decomposer
2. Food Chain in the Sea
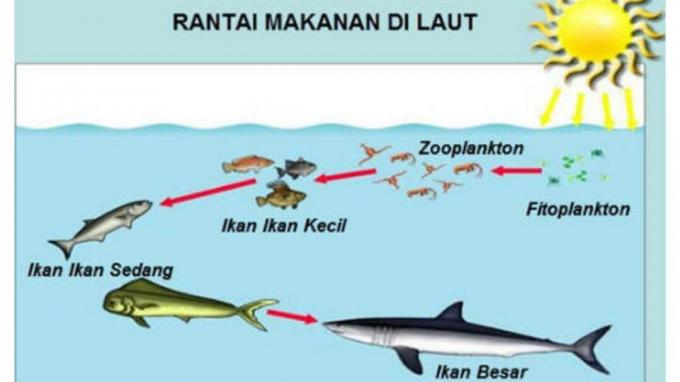
In marine ecosystems, we can find high biodiversity sharing.
This is in line with the size of the sea which is very wide. In fact, all the contents on this earth are mostly found in water.
The sea is one of the most extensive natural ecosystems. There is also a food chain in the sea that we can encounter as a process of eating and also being eaten in living things in the sea.
Living things found in the sea include: phytoplankton, zooplankton, predators and decomposers.
Phytoplankton is a single-celled living creature with a small size and hovering in the middle of the sea.
Phytoplankton in marine ecosystems has a role as a producer. Phytoplankton can make their own food with the help of sunlight.
This is because phytoplankton have chlorophyll for photosynthesis.
Zooplankton is an animal that has a small size and also lives floating in the water.
This is the same as that of phytoplankton, although they are larger in size and these organisms are not has chlorophyll so it acts as a first-level consumer who will eat phytoplankton as a source of energy.
Predators are one of the animals that are at the highest position on the food chain pyramid in marine ecosystems.
One example is the whale. These fish can eat large fish as well as small fish as a medium for obtaining energy. Because whales can't make their own food.
Decomposer This has a role in breaking down living things that have died into smaller parts so that they can be used by phytoplankton as ingredients to make food as an energy source.
One example is benthos who live on the seabed.
Benthos has an important role in maintaining the balance and stability of the food chain in marine ecosystems.
Example The food chain in the sea includes the following:
- Solar energy → Algae → Minnow → Sharks → decomposers
- Solar energy → Phytoplankton → shrimp → fish → sea lions → shark → decomposer
- Solar energy → Phytoplankton → zooplankton → shrimp → Octopus → Human
- Plankton → minnow → tuna → humans → decomposer
3. Rntai Food on the River
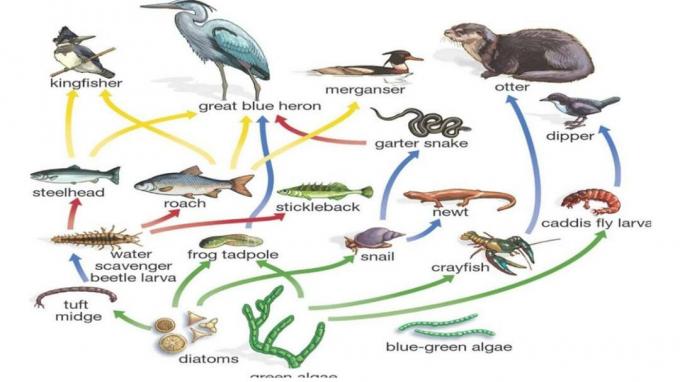
The river ecosystem is one of the ecosystems in which it contains plants and animals that are able to live in flowing water.
In the river there is also an interaction between living things which will eat each other between components in a food chain.
In the river ecosystem we can find a variety of living organisms. For example algae and also phytoplankton which have a role as producers.
This is because the two organisms can make their own food or are often known as autotrophs.
Example The food chain in the river includes the following:
- Sun → algae → trout → crane → crocodile → decomposer
- Sun→ algae→ salmon → decomposing bear
- Sun→ Phytoplankton → yuyu→ crane→ decomposer
4. Rntai Food in the Forest
Forests are one form of an example of a natural ecosystem.
There is a lot of biodiversity that we can find there. Therefore, there will be interactions between living things and their environment.
Of course, the living beings within will benefit each other.
Example The food chain in the forest includes the following:
- Sun→ grass → rabbit → snake → eagle→ decomposer
- Sun→ plants→ mice→ snake→ eagle→ decomposer
- Sun → grass → goat → tiger → decomposer
The sun is one of the main sources of energy for plants to grow and develop properly.
