Definition of Sedimentation, Types, Factors, Process Forms & Examples
Definition of Sedimentation
Sedimentation is a process of deposition of material attracted by water, wind and glaciers. The deposition can or can form in land, sea and river areas. The attracted material comes from abrasion or porous. The deposition will then be formed for a long time and after that it will make sedimentary rock, namely rock in the form of the effect of the sedimentation process.
This sedimentation is an event or event of a depositional process that occurs in several abiotic components that exist in the environment around us such as soil and also sand. The process of deposition or sedimentation can also be caused by several things, such as the flow of water or gusts of wind that can cause flooding or it can move small particles from soil or sand to another place until they are deposited and form something new. The process of sedimentation or deposition can or can occur in all kinds of places such as on land, at sea or also in river ecosystems. The material that is transferred is residual material from weathering or even erosion that lasts for a long period of time so that it is easy to transport.
Process of Sedimentation
Sedimentation is a depositional process that involves all kinds of external factors. The sedimentation process includes the process of deposition or deposition, erosion, transportation or transportation, and compaction (compaction). In general, the sedimentation process is divided into two types, namely the geological sedimentation process and the accelerated sedimentation process.
Geological sedimentation process
Basically the geological process of sedimentation is a process of soil erosion that runs normally or normally. This means that the ongoing deposition process is still within the permissible limits or is still in the natural balance of the agradation process as well as the degradation of the earth's crust as a result of the presence of weathering.
Accelerated sedimentation process
The process of accelerated sedimentation is a sedimentation process that takes place in a fairly short period of time. The sedimentation process deviates and is very different from the biological sedimentation process. The accelerated sedimentation process has a negative impact, is detrimental or destructive, disrupts the balance of nature or also environmental sustainability. The accelerated sedimentation process usually occurs or is caused by human activities or activities in cultivating the soil.
Errors in cultivating the soil will then cause soil erosion and also high sedimentation rates. the result of the sedimentation can or can be in the form of breccia rocks and also conglomerate rocks that are deposited not far from the source or also origin, while the sandstone was deposited further from the breccia and conglomerate stones, while the clay was deposited far from the source.
Sedimentation Form
The impacts of this sedimentation are as follows:
Fluvial sedimentation

-
Delta
one of the consequences of this sedimentation is the formation of a delta, the delta is formed at the mouth of a river where the sea is shallow and the river flow carries a lot of sediment material. The delta area is usually fertile. Based on its physical form, the delta can be in the form of a bird's foot, a triangular bow, and it can also be an axe. The delta land can also be used for livestock, agriculture, and fisheries activities. -
Natural Embankment
This natural embankment is formed on the bank of the river which is the result of a pile of material carried away when a flood has occurred. The material is then deposited on either side of the river. The embankment then gets taller and can or may resemble an embankment. -
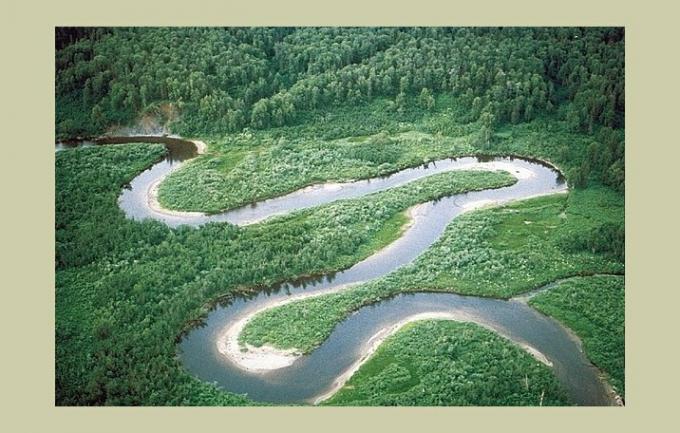
Meander
This meander is a bend in the river channel. The meander is formed after the erosion and deposition process that occurs on the inside or outside of the river basin. In the part of the river where the flow is fast, erosion will occur. The part of the river that flows slowly will make a deposition. This process takes place continuously so that it will then form a meander. -
Horseshoe Lake (Oxbow Lake)
Oxbow Lake was formed due to a continuous process of sedimentation in the river meander. Because of the cause of the deposition process, the sedimentary material will then cut the river channel so that it will become straight. The basin of the cut river channel will then form a puddle which later becomes a lake. -
Sand Dunes
The sand dune is formed due to the result of a deposition by the wind. Strong winds in the desert or beach areas will then form a sand dune. The sand dunes are also found in the area along the west coast of the Netherlands which is a sea wall in the country and also on the Parangtritis beach in Yogyakarta.
Marine sedimentation

