Plant Cell Organelles: Structure, Pictures, Functions (Complete)
Plant Cell Organelles – Actually, on previous occasions, we have discussed in detail about cell organelles but unfortunately there are still mixed up between plant cell organelles and animal cell organelles.
Where I recommend that you read the article first Structure, Image, and Function of Cell Organelles so that it is easier to understand this discussion about plant cell organelles.
Plant cells are a group eukaryotic cellEukaryotic cells are a group of cells that have genetic material (DNA) wrapped in a membrane.
Plant cells have a unique structure compared to other eukaryotic cells.
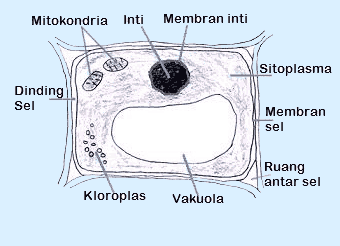
The most basic difference is the rigid shape of plant cells. This form is obtained from the outermost cell wall in plant cells.
The cell wall is made up of compounds cellulose, pectin, hemicellulose, and lignin which will strengthen the plant structure.
Even though animals and plants both have eukaryotes, they differ in certain characteristic features.
For example, plant cells have well-developed cell walls and large vacuoles, whereas animal cell organelles does not have that structure.
Apart from differences in structure, in animal cells there are centrioles and middle filaments which are not found in plant cells.
The characteristic feature of plant cells is that they consist of organelles and cytoplasm, where all organelles (except the cell nucleus or nucleus) and subcellular structures in the cytoplasm will be covered by cell membrane or cell wall as a protective layer.
Structure, Figure, Function of Cell Organelles
1. Plant Cell Organelle #Nucleus (Cell Nucleus)
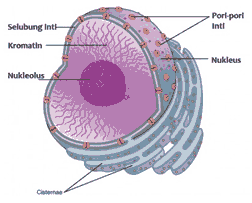
Nucleus (cell nucleus) namely cell organelles that are very unique and important, as the main place for cells to store chromosomes (genetic components) of certain cells.
The nucleus has the function of coordinating metabolic processes, for example cell division, cell growth, and protein synthesis. The nucleus and its contents are called the nucleoplasm.
2. Plant Cell Organelles #Plastides (Chloroplasts)
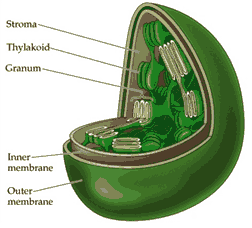
Plastids (chloroplasts) is a collective term for organelles that working to carry the pigment. Chloroplasts have a very prominent shape from plastids which contain the green chlorophyll pigment.
Because there are plastids (chloroplasts) that contain green chlorophyll, plants are able to undergo this process photosynthesise well in the presence of water, sunlight, and carbon dioxide for food synthesis alone.
3. Plant Cell Organelles #Ribosomes
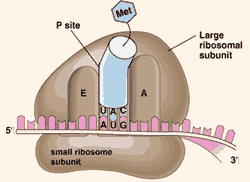
Ribosomes are cell organelles that are small in shape, namely in the form of granules nucleoprotein. Ribosomes are composed of large subunits and small subunits, containing ribosomal RNA and RNAr and proteins in it.
Ribosomes are divided into 2 types which are found in the cytoplasm, namely: bound and free ribosomes.
The main function of the ribosome i.e. producing and synthesizing protein substances present in cells. To understand more about ribosomes please read Structure and Function of Ribosomes (Cell Organelles).
4. Plant Cell Organelles #Mitochondria (The Power House)
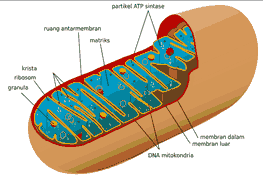
Mitochondria are large, rod-shaped organelles present in the cytoplasm of plant cells. Mitochondria are useful in breaking down complex carbohydrates and used sugars.
Mitochondria contain certain enzymes which are useful and important as energy supply to plant cells.
Mitochondria have a function as a place of aerobic respiration in the formation of ATP as a source of energy. Mitochondria are also known as the powerhouse of the cell.
5. Plant Cell Organelles #Golgi Body (Golgi Apparatus)
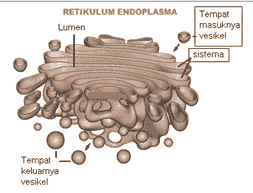
The Golgi apparatus (golgi apparatus) consists of a collection of flattened vesicles that have cisternae (winding) or flattened pouches. Golgi bodies located in plant cells are called dictyosome, its presence is mostly found near cell membranes.
The main functions of the Golgi apparatus are: to lift chemicals in and out of cells, after the ER (Endoplasmic Reticulum) synthesizes proteins and fats. The Golgi apparatus converts it and prepares it for export outside the cell.
6. Plant Cell Organelles # Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
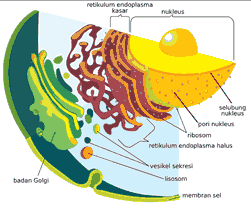
Endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle that connects the nucleus (nucleus) with the cytoplasm in plant cells.
Basically it is an interconnected network, the ER has convoluted pockets. There are 2 types of Endoplasmic Reticulum: Rough RE and Smooth RE.
The structure of the Endoplasmic Reticulum can only be seen with an electron microscope. Functions of the endoplasmic reticulum namely as a synthetic transporter of fats and steroids, a place to store phospholipids, steroids, glycolipids, carry out detoxification of drugs and toxins.
7. Plant Cell Organelles #Vacuoles
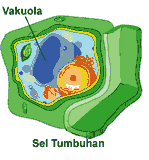
The vacuole is a membrane, as a storage area that helps in regulating the turgor pressure of the plant cell.
In plant cells generally found more than one vacuole. But vacuoles take up more space than others, which store a wide variety of chemical compounds.
Vacuole works as well as the excretion of waste products and the intracellular digestion of complex molecules.
8. Plant Cell Organelles #Peroxisomes (Micro Bodies)
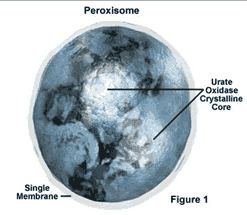
Peroxisomes are cytoplasmic organelles of plant cells that contain certain oxidative enzymes. The enzyme is used in the metabolic breakdown of fatty acids into simple sugars.
Peroxisome function is to break down fatty acids into sugars and help chloroplasts in the process of photorespiration.
That is a brief description of the meaning of plant cell organelles with structure, pictures of plant cell organelles, and plant cell functions.
If you want to learn also about the material of animal cell organelles, Yuksinau.id also discussed it. Hopefully the conclusions above can be useful.
Maybe you also like this article.
