Algebra: Elements, Counting Operations, Fractions of Magical Forms
Algebra is a form of mathematics in which the presentation includes various letters that represent unknown numbers.
The algebraic form is usually used to solve a problem in everyday life.
The use of algebra is widely used for various unknown things such as the amount of fuel oil needed a bus per week, the distance covered in a given time, or the amount of fodder needed in 3 day. We can find the results using algebra.
Table of contents
Elements of Algebra
1. Variables, Constants and Factors
Take a look at the algebraic form below:
5x + 3y + 8x – 6y + 9.
In the algebraic form above, the letters x and y are also referred to as variable.
Variable is a symbol or a substitute symbol for a number whose value is not clearly known.
Variables also have other names, namely variable. Variables are generally denoted by using lowercase letters a, b, c, …, z.
The number 9 in the algebraic form above is called constant.
Constant is a term of an algebraic form in the form of numbers and does not contain variables.
If a number a can be changed to a = p X q where a, p, q are integers, then p and q are called factors of a.
In the algebraic form above, we can decompose 5x into 5x = 5 X x or 5x = 1 X 5x.
So, the factors of 5x are 1, 5, x, and 5x. As for what is meant by coefficient namely the constant factor of a term in algebraic form.
Consider the coefficients for each term in the following algebraic form: 5x + 3y + 8x – 6y + 9.
The coefficient on the 5x term is the number 5, the 3y term is the number 3, the 8x term is the number 8, and the 6y term is the number -6.
2. Similar and Unsimilar Tribes
a) Tribe
The term is a variable as well as its coefficient or constant in algebraic form which is separated by the operation of sum or difference.
Similar tribes is a term that has the same variable and power of each variable.
As an example:
5x and –2x, 3a2 and a2, y and 4y, …
Dissimilar tribe is a term that has a variable and the power of each variable is not the same.
As an example:
2x and –3×2, –y and –x3, 5x and –2y, …
b) First Tribe
The first term is an algebraic form that is not related by the operation of sum or difference.
As an example:
3x, 2a2, –4xy, …
c) Second Tribe
The term two is an algebraic form associated with a sum or difference operation.
As an example:
2x + 3, a2 – 4, 3×2 – 4x, …
d) Tribe of Three
The third term is an algebraic form associated with two operations of addition or difference.
As an example:
2×2 – x + 1, 3x + y – xy, …
An algebraic form that has more than two terms is called a polynomial.
Operations to Calculate Algebraic Forms
Algebraic arithmetic operations can take the form of multiplication of one term with two terms, multiplication of two terms with two terms of two, division of algebraic forms, and exponents of algebraic forms.
However, before you learn more about arithmetic operations on algebraic forms, you need to know about the following three algebraic properties:
-
Commutative Properties
a + b = b + a, with a and bR (real number)
-
Associative Properties
(a + b) + c = a + (b + c) where a, b, and cR (real number)
-
Distributive Properties
a (b + c) = ab + ac, where a, b, and cR (real number)
The three properties above have their respective important roles in understanding the concept of factorization of algebraic forms.
And before you learn about factoring algebraic forms, you need to understand the arithmetic operations of the algebraic form. jabar consisting of addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and also power which will be discussed below this.
Read carefully the following review until it's finished.
1. Addition and Subtraction of Algebraic Forms
In algebraic form, addition and subtraction operations can only be performed on similar terms.
The trick is simply to add or subtract the coefficients on similar terms.
As an example:
The sum of 3 watermelons with 2 results is not five watermelons and not 5 mangoes.
The result will still be 3 watermelons and two mangoes.
So, what does this have to do with algebraic addition and subtraction?
This is just an example, for example, watermelon represents the variable x and pineapple represents the variable y. The sum of 2x and 3y is not 5x or 5y. The result will still be 2x and 3y.
See further explanations regarding addition and subtraction of algebraic operations below. We will give examples of mistakes that are often done as well as correct examples of addition and subtraction operations in algebraic forms
Example Wrong (often made mistakes):
8x – 5y = 3x
8y – 5y + 3x = 6y
8x – 5x +3y = 6x
Correct Example (correct result):
8x – 5y = 8x – 5y
8y – 5y +3x = 3y + 3x
8x – 5x + 3y = 3x + 3y
Pay close attention to the variables, addition and subtraction operations only apply to the same variable.
2. Multiplication
You need to remember that in the multiplication of integers the distributive property of multiplication applies to addition, namely a × (b + c) = (a × b) + (a × c).
And also the distributive property of multiplication on subtraction, namely a × (b – c) = (a × b) – (a × c), for the integers a, b, and c, respectively. This property also applies to the multiplication of algebraic forms.
Here we will show you how to multiply the operations of algebraic forms.
Multiply one term by two terms
Watch how to multiply one term by two in the image below!