Formations that can be created from marine sedimentation include the following:
-
Spit
This is one of the formations that occur as a result of marine sedimentation. This spit is a long plain and is also around the coast. The spit plains are formed as a result or impact of coastal currents that carry the sediment material to the sea. The materials carried are in the form of sand on the coast. The spit is elongated in shape and will continue to be more elongated and there will be ocean currents that carry these materials to be deposited. -
burn
This is a form with the appearance of a small plain located in the middle of the sea. So we can say that this burnt is like a small island located in the middle of the sea. The charred can or can be formed due to a sudden change in ocean currents. The burn is not like alluvial which is conical in shape, but the burn is flat, flat and wide. Because the shape of the surface is flat and wide, the burnt usually has very unique shapes. -
Button
this is a natural bridge that connects the big island with the small island that is right nearby. For the formation process, the button is also the same as the spit. The existence of the button can or can be used by the community to be able to cross to a small island in the middle of the sea. -
Nehrung
it's a sand dune that lies around the beach. for the process of formation of the nehrung from sea water that goes to the beach carrying materials that after that settle around the beach. -
beach barrier
This is a marine sedimentation formation that looks like a natural embankment. The beach barrier is actually a canal from the spit. The spit that continues to extend until it surrounds the shoreline is called the beach barrier or also the natural embankment on the beach.
Glacier Sediment
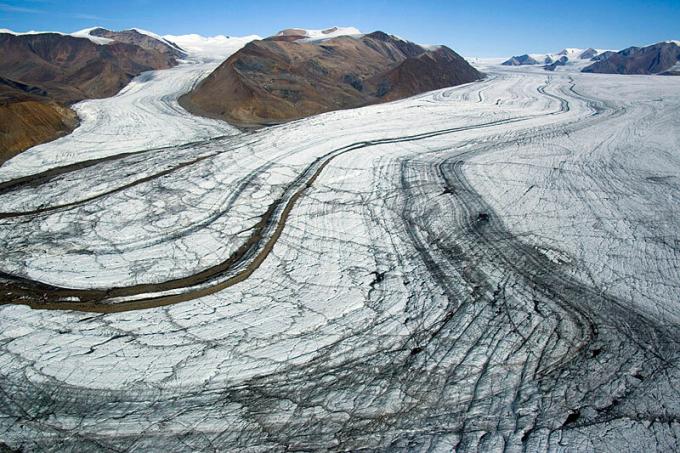

The forms of glacier sedimentation include the following:
- Oscar, sediments that have a narrow and long dorsal shape
- Kame, sediments that have a plateau shape.
- Drumlin, sediment that has the shape of a small hill
- Till Plain, sediments that have a flat shape.
Factors Causing Sedimentation
Sedimentation, also known as deposition, is a natural process. This natural process can occur in time that continues to repeat itself. In a long time the sedimentation will then produce all kinds of formations.
Several factors that can cause or encourage the occurrence of sedimentation include the following:
- There is a material, such material as sand, soil or dust which will then become material that settles.
- There is a depositional environment that is suitable for both terrestrial, marine and transitional areas.
- The occurrence of transportation of material sources is said to be transportation carried out by water, wind and also by ice.
- The occurrence of a deposition that occurs is due to differences in currents and forces.
- The occurrence of replacement (replacement) and also recrystallization (change of material)
- Diagenesis is a change that occurs when precipitation takes place either chemically or physically.
- Compaction, this is the result of a heavy force from the sedimentary material which then forces the volume of the sedimentary layer to decrease.
- Lithification, this is the end of the continuous compaction so that the sediment will then harden.
Sedimentation Type

