River Flow Pattern
You need to know that rivers also have different water flow patterns. Which means, the river does not always flow straight, but there are also meandering things.
This is due to the erosion and deposition processes that occur along the direction of river water flow.
For more information, read carefully the reviews below.
Table of contents
Definition of River

The river is a flow of water with a large size and lengthwise and flows continuously from upstream to downstream.
This river does not have to be in the form of water flow that is on the surface of the ground, but it can also be underground or also known as an underground river.
Along the flow of this river will later form certain streams that will adapt to nature.
Various kinds of river patterns will also flow which will eventually empties into the sea.
River types can be categorized based on the amount of water, genetics, and also the source of flowing water, here is a full explanation:
- Based on the amount of water
Includes periodic rivers, permanent rivers, intermittent rivers and ephemeral rivers. - Based on genetics
Includes subsequent, consequent, intermittent, obsequent, andesen, resekwen, and anaclinal rivers. - Based on the water source
Includes glacier rivers, rain rivers, and mixed rivers.
Understanding River Flow Patterns

The river flow pattern is a collection of rivers that have the same shape where it describes the profile and genetic conditions of the river itself.
The creation of this river pattern is due to several natural factors such as soil and rock types, morphology, topography, slope, erosion rate and geological structure.
Over time, the network system of the river will form a branched flow pattern and will adapt to environmental factors.
Types of River Flow Patterns
According to its configuration, river flow patterns have several types, including the following:
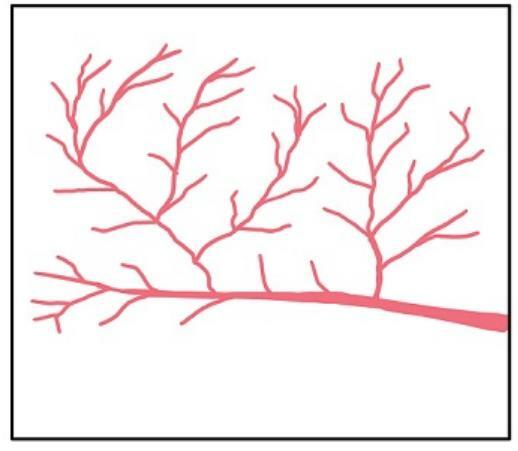
1. Dendritic Flow Pattern

The dendritic pattern is the simplest river flow pattern.
This one pattern has many branches that lead in all directions then contribute to form like tree branches and will eventually empties into the main river.
This flow will follow the slope of the homogeneous rock type and is in a V-shaped valley.
The pattern of this river will also adjust to the types of rock arrangements that exist along its flow.
The dendritic pattern has articulation as the length of the river per unit area.
This can be attributed to the presence of a river flowing from the top of the rock which is less resistant to slow erosion which will gradually form a dense river.
Meanwhile, when the river flows in rocks that are resistant to erosion, it will form a pattern of river flow that tends to appear more tenuous.
The resistance of rocks to erosion has a major influence on the process of river channel formation. Because rocks that are not resistant will easily erode and form new flow paths.
2. Trellis Flow Pattern
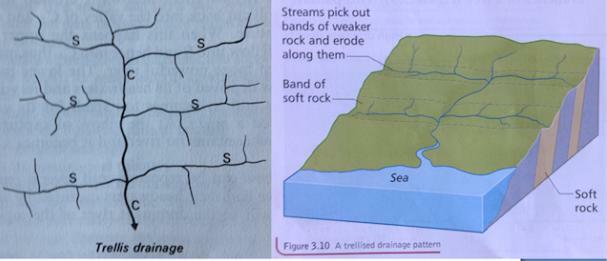
Trellis pattern is a river pattern that has a fence-like shape that is controlled by a geological structure in the form of syncline and anticline folds.
The characteristics of rivers with this flow pattern are:
- In the form of a collection of waterways that have a parallel shape.
- Flows following the slope of the slope.
- Perpendicular to the main stream.
- In general, the direction of the main channel is in the direction of the fold axis.
Trellis flow is a combination of consequent and subsequent river types.
Not only that, this one pattern can also form along parallel valleys in the mountain fold belt.
The streams will cross the valley and then meet again in the main channel.
3. Rectangular Flow Pattern