Examples of common mistakes:
2(x – y) = 2xy
3x (2x – y) = 6x – 3xy
Correct Example (correct result):
2(x – y) = 2x – 2y
3x (2x – y) = 6x2 – 3xy
Multiplying Two Terms by Two Terms
Take a look at how to multiply two terms in the image below!
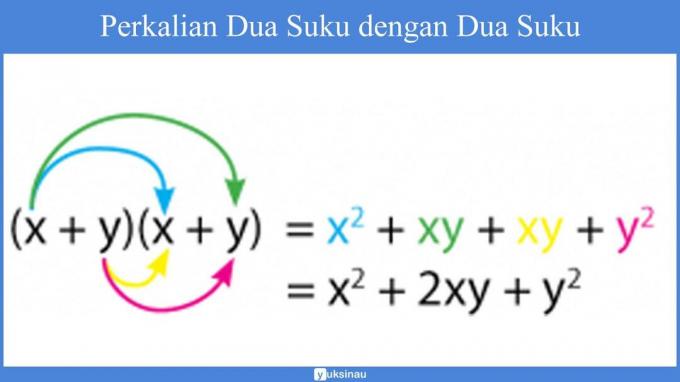
Examples of common mistakes:
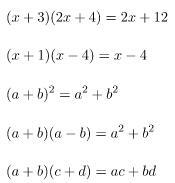
Correct Example (correct result):
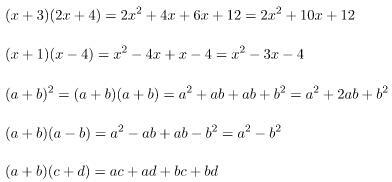
3. Rank
Try to remember about the exponent operation on integers.
The exponent operation is defined as repeated multiplication of the same number.
This also applies to the power of algebraic form.
On the power of algebraic form of two terms, the coefficient on each term is determined according to Pascal's triangle.
For example, we will determine the pattern of coefficients in the translation of the two-term algebraic form (a + b) n, with n natural numbers.
Look at the image below:

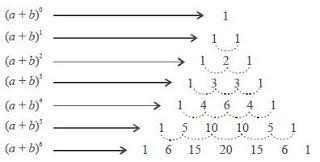
In Pascal's triangle above, the number below it is obtained by adding the adjacent numbers above it.
Examples of common mistakes:
(x + y)2 = x2 + y2
(x – y)2 = x2 – y2
(2x)5 = 2x5
Correct Example (correct result):
(x + y)2 = x2 + 2xy + y2
(x – y)2 = x2 – y2
(2x)5 = 2x5
4. Share
You can get the quotient of two in the algebraic form of numbers by first determining the common factor in each of the algebraic forms.
Next, divide the numerator and denominator.
Examples of common mistakes:
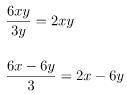
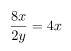
Correct Example (correct result):
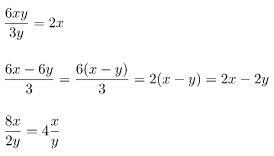
Don't ignore the variables. Be careful with divisions as well as denominators or quantifiers that have additions like the following:
5. Substitution on Algebraic Forms
We can determine the value of a number in algebraic form by substituting any number in the variables of the algebraic form.
6. Determining the KPK and FPB in Algebraic Forms
Try to remember again about how to determine the LCM and GCF from two or more integers.
This also applies in algebraic form. To find the LCM and GCF from algebraic forms, we can do this by declaring the algebraic forms to be the product of their prime factors.
Algebraic Fractions
1. Simplifying Fractions of Algebraic Forms
An algebraic fraction is said to be the simplest if the numerator and denominator have no common factors except 1.
And the denominator is not equal to zero.
To simplify fractions in algebraic form, we can do this by dividing the numerator and denominator of the fraction by the GCF of both.
2. Operations to Calculate Algebraic Fractions with Single Term Denominators
- Addition and subtraction
In the previous chapter, we have seen that the results of addition and subtraction operations on fractions are obtained by equating the denominators.
Then add or subtract the numerators next.
You must also remember that to equate the denominators of the two fractions, determine the LCM of the denominators.
In the same way, it also applies to addition and subtraction operations of algebraic fractions.
Consider the following example questions:

- Multiplication and division
Multiplication of algebraic fractions is not much different from that of multiplication of fractions.
Consider the following example questions:

- Algebraic powers of fractions
The exponent operation is repeated multiplication of the same number. This also applies to the power of fractions in algebraic form.
Consider the following example questions:

Thus a brief review this time that we can convey. Hopefully the above review can be used as your study material.