Gases: Definition, Properties, Formulas, Differences (Solids, Liquids, Gases), Examples
In everyday life, we often encounter substances that participate in completing our needs. These substances include solids, liquids, and gases.
For example, the camphor that we put in the cupboard will eventually shrink because of the camphor together with the air in the cupboard and turns into a gas, this kind of thing is also called sublime.
So, what is the meaning of the gas itself? Come on take a good look at the reviews below:
Table of contents
Definition of Substance
Matter is something that has mass and occupies space. In all objects must consist of matter or can also be called matter.
And based on its form, substances are grouped into three kinds, namely solid, liquid, and gas.
Definition of Gases
Is a material or substance that has a volume and shape that will always change according to the shape of the container it occupies.
Examples include: balloons, bicycle tires and motorcycle tires, empty glasses, empty bottles, and others.
Nature
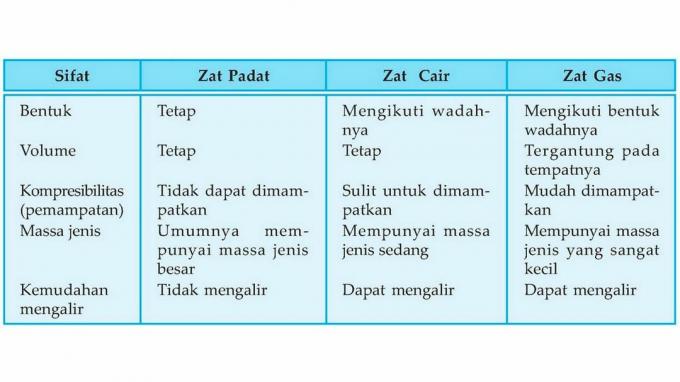
| 1 | Form | Change, follow the container or the place |
| 2 | Volume | Change |
| 3 | Particle location | So far away |
| 4 | Particle movement | Very free |
| 5 | Particle style | Very weak |
| 6 | Particle arrangement | Very far apart and disorganized |
| 7 | Easy to compress |
Expansion Formula

Boyle's Law
pV = k
Information:
- p = system pressure
- V = volume of air
- k = constant
Boyle's law equation is as follows:
p1V1 = p2V2
Difference between Solid, Liquid and Gas

Solids have a definite shape and volume. The distance between the particles in a solid is very close. The particles in a solid cannot move freely.
Liquids have a definite volume, but do not have a fixed shape. The liquid form depends on the medium or container used.
The distance between the particles in a liquid is less. Particles in a liquid can move freely but their motion is limited.
Substances in gases do not have a definite volume and shape.
The distance between the particles in the gas is very wide. Particles in gases can move very freely.
Example

- Air
- Ozone
- Atmosphere
- Xenon
- Radon
- Propane
- pentane
- Sulfur hexafluoride
- Sulfur dioxide
- Nitrogen trifluoride
- Nitrogen monoxide
- Nitrogen dioxide
- Methyl chloride
- Ethylene oxide
- Benzene
- Vinyl chloride
- Ethylene
- Carbon monoxide
- Carbon dioxide
- Oxygen
- Hydrogen
- Water vapor
- Detrium
- krypton
- Methane
- Butane
- Neon
- Argon
- Helium
- Sulfur hexafluoride
- hexane
- Hydrogen
- Nitrogen
- Cloud
- Ammonia
Changes in the Form of Substance (Object)
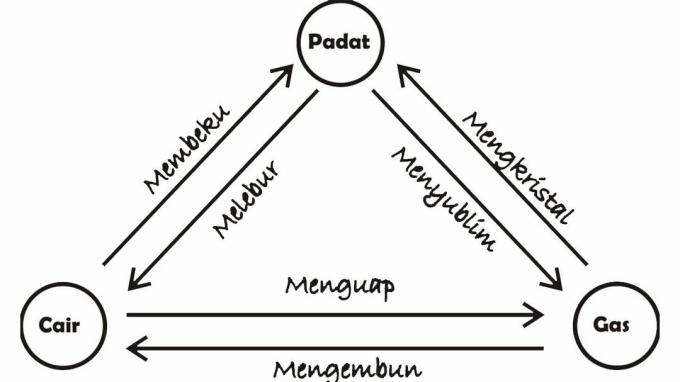
Not only that, substances such as solids, liquids and gases can also experience changes in form, in physics the changes in the form of these substances include:
- Melt, which is a change of state from a solid to a liquid. Example: the ice melts, burns the candle.
- Freeze, which is a change of state from a liquid to a solid. Example: frozen ice.
- Condense, which is a change from a gas to a liquid. Example: dew.
- yawn, which is a change of state from a liquid to a gas. Example: water vapor.
- Sublime, which is a change of state from a solid to a gas. Example: mothballs that have long been used up.
- Crystallize or crystallize (deposition), which is a change of state from a gas to a solid. Example: crystal.
Thus a brief review of this article, hopefully it can help your learning activities, okay?