Grass and plants in forest ecosystems have a role as producers which are a source of energy for first-level consumers.
Having a role as a producer, plants utilize solar energy in helping the process of photosynthesis.
In the food chain, plants that act as producers are located at the lowest trophic level.
The food chain in the forest is very complex considering that there are many living things that live there and there is a lot of biodiversity there.
It is determined that there will be interactions between plants and animals that live in the forest.
In the interaction between living things that eat each other, there is a process of energy transfer between biotic organisms in the forest ecosystem.
The transfer of energy certainly has a goal in maintaining a balance in the forest ecosystem.
5. Rntai Food in the Garden
Gardens are one example of an artificial ecosystem that is deliberately created by humans. In general, many gardens are planted with cultivated plants. For example vegetables and fruit.
The size of the garden will usually adjust to the tastes of each owner who will make it.
In the garden, of course there will be many kinds of interactions between biotic factors and the environment. In it there is the process of eating and eating in a food chain.
In this case, plants have a role as producers that can make their own food or are often known as autotrophs by using sunlight.
The energy will then be transferred to other living things in a food chain in the garden.
Example The food chain in the garden includes the following:
- Solar energy → cultivated plants → insects → frogs → Snakes → decomposers
- Solar energy → plants→ chicken→ ferret→ decomposer
- Solar energy → plants → caterpillars → grasshoppers → birds → snakes → decomposers
6. Food Chain in the Sea

Lake is a natural ecosystem. But there are also lakes that are deliberately made by humans.
For example, a man-made lake is a reservoir. The reservoir is deliberately made by humans with the aim of helping the irrigation process in a place, or also as a source of hydropower.
The lake has a function as a medium in providing clean water, hydroelectric power, as irrigation, fish farming, recreation areas, preventing flooding and erosion.
Not only that, the lake can also be used for habitat and shelter for plants and animals, transportation media and others.
The lake is divided into four areas, including: the littoral area or shallow area, the limnetic area, the profundal area and the benthic area.
In the littoral area we can find aquatic plants with roots and leaves appearing on the surface as well as algae.
Not only that, we can also find snails, insects, fish, amphibians, reptiles and other animals.
In the limnetic area we can find living organisms such as phytoplankton, algae and also cyanobacteria, small fish, large fish, snakes, turtles and others.
In the deep area we will find living organisms such as worms and microbes.
In the benthic area we can find benthos and the remains of dead organisms.
Example The food chain in the lake includes the following:
- Sun → phytoplankton → zooplankton → dragonfly larvae → fish → birds → decomposers
- Sun→ phytoplankton→ fish → snakes → birds → decomposers
7. Food Chain in the Pool
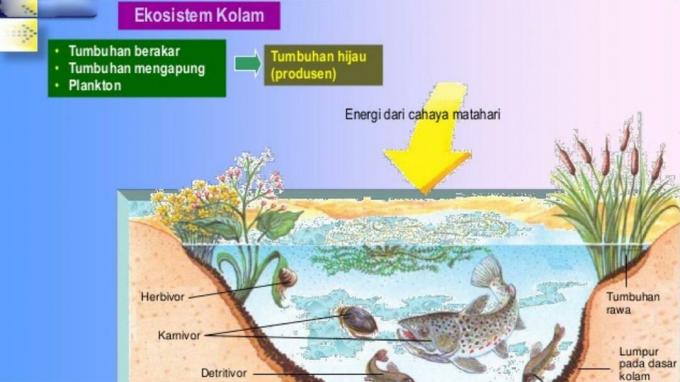
The components of the food chain in ponds are not as numerous as those in the food chain in natural ecosystems.
This is because in the pond ecosystem the organisms in it will be determined by the owner. This is what will make the pond included in the category of artificial ecosystems.
A pond is an artificial ecosystem that is intentionally created by humans and is designed to resemble its natural habitat.
In general, this pond was made in order to be used as land for fish cultivation. In general, the components of organisms in the pond consist of biotic and abiotic components.
Although the pond is included in the artificial ecosystem, but in it there is an interaction between the organisms contained in it.
This interaction can be in the form of eating and eating between organisms. In it there are also producers in the form of phytoplankton, algae and other organisms that will be a source of energy for fish.
In the pool there is also a flow of energy in the food chain.