The rectangular river pattern is a flow pattern that generally exists in igneous rock areas.
The shape of this one river channel is straight following the fault structure, which is indicated by the shape of the river that is perpendicular.
Rectangular flow generally develops in erosion-resistant rocks with the erosion type tending to be uniform, but controlled by jointing in two directions at right angles to each other.
Joints are geological separation or breakdown of rock which tends to be less resistant to erosion processes so that allows the flow of water to expand through the fracture and in the end will form a flow pattern according to the flow of fractions rock.
Rivers that have a rectangular pattern are often found in fault areas with the main characteristics of river flow will follow a path that is less resistant and collects in rocky outcrops that are soft.
In the branching of the river it will form an obtuse angle as the main river.
4. Centripetal Radial Flow Pattern
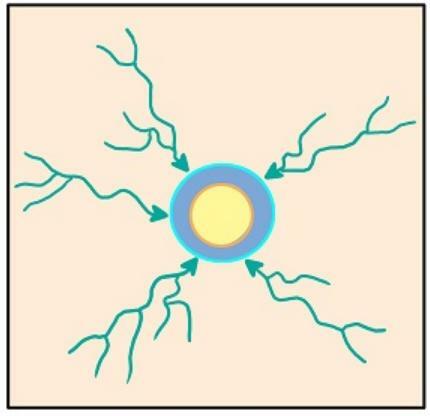
Centripetal radial flow has a branching flow pattern of tributaries in all directions whose center is in one spring.
The shape of the centripetal radial pattern is like the distribution of tributaries that gather in one main river. Where the flow of rivers from various springs will be centered towards one spring.
With such a pattern, radial centripetal resembles the distribution of tributaries flowing towards one point like a large basin.
Areas that have this pattern are in the northwestern United States.
In the process, this one pattern will develop to form an annular pattern.
The annular pattern is a pattern that at first is radial but after it appears obsequent rivers give rise to the river is parallel to the successive river so that the flow will eventually lead to the center of the gathering Genre.
5. Radial Flow Pattern
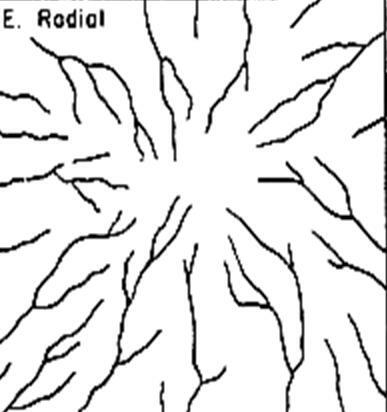
Radial has the meaning of the word that is spreading in all directions.
As the name implies, this one pattern is a river flow pattern that has one center of the river and the distribution of river flows that spreads in all directions.
You can find this pattern in several springs in the mountains / mountains.
Not only mountain springs, this river flow pattern is also found in the crater and magma patterns at the top of the volcano.
The pattern formed from the presence of magma or crater tends to follow its natural convex shape so that the shape of the flow pattern of this one crater is in the form of dome stretches.
6. Annular Flow Pattern

The annular flow pattern is a variation of the river pattern that has a radial flow.
You can find the annular river pattern in the dome and adult staium caldera areas which also exist in consequent, successive, subsequent, and obese rivers.
7. Parallel Flow Pattern

Parallel river flow patterns are river patterns that exist in a very wide area with a steep slope.
The slope of this one causes the river gradient to become large so that it will flow water to the lowest place by forming an almost straight path.
For this one river flow pattern, you can find it in a young coastal land area with an original slope whose slope leads to the sea.
8. Angular Flow Pattern
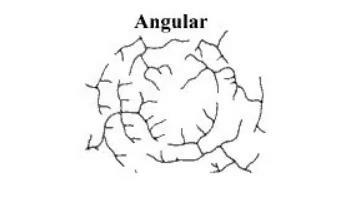
An angular flow pattern is a river pattern that is larger or smaller than a 90 degree angle.
Rivers that have this one pattern will usually appear to follow fault lines.
9. Pinnate Flow Pattern
The pinnate flow pattern is a pattern of river water in the estuary of a tributary by forming an acute angle on the main river.
In general, the slopes of this pinnate river pattern are steeper.
You can find this type of river on hills that have steep slopes.
10. Centrifugal Radial Flow Pattern
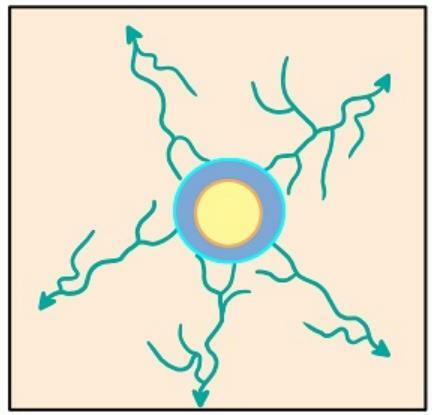
Centrifugal radial pattern is a pattern that spreads radially from a certain height.
In general, rivers that have this one type of flow pattern are in mountainous areas where the water flow spreads towards the slopes.
Also learn: Indonesia's Geographical Location
River Flow Shape
There are 12 types or forms of river flow in general, here is more information:
| No. | River Flow Shape | Information |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Antecedent River | A river that has a steady flow direction because it balances the uplift that occurs. This river is only formed when there is slow transportation. |
| 2. | Anaklinal River | Rivers that flow on the surface at a slow speed, are uplifted and the direction of uplift is opposite to the direction of the river's current. |
| 3. | River Compound | Rivers that carry water from areas of opposite geomorphology. |
| 4. | Incident River | A river whose flow is formed without any real cause. This one river flows without following the rock layers. The flow is erratic and follows a dendritic flow pattern. |
| 5. | Composite River | Rivers that flow from areas with different geological structures. Examples of rivers are in the big rivers in Indonesia. |
| 6. | Longitudinal Consequent River | A river that has a flow direction parallel to the anticlinal or the crest of a mountain wave. |
| 7. | Lateral Consequential River | A river that flows down the original slope on the earth's surface, such as a block, dome, mountain or newly raised land. |
| 8. | Obsekwen Sungai River | A river whose flow descends from the fault surface and opposes the dip of the fault formations. |
| 9. | River Reserve | A river that is unable to maintain its flow direction against uplift, so that the direction of its flow can change and adjust. |
| 10. | Resequent River | A river where the direction of the water flow is down the dip slope. The water flow is in the same direction as the lateral resected river which is generally formed from the subsequent river flow. |
| 11. | Superimposed River | A river that flows in a flat layer of sediment that covers the rock layers of rock that are below it. If rejuvenation takes place, the river will erode the cover layer and then cut the initial rock formation, so that the flow does not match the rock structure. |
| 12. | Subsequent river | Rivers formed in lateral consequent rivers that experience erosion retreat to the top of their slopes. This one river will experience erosion to the side and widen the valley so that new flows will appear following the fault direction. |
