Sounds of Newton's Laws (1, 2, 3) Formulas, Examples (Complete)
Newton's Laws (1, 2, 3) – Before discussing in detail about the sound of Newton's 1st, 2nd, 3rd laws, it is better if we know first who created Newton's 1st, 2nd and 3rd laws.
That person is Isaac Newton, an English physicist, astronomer, natural philosopher, alchemist, mathematician, and theologian who had a great influence on the world Physics.

Now, after knowing who discovered Newton's 3 laws, let's go into a complete explanation starting from the sound of Newton's laws 1, 2, 3, formulas and examples of application in everyday life.
What is Newton's Law?
Newton's laws are 3 basic formulations of classical mechanics which provide an overview of the forces acting on an object and the motion caused by it.
Also called law monumental motion, developed in the book by isaac newton himself, namely Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy (The Principia).
Table of contents
Newton's Laws (1, 2, 3) Formulas & Examples
Newton's 1st Law
Sound: "If the resultant force acting on an object is equal to zero, then the object that was initially at rest will remain at rest. An object that initially moves in a straight line will remain in a straight line at a constant speed
Newton's 1st law means that an object at rest will remain at rest and will not move until there is light (push or pull) which then makes it move, and the moving object will continue to move and will be at rest if there is a force that affects it to rest.
Newton's 1st law formula is F = 0 i.e. resultant force (Kg m/s2)
Newton's 1st law examples in everyday life:

- When the car is moving fast and suddenly brakes, the passenger will feel pushed forward
- A car that is in a stopped condition, then moves quickly forward, the passengers will be pushed back
- The coin on the paper on the table will stay still if the paper is pulled quickly
Newton's 2nd Law
Sound: "The acceleration (change of velocity) of an object will be proportional to the resultant force (amount of force) acting on the object and inversely proportional to the mass of the object.
mean newton's law 2, namely the mass of an object is very influential on the forces in a system. Addition or subtraction of mass will produce a change. The formula is F = m.a
Information:
F = Resultant Force (kg m/s2)
m = Mass of Object (kg)
a = Acceleration (m/s2)
Newton's 2nd law examples in everyday life:
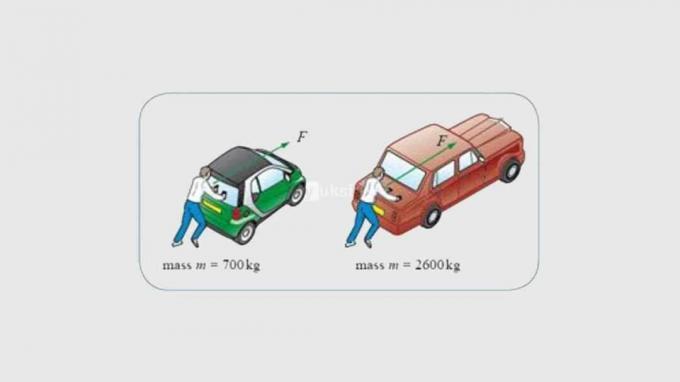
- The car on the left is going faster than the car on the right because it has a small mass (according to Newton's 2nd law)
- A car traveling on a highway will have an acceleration that is proportional to the force and inversely proportional to the mass of the car itself.
Newton's 3rd Law
Sound: "Every action will cause a reaction, if one object exerts a force on another object then the object is hit the force will exert a force equal in magnitude to the force received from the first object, but in the direction opposite“
The purpose of Newton's 3rd law is that an object will only interact if someone gives it a force, this form of interaction by reciprocating the force that has been given to the object in the direction of otherwise.
A force never acts on one object, but always acts on two objects and every force always has two ends, the end of one to object one, and the end of two to the second object.
Formula:
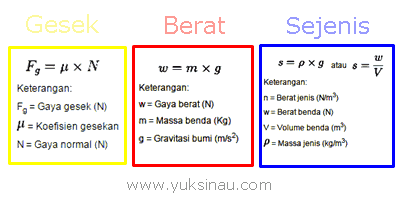
Newton's 3rd law formula can be written as law (f) action – law (f) reaction, which I marked in the yellow box as the formula for friction, the red one is the gravity, and the blue one is the formula for similar gravity.
Newton's 3rd law examples in everyday life:
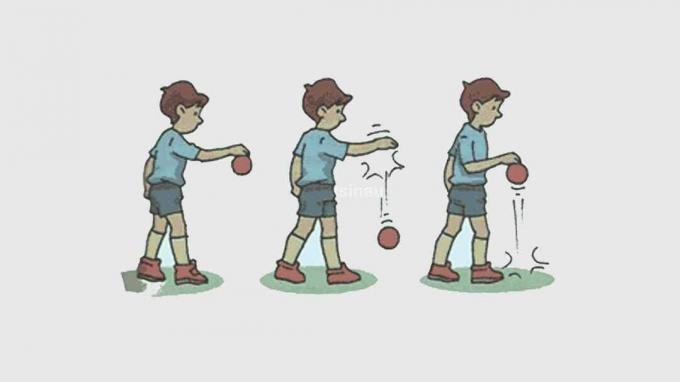
- A basketball that bounces off the ground will bounce back
- A person sitting on a weight chair pushes the chair down while the chair pushes (hold) body up.
- Someone who wears roller skates and pushes his body against a wall, then the cold will push back as much as the force exerted, so away from the wall.
- The existence of magnetic force, electric force, and gravitational force are also examples of Newton's 3rd law
That's a complete discussion of the meaning, purpose, sound of Newton's laws 1, 2, and Newton 3 along with formulas and complete examples with pictures.
