Density: Definition, Formulas, Units, Example Problems
Before you know the various formulas related to density, you must know the meaning of density itself, take a good look at the reviews below.
Table of contents
What is Density?

Have you ever seen a boat floating on water?
Boats made of wood can float on water because the density of wood is smaller than the density of water.
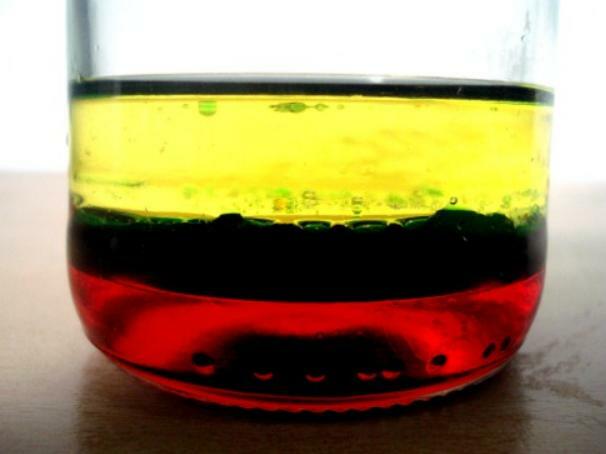
Then the oil mixed with water in a container will separate the substances and float on the water.
This is because the density of water is greater than that of oil.
The concept of density can be interpreted as how heavy or how light an object is in its volume.
Density alone is a measurement of mass per unit volume of an object.
The higher the density of an object, the greater the mass in each volume.
The average density of each object is the total mass divided by the total volume.
The density of a substance is referred to as its density which is denoted by using (rho), which is the product of the mass of a substance by its volume.
This is in accordance with the main properties of a substance, namely mass and volume.
State of Matter based on Density
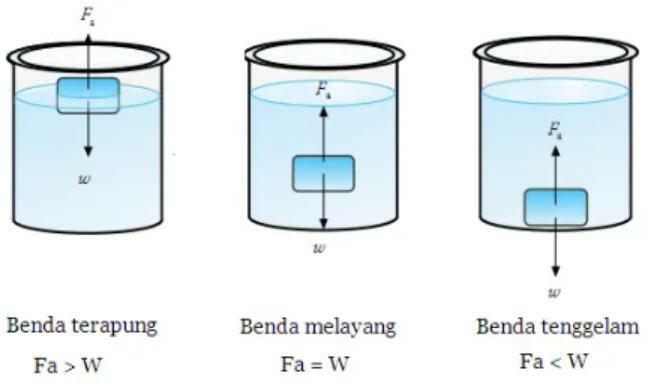
Here are some conditions of objects in water based on the size of the density of the object itself, including:
1. Flying
In order to float, an object in water must have the same density as the density of the water itself.
An object can be said to float if all of its parts are in the liquid.
When an object is placed in a liquid, the object will neither move up nor down (float), which means that the upward force (Fa) is equal to the gravity (w).
2. Floating
In order to float, an object in water must have a density less than the density of water.
An object can be called floating if all or part of it is above the surface of the liquid.
When an object is placed in a liquid, the object will move upward, so the upward force (Fa) will be greater than the gravity (w).
3. drown
An object can be said to sink if the object has a greater density compared to the density of water, so the object will experience a net downward force that is not the same with zero.
Which means the object is at the bottom of the container / place of liquid.
When an object is placed in a liquid, it will move downward until it touches the bottom of the container liquid and remains at the bottom, so the upward force (Fa) will be smaller than the weight.
Density Formulas and Units

To determine the density of an object, you can use the equation or formula below:
= m / V
Information:
- = density of the object (kg/m3) (g/cm3)
- m = mass of object (kg)
- V = volume of the object (m3 or cm3)
Density has the symbol which is read as “rho”.
The formula for density is the result of dividing the mass of the object by the volume of the object.
The unit of density according to the international system of units is Kg/m3 / Kg m-3.
Mass has units of Kg and its unit volume is m3.
Here are some other unit conversions you need to know:
- 1 Kg/m3 = 0.001 g/cm3
- 1 g/cm3 = 1000 Kg/m3
- 1 liter = 1000 milli liter = 1000 cm3
What is the difference between a mass and the density of an object?
Answer: Mass indicates the number of particles present in an object, while density tells how tightly, densely a particle is arranged.
Measuring Density