Examples of food chains in ponds include the following:
- Solar energy → aquatic insects → frog → snake → ferret → decomposer
- Solar energy → algae → small fish → catfish → humans → decomposers
- Solar energy → phytoplankton → fish → storks → pegurai
- Solar energy → algae → fish → snake → eagle → decomposer
8. In the Meadow
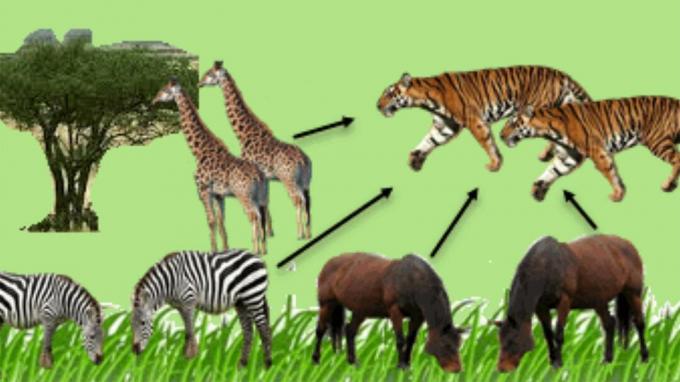
Grassland ecosystems are often also referred to as savanna ecosystems.
Grasslands are one of the ecosystems that fall into the natural category.
This ecosystem is formed as a result of a subtropical climate or a subtropical climate. Grasslands are also formed along with rainfall between 25-30 cm each year.
In grasslands, organisms that have a role in decomposing organic matter are heterotrophs.
They describe dead animals, leaves, trees and whatnot.
Examples of these organisms include fungi and bacteria. Both organisms play a role in helping to decompose the remaining organic matter.
Next, organic materials as well as plant remains will decompose so that they are good for arranging soil in the meadow. And this will cause the plants that grow there to thrive.
These plants become a source of food for organisms that live in the grasslands. Finally, there is an interaction that forms a food chain.
Example The food chain in the grasslands includes the following:
- Sun → grass → sheep → humans → decomposers.
- Sun → grass → zebra → lion → decomposer.
- Sun → grass → giraffe → lion → decomposer.
- Sun → grass → giraffe → lion → decomposer.
9. Rantai Food Detritus
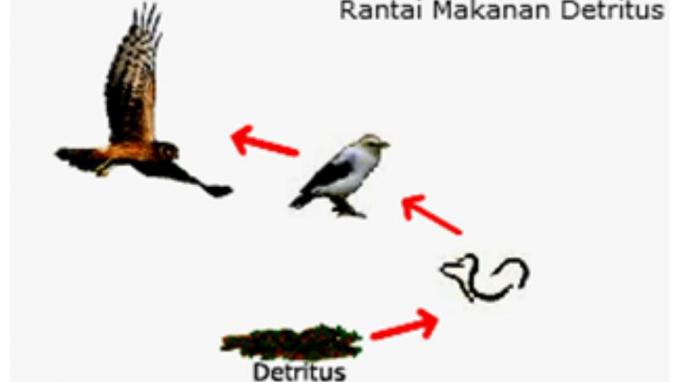
Detritus is a material that comes from the results of the weathering process of organic materials.
We can find detritus in the form of fallen leaves, dead tree trunks, animal carcasses and others.
Organisms that have a role as detritivores include termites, earthworms, keluwing and also sea cucumbers.
The detritus food chain begins with the presence of detritus which has a role as an early trophic. The detritus will then be eaten by the detritivores while the detritivores will be eaten by the carnivores.
Example The detritus food chain is as follows:
- Leaf drop → worm → chicken → human
- Litter→ worm → duck → human
10. In Desert Ecosystem

In an ecosystem there must be a food chain.
Every living thing in the food chain has a different role. This is because in the food chain there are creatures that act as producers, consumers and decomposers.
In desert ecosystems, cacti and some plants that can survive in an arid environment are a source of producers.
Within the food chain in a desert ecosystem, producers are the food source for level 1 consumers.
For example: Cottontail rabbit, kangaroo mouse, spiked mouse, gerbil and others.
Level 1 consumers will be a source of food for level 2 consumers.
For example: animals that are included in level 2 consumers are carnivorous animals such as horned lizards, snakes, birds, spiders, kit foxes and others.
Level 3 consumers get their energy sources from level 2 consumers.
For example, animals included in level 3 consumers are coyotes, birds of prey, mountain lions, foxes and others.
On the food chain in the desert region level 3 consumers are the pinnacle of predators.
Example Food Chains in Desert Ecosystems include the following:
- Solar energy → grass → small insects → mice → snake → decomposer
- Solar energy → cactus → decomposer
- Solar energy → grass → insects → lizard → snake → eagle → decomposer.
Thus a brief review this time that we can convey. Hopefully the above review can be used as your study material.
