Understanding Solar Cells, Types, Structures, Circuits & Principles
Education. Co. ID – This opportunity we will discuss about the Definition of Solar Cells, more about Solar Cells will be described as follows:

Understanding Solar Cells
A solar cell is a device or component that can convert sunlight energy into electrical energy using the principle of the photovoltaic effect. What is meant by the Photovoltaic Effect is a phenomenon in which the emergence of an electric voltage is caused by: the existence of a connection or contact of two electrodes connected to a solid or liquid system when getting energy light. Therefore, solar cells or solar cells are often referred to as photovoltaic (PV) cells. Now the Photovoltaic effect was discovered by a man named Henri Becquerel in 1839.
The electric current appears due to the photon energy of sunlight it receives managed to free the electrons in the N-type and P-type semiconductor junctions to flow. Just like a photodiode, this solar cell also has a positive leg and a negative leg that is connected to a circuit or device that requires a power source.
Basically, this solar cell is a photodiode that has a very large surface. The large surface area of the solar cell makes the solar cell device more sensitive to light incoming light and also produces a voltage and current that is stronger than a photo diode generally. For example, a solar cell made of silicon semiconductor material is capable of producing a voltage as high as 0.5V and a current as high as 0.1A when exposed to sunlight.
Currently, many have applied the Solar Cell device to various types of use. Starting from a power source for calculators, toys, battery chargers to power plants and even as a power source to drive the satellites orbiting our Earth.
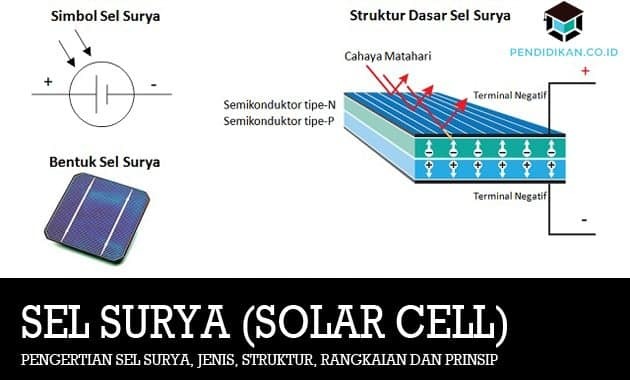
Basic Structure and Symbol of Solar Cells (Solar Cell)
The following is the Basic Structure, Shape and Symbol of a Solar Cell (Solar Cell).
Solar Cell Working Principle
Sunlight is made up of very small particles called photons. When exposed to sunlight, photons, which are particles of sunlight, hit atoms solar cell silicon semiconductor so that it generates energy large enough to separate electrons from its atomic structure. The separated electrons and negatively charged (-) will be free to move in the conduction band region of the semiconductor material. Atoms that lose electrons will have a vacancy in their structure, the vacancy is called a "hole" with a positive (+) charge.
This semiconductor region with free electrons is negative and acts as an electron donor, this semiconductor region is called an N-type semiconductor (N-type). Meanwhile, the semiconductor area with holes has positive properties and acts as an electron acceptor, which is called a P-type semiconductor.
At the junction of the Positive and Negative regions (PN Junction), there will be energy that pushes electrons and holes to move in opposite directions. The electron will move away from the negative region while the hole will move away from the positive region. When a load is given in the form of a lamp or other electrical device at this Positive and Negative Junction (PN Junction), it will cause an electric current.
Types of solar cells
The types of solar cells are classified based on the technology of manufacture. Broadly speaking, solar cells are divided into three types, namely:
1. Monocrystalline
Mono (Mono-crystalline) This is the most efficient solar panel produced with the latest technology and also produces high electrical power. This mono-crystalline solar cell is made using pure crystalline silicon that has gone through a Czochralski process which results in Ingot.
This ingot is then sliced thinly. So that it will be circular or circular, the shape is the result of the Czochralski process.
2. Polycrystalline
While Polycrystaline silicon, it is a solar panel that has a random crystal arrangement. This type is made of several silicon crystal rods which are melted or melted after it is poured back into a rectangular mold. Polycrystal silicon was introduced to the market in 1981. This polycrystalline does not require the Czochralski process.
The Czochralski process is a process of purification of a material by means of crystallization, the material to be processed is crystallize it is put in a place that is difficult to react with other substances such as quartz and noble gases argon.
3. Thin Film Solar Cell (TFSC)
This Thin Film Solar Cell is a solar panel consisting of two () layers made by adding one or more thin films, or thin films of photovoltaic material onto a substrate such as glass, plastic or metal
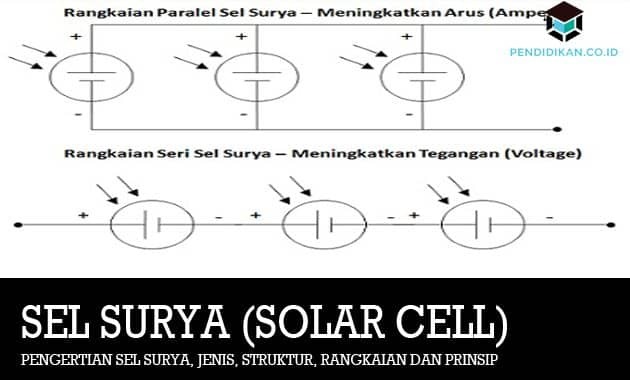
Solar Cell Series and Parallel Circuits (Solar Cell)
Like batteries, solar cells can also be connected in series or parallel. In general, each solar cell produces a voltage of 0.45 ~ 0.5V and an electric current of 0.1A when receiving bright light. Similar to Batteries, Solar Cells connected in Series will increase the Voltage (Voltage) while for Solar Cells which are connected in Parallel will increase the Current (Current).
Thus an explanation of the Definition of Solar Cells, Types, Structures, Circuits and Principles, hopefully what is described can be useful for you. Thank you.
See AlsoUnderstanding Assembled Maps, Objectives, and Working Standards
See AlsoDefinition of Groundwater
See AlsoUnderstanding the bronchi, structures, parts, and their functions