Below are the types of sedimentation, including the following:
Based on Sediment Process
-
Fluvial Sediment
This type is a deposition of erosion results that occur in river areas which then form fluvial sediments. The results of deposition in the river can usually be in the form of sand, gravel, millstone, and also mud which then covers the river water. The fluvial sediments can or can be used for building materials or also for paving roads. Many of the residents make a living as a collector of sand, gravel, or also rock from fluvial sediments. -
Limnis sediment
This limnic sediment is one type of sediment whose deposition is the result of erosion that occurs in the lake and then forms limnic sediment. The results of deposition in the lake are usually in the form of layers of gravel, delta, sand, and mud. -
Marine sediments
Marine sediment is a deposition of erosion that occurs most often in the sea. The deposition of erosion results in the sea will then form a marine sediment. One of the forms of marine sediments is sand dunes. The sand dunes usually come from sand that is lifted into the air when the waves break on a sloping beach. Furthermore, the sand will then be carried by the wind towards the land and also deposited and form a heap of sand. -
Glacial or Glacier Sedimentation
Glacial sediments are deposited by glaciers after which they form valleys. When spring arrives, there is erosion of glaciers that slide down the valley and also carry rock or soil material.
Based on Sediment Location
Based on the place of occurrence of the deposition, the deposition can be or can be grouped into 5 types, namely:
- Terrestrial sediments are deposits that occur on land or flood plains.
- This Fluvial Sediment is a deposition that occurs at the bottom of the river and will cause silting of the river.
- Limnis sediments are deposits that occur in swampy areas.
- Marine sediments are deposits that occur in marine waters.
- Lacustrine sediments are deposits that occur at the bottom of a lake.
How to Overcome Sedimentation

In an effort to overcome sedimentation that can or can cause water flow disturbances, such as silting of rivers that can or can cause flooding. So of course it must begin with finding the source of the cause of the sediment.
Steps that can or can be taken to prevent sedimentation include the following:
-
Countering Surface Erosion
- Planting vegetation or plants to prevent damage and repair surface cover crops, so that erosion on the surface can be suppressed. For example, by making living fences, preventing forest fires, preserving watersheds, reforestation and reforestation, maintaining soil humus, and so on.
- Making constructions to prevent erosion can be done with the aim of slowing the flow of water.
- The trick is to reduce the slope or slope by making a terrace and also making embankments parallel to contour lines and waterways.
-
Controlling Sediment Material
The sediment transport is very influential on a change in river morphology. Control of this sedimentary material is one of the efforts so that the sediment can or can be carried away by the flow water to a certain place that does not cause harm or at least minimizes it, in the following ways following:
- The bottom control structure is to regulate the slope of the riverbed, so that the flow is still able to carry the sediment without eroding the river flow.
- Sabo dam manufacture.
- Making ground sills.
- Making mud bags.
- Sediment retaining construction.
-
Sedimentation Control
This control effort is carried out so that the deposition that occurs is placed at certain location points. The way is by way
- construction of sedimentation sites in rivers,
- create a mud bag in the reservoir (reservoir),
- mining of minerals C, as well as
- sediment dredging.
Examples of sedimentation results
This sedimentation is a continuation of the erosion process. The sedimentation is the deposition of material resulting from wind erosion, sea waves, water, and also glaciers. This deposition can be found starting from river valleys, mountains, river valleys, beaches, shallow seabeds, also to the deep seabed. Based on the place of deposition, the sedimentation process can be divided into fluvial sedimentation, eolis sedimentation, and also coastal sedimentation.
1) Fluvial Sedimentation
This river is an effective actor in the process of erosion. Thus, this river is also an effective actor in the sedimentation process. The process of deposition of material transported by rivers and also deposited along lake streams, This river, reservoir, or river estuary is commonly referred to as sedimentation fluvial. The sediment in the lake can be called lacustrine sediment. Examples of fluvial sedimentation results are:
- riverbanks,
- delta,
- meander (winding river).
2) Sedimentation by Seawater
This sedimentation is commonly referred to as marine sedimentation, this is caused by coastal abrasion which is then deposited back around the coast. There are various forms of sedimentation by sea water. The forms of sedimentation that we can easily find include beaches and sand dunes.
3) Sedimentation by Wind
We must have felt how it feels to be hit by the dust that is blown by the wind. This is an example of the role of the wind in moving natural matter. But it's not just dust that can or can be carried by the wind. The sand can also be blown away by the wind. The sand and dust carried by the wind will then form sand dunes. This deposition by wind is known as eolis sedimentation.
4) Sedimentation by Glaciers
Glacial sedimentation is sedimentation carried out by ice or glaciers. The sedimentation occurs due to the presence of moraine. Moraine is gravel, sand, and other materials that are carried by ice, and then also settle. Sedimentation by the glacier also flows from the high to the low.
Thus an explanation of the Definition of Sedimentation, Types, Factors, Process Forms & Examples, hopefully what is described can be useful for you. thank you
See AlsoUnderstanding Monopsony Market, Characteristics, Strengths and Weaknesses
See AlsoUnderstanding Space, Interaction Between Spaces, Forms and Conditions
See AlsoDefinition of Pronouns, Types, Characteristics and Examples
