Endogenous Forces (Volcanism, Seism, Tectonism) + Examples
Endogenous energy is the energy that comes from within the earth that produces changes in the earth's crust. The nature of endogenous energy is to make the earth's surface uneven.
For example, in an area that used to have a flat or flat earth surface, but due to endogenous forces it turned into mountains, hills, or mountains.
So that it affects the shape of the earth. Endogenous energy is generally divided into 3 types, namely: volcanism, seism, and tectonism.
Table of contents
Volcanism

Volcanism is magma activity that moves from the lithosphere layer to the earth's surface, the magma family event to the earth's surface is called a volcanic eruption.
The science that studies volcanoes is called volcanology.
Magma is a massage liquid silicate material composed of liquid, solid, and gaseous objects in the earth's lithosphere. The temperature of magma under normal conditions is 900 – 1,200 degrees Celsius.
The movement of magma that stops when it reaches the earth's surface is called magma intrusion, and the successful movement of magma to the earth's surface is called magma extrusion.
A volcano is a hole in the earth's crust that emits molten rock, ash, and gas.
Volcanoes are often formed from fragile points in the earth's crust, usually along the boundaries of the earth's plates, such as Indonesia which has many mountains.
Melted rock when a volcano erupts is called magma, magma that reaches the earth's surface through a gap in the earth's layer is called lava.
According to the type of eruption (mountain eruption), volcanoes are divided into 3 types, namely: srato shape (cone), maar shape (funnel), and shield shape (prism).
1. Strato Volcano (Cone)
Strato volcano is a volcano that looks like a giant version of a cone.
This volcano is formed due to volcanic eruptions that repeatedly alternate between explosive eruption (explosion) in the form of molten lava and solid material and epic eruption (melt magma).
Because in Indonesia there are many volcanoes with the shape of a cone, so you certainly don't see them often. Examples are Mount Ceremai in West Java, Mount Gede, Mount Pangrango.
2. Maar Volcano (Funnel)
Maar volcano is a volcano with a funnel-shaped peak, so it is often called a funnel mountain.
Formed by a very powerful eruption that occurred once, leaving a very large hole like a funnel.
Examples of this funnel volcano are Mount Monte Nouvo (Italy), Mount Merdada (Dieng, Indonesia), Mount Lamongan (East Java, Indonesia), Mount Pinacate (Mexico).
3. Shield Volcano (Prism)
Shield volcano has the shape of a mountain whose slopes are sloping so that it covers a very wide lake.
Formed by effusive eruption (very liquid). Yuksinau.id I think we rarely see volcanoes in the form of shields or prisms because they don't exist in Indonesia.
Examples of shield volcanoes are Mount Mauna Loa and Mount Mauna Kea in Hawaii.
Seism (Earthquakes)

Seism or earthquakes are shocks or vibrations that occur on the earth's surface due to earthquakes endogenic process produced when the earth's plates move.
Damage will occur when the shock reaches the surface.
Earthquake vibrations originate underground at a point called the focus. Then the vibrations propagate from the focus in the form of concentric circles to the surface of the water.
The result is damage, the most devastating damage when the point of the surface is precisely in focus. Earthquakes are measured using a tool Siesmometer.
The damage caused by an earthquake can be in the form of fires, landslides, avalanches, tsunamis, collapsed buildings, and others.
There has been a major event in Indonesia in 2004, namely the tsunami in Aceh which caused a lot of casualties.
Most earthquakes occur when the plates that make up the Earth's crust collide. So that the movement causes pressure on the stone so that it separates.
Some terms that have something to do with seism or earthquakes:
- Seismology is the study of earthquakes, scientists who specialize in studying earthquakes are called seismologists.
- Seismograph is a tool to record or measure the strength of an earthquake.
- Hypocenter is the epicenter of the earthquake on the earth's surface.
- Epicenter is a point on the earth's surface where earthquake waves propagate.
Cause of earthquake:
- Tectonic earthquake An earthquake that occurs due to tectonic processes in the earth's crust, in the form of a shift in the rock layer structure horizontally or vertically.
- Volcanic earthquake an earthquake that occurs due to volcanic activity, either after or before a volcanic eruption letusan
- Ruin earthquake runtuh is an earthquake that occurs due to the collapse of a giant rock mass and soil or due to the collapse of a cave which is very large so that it causes vibration, the vibration is not too strong like a volcanic earthquake and tectonic. This collapse earthquake is also known as a bound earthquake.
tectonism
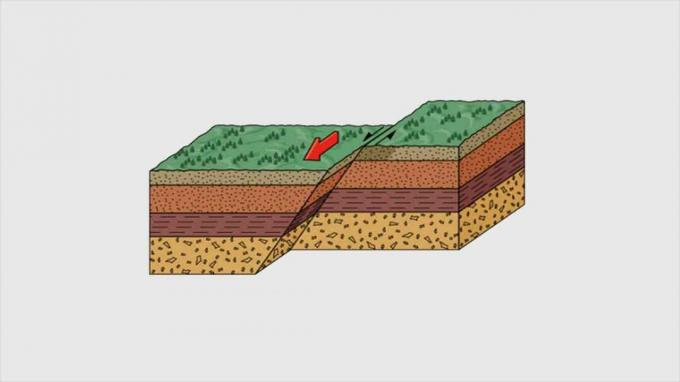
Tectonism is a process that occurs because folds, fractures, movements, and rapture on the soil structure somewhere.
Included in the formation of the earth's surface comes from endogenous energy without being influenced by magma. Diatropism is a structural process that gives rise to folds and faults.
fold is the shape of the earth's surface as a result of vertical and horizontal pressure movements that cause the earth's surface layer to become covered and wrinkled.
Fault is the earth's surface as a result of the movement of vertical and horizontal pressure which causes the earth's layers to break and crack.
There are 2 types of tectonism, namely: Epigenesa and Orogenesis.
Epirogenesis is the process of changing the shape of the land due to slow energy from within the earth in a vertical direction, either downwards or upwards through a very large area.
There are 2 Epigeneses:
- Positive epigenesa is an activity that causes the earth's crust to fall, so that sea levels appear to rise and land to decrease. Example: The sinking of the island.
- Negative epigenesa is an activity that causes the earth's crust to rise, so that the sea level looks down and the land rises. Example: The emergence of a new island.
Orogenesis is the rapid movement of tectonic plates over a narrow area.
Orogenetic tectonics are generally accompanied by warping and folding processes that arise due to pressure in the horizontal direction on a flexible rock layer.
Folds are made up of 2 basic shapes: anticlinal and syncline.
Faulting occurs due to the influence of very strong horizontal and vertical stresses. There are 2 types of faults, namely horst and graben (slenk), and cracks (joints).
One example of the results of Orogenesis is the series of the Mediterranean Curve.
1. fold
Folds arise due to the horizontal movement of endogenous forces from two opposite directions. The top fold part is called anticlinal and the lower part is called syncline.
There are several kinds of folds, namely upright folds, inclined folds, lying folds, and petal folds. As a result of pressure, the earth's crust forms the peaks of folds and valleys of folds.
2. Fault
Fault is a tool formation due to fracture in the rock layers that make up the earth's crust. Faults generally occur because there are cracks in a stretch.
Faults can also occur due to the reduction of layers in the earth's crust. For example, due to volcanic eruptions, part of the earth's crust descends into the surrounding area.
