Part of Speech
In English, by grammar good and right, the term of the sentence builder is referred to as part of speech, which consists of 9 types.
This part of speech is grouped based on the function of the word in the sentence that is formed. Read more in the review below.
Table of contents
Understanding Part of Speech

Part of speech is various types of words to assemble a sentence so that it becomes coherent and can provide understanding to the readers / listeners.
The most important thing in this part of speech is knowing how to use it according to the existing grammar rules.
When you learn grammar again, an easy way to learn it is by learning this part of speech.
Part of Speech Komponen
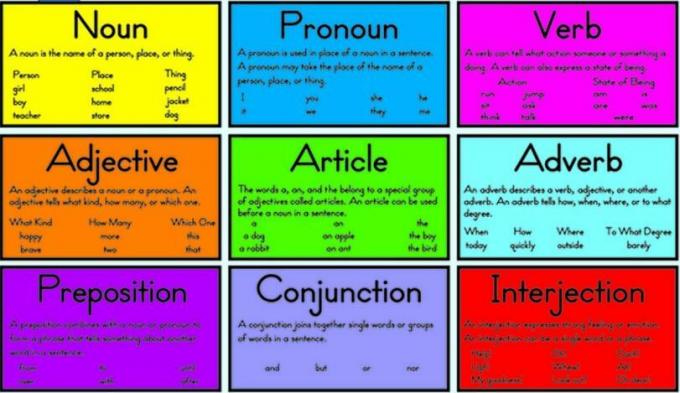
This part of speech actually refers to the various words that make up a sentence.
In English, a sentence can be called "whole" if it contains at least a noun and a verb.
Not only nouns and verbs, there are at least 6-7 other components needed to compose a complete sentence.
The following is a complete description of the 9 Parts of Speech and examples, including:
1. noun
Noun is a word used to refer to objects, people, places, to something abstract. All types of words that refer to objects are included in the noun group.
In Indonesian, nouns are called "nouns"
There are 2 types of nouns in English, namely:
- Proper noun: A noun in the form of a name / nickname so that the first letter must be capitalized.
Examples: Names of people, movie titles, places, and more. - Common noun: A noun that usually doesn't take the form of a name or nickname and doesn't need to be capitalized
2. Interjection
Interjection is an additional word that actually has no meaning, or does not enter the English dictionary.
However, this word is often used to express the reader's feelings.
If you want to use an interjection, you can put it at the beginning, middle, or end of the sentence.
Some examples of interjection words that are commonly used natively are yep, well, wow, and others.
3. Conjunction
Conjunction serves as a liaison between two sentences to form a unified whole sentence.
However, in conjunction, two sentences that are combined can actually stand alone. The use of conjunctions was chosen to make the pronunciation of the two sentences more efficient.
There are 4 types of conjunctions that you can learn, including:
- Coordinating conjunctions: Used to connect two sentences with equal position Example: For, yet, but, so, etc.
- Correlative conjunctions: Used as a link between two sentences that have the same meaning. Example: Either / or, neither / nor, etc.
- Subordinating conjunctions: Used as a liaison between dependent and independent sentences. Example: Because, although, since, etc.
- Conjunctive adverbs: For more, visit the page conjunctions.
4. Preposition
Prepositions are words used to connect pronouns, nouns or other phrases in a sentence.
Here are some types of prepositions and their brief explanations:
- Preposition of place: Preposition used to indicate a place. Includes: In, at, on, in front of, under, between, etx.
- Preposition of time: Preposition used to show time. Includes: In, at, on, before, during, after, etc.
- Preposition of movement: Preposition used to show movement / displacement. Includes: To, through, across, into, etc.
Actually there are more than 100 prepositions in English, but don't worry, because it's easy to learn, especially if you use it often.
5. Adverb
Adverb is a word used to give an "adjective" to a verb.
The purpose of using this adverb is to explain additional information related to the verb being used.
For example when you run, you can run very fast (quickly) or slowly (slowly).
Adverbs are also divided into four different types, including:
- Adverbs of manner: Adverbs that show behavior. Example: Sadly, angrily, happily, etc.
- Adverbs of place: Adverbs that show the location of the verb. Example: Ahead, in front of, near, etc.
- Adverbs of time: Adverbs that show a period of time. Example: Now, tonight, early, etc.
- Adverbs of frequency: Adverbs that show the degree of intensity. Example: Seldom, sometimes, rarely, etc.
6. Determiner
Actually, this determiner belongs to the group of adjectives. However, in this discussion, the two are deliberately separated because determiners have many types.
Determiners have at least 9 types of variance with different functions and uses.
Here are the types:
- Definite articles
- Indefinite articles
- Possessive determiners
- Demonstratives
- Quantifiers
- Distributives
- Numbers
- Pre-determiners
- Difference words
7. adjective
Adjectives in Indonesian are known as "adjectives". This adjective is a word used to describe a noun / pronoun.
As the name implies, the use of adjectives has a purpose to describe the characteristics inherent in an object.
There are two types of adjectives, namely:
- Common adjectives are adjectives in general. Examples: Kind, gorgeous, pretty, nefarious, and others.
- Articles are a, an, and the.
8. Verb
Verb is a word used to describe something that a noun or pronoun does. This verb has many types depending on the point of view used.
Based on its use, there are three types of verbs, namely:
- Infinitive verb (V1)
- Past Verbs (V2)
- And past participle verb (V3).
Based on the form of the word, the verb consists of two types, namely:
- Regular verbs: Verbs that do not change drastically when converted to V2 and V3.
- Irregular verbs: Verbs that undergo significant changes when converted to V2 and V3.
9. Pronoun
A pronoun is a verb that is used to replace a noun.
In general, pronouns consist of they, we I, you, he, she, it. However, there are many other types of pronouns, such as the following:
- Subject pronoun: Included in the category of personal pronouns. Includes: I, you, we, they, he, she, and it.
-
Object pronoun: Pronoun used to refer to the noun that is the object of conversation.
Includes: you, me, them, us, her, him and it. -
Possessive adjective: Used to show ownership of a noun to another noun.
Includes: your, my, their, our, her, his and its -
Possessive pronoun: Also used to show ownership. However, the possessive pronoun is preceded by the noun it has.
Includes: yours, mine, theirs, ours, his and hers. -
reflexive pronoun: Used to reflect on oneself.
Includes: yourself, myself, themselves, ourselves, herself, herself and herself.
In addition to the five main pronouns above, there are also several other types of pronouns such as:
- Demonstrative pronoun
- Indefinite pronoun
- Relative pronoun
- Reciprocal pronoun
- Interrogative pronoun
- Intensive pronoun
For more information about pronouns, please visit the page: Pronoun
Example Sentences of Part of Speech

So that you understand more about the part of speech, here we present an example of a sentence from the part of speech and its components, including:
| Information | Example Part of Speech |
|---|---|
| Noun + Verb |
|
| Pronoun + Verb |
|
| Pronoun / Noun + Verb + Noun |
|
| Noun + Verb + Adverb |
|
| Noun / Pronoun + Adjective + Noun |
|
| Noun + Verb + Adjective + Noun |
|
| Interjection + Noun + Adjective |
|