To measure the density of an object, you must first know the mass of the object and its volume.
- You can measure the mass of an object using a balance.
- Volume can be measured in various ways, such as:
If the object is a regular shape (cube, block, or sphere) you can measure the length of its sides and then calculate the volume using the volume formula for each shape.
However, if the object being measured has an irregular shape (stone) then you can use a measuring cup to measure its volume. - Density is found by dividing the mass of an object by its volume.
The thing you need to know is that every object has a different mass density.
It is the density of the mass that will determine how tight/hard the material is.
Here are the mass densities of various materials as well as materials:
| Substance name | in kg/m3 | in g/cm3 |
|---|---|---|
| Water (4 degrees Celsius) | 1,000 kg/m3 | 1 gr/cm3 |
| Alcohol | 800 kg/m3 | 0.8 gr/cm3 |
| Mercury | 13,600 kg/m3 | 13.6 gr/cm3 |
| Aluminum | 2.700 kg/m3 | 2.7 gr/cm3 |
| Iron | 7,874 kg/m3 | 7.87 gr/cm3 |
| Gold | 19,300 kg/m3 | 19.3 gr/cm3 |
| Brass | 8,400 kg/m3 | 8.4 gr/cm3 |
| Silver | 10,500 kg/m3 | 10.5 gr/cm3 |
| Platinum | 21,450 kg/m3 | 21.45 gr/cm3 |
| Zinc | 7,140 kg/m3 | 7.14 gr/cm3 |
| Air (27 degrees Celsius) | 1.2 kg/m3 | 0.0012 gr/cm3 |
| Ice | 920 kg/m3 | 0.92 gr/cm3 |
*) Density is another name for density or density.
Problems example
To make it easier for you to understand the material above, here we provide some examples of questions and discussions related to density, including:
1. It is known that one 5 liters of mud weighs 6 kilograms. Calculate the density of the mud in kilograms/liter!
Answer:
Is known:
- m = 6 kg, V= 5 L
Solution:
Density = 6/5 = 1.2 kg/L.
2. It is known that 2 cubic meters of wood weighs 1,400 kg. What is the density of the wood?
Answer:
Is known:
- m = 1,400 kg, V= 2 m³
Solution:
Density = 1,400/2 = 700 kg/m³
3. It is known that an object in the form of a solid cube made of synthetic material has a side length of 10 cm. The object weighs half a kilogram. Calculate the density of the object in kilograms per cubic meter!
Answer:
Is known:
m = 0.5 kg, s = 10 cm
Solution:
Volume of cube = V = 10 x 10 x 10 = 1000 cm³ = 0.001 m³
So, the density is:
= 0.5/ 0.001 = 500 kg/m³
4. What is the mass of water, if it has a volume of 1 liter?
Answer:
Is known:
- V = 1 liter = 0.001 m³
Solution:
It is known that the density of water = 1000 Kg/m³.
So by using the density formula, we get:
m = V = (1000)(0.001) = 1 Kg
5. An irregularly shaped iron weighs 14 kg. The volume of the iron will then be measured using a measuring cup filled with water. Before adding iron, the volume of water fills the measuring cup. After inserting an iron, the water in the glass spilled. How much water was spilled?
Answer:
Is known:
- Mass of stone (m) = 14 kg
Solution:
It is known that the density of iron ρ = 7.874 Kg/m³, so that
The volume of stone that is put into a measuring cup filled with water makes the water in the glass spill wasted. Which means Volume of spilled water = Volume of Stone
v = m / = 14 / 7.874 = 1.77 m³.
So that the wasted water is 1.77 m³.
6. A measuring cup is initially filled with water to a height of 45 ml. After being filled with stones, the water in the measuring cup rises to 75 ml. Calculate the density of the rock if the mass of the rock is 120 grams.
Answer:
Is known:
m = 120 g
V = 75 ml – 45 ml
= 30 ml, or
= 30 cm3
Asked:
- ρ….?
Solution:
ρ = m/V
= 120 g/30 cm3
= 4 g/cm3
So it can be seen that the density of the rock is 4 g/cm3
