Understanding Anabolism, Characteristics, Functions, Roles, Reactions and Examples

Definition of Anabolism
Anabolism or biosynthesis or also called assimilation is a process of compiling simple chemical compounds into chemical compounds or complex molecules. These complex compounds are usually referred to as macromolecular compounds. The formed macromolecules can or can be in all kinds of forms such as nucleic acids, fats, carbohydrates and proteins. These events require energy from the outside, after which the energy is then used to bind these simple compounds into more complex compounds.
Anabolic Process
Anabolism is a metabolic pathway that compiles some of these simple organic compounds into chemical compounds or complex molecules. This process requires external energy. The energy used in this reaction can or can be in the form of light energy or chemical energy. This energy is then used to bind these simple compounds into more complex compounds. So, in the process the required energy is not lost, but instead is stored in a form of chemical bonds in the complex compounds formed. In anabolic reactions, energy is needed which is also obtained from catabolic reactions.
The reactions in these cells can or can be grouped into two categories:
- The anabolic reaction is a formation reaction, namely the synthesis of large molecules from simple or small molecules. The anabolism process requires energy, and the process is called an endogenic reaction.
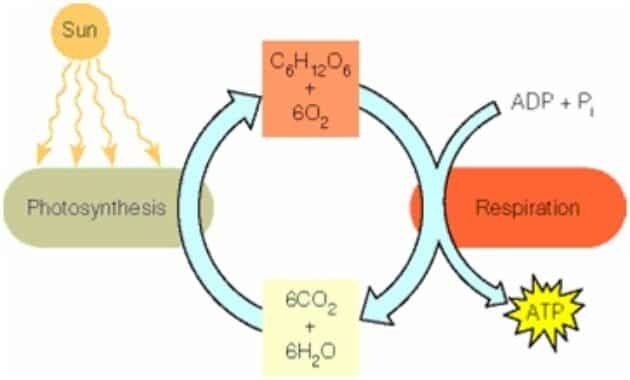
- This catabolic reaction is a breakdown reaction. This catabolism is the breakdown of large molecules into simpler ones accompanied by the release of energy called exergonic reactions. The total sum of these anabolic and catabolic reactions is called metabolism (formation and breakdown). An example of this catabolic process is respiration, while an example of an anabolic process is photosynthesis (Green et al, 1988).
The products of anabolism are useful in essential functions. These products, such as glycogen and protein, are used as fuel in the body, nucleic acids for later copying of genetic information. These proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates then make up the body structure of living things, be it intracellular or extracellular. If the synthesis of these materials is faster than their breakdown, the organism will then grow.
Anabolism Stage
The anabolism includes 3 basic stages.
- Production of precursors such as amino acids, monosaccharides, and nucleotides.
- The activation of these compounds then becomes a reactive form using energy from ATP.
- The incorporation of these precursors will then form complex molecules, such as polysaccharides, proteins, fats, and nucleic acids.
Anabolism that uses light energy is known as photosynthesis, while anabolism that uses chemical energy is known as chemosynthesis.
Difference Between Anabolism and Catabolism
- This anabolism is a process of synthesizing small chemical molecules into larger molecules large, while catabolism is a process of breaking down large molecules into molecules small.
- Anabolism is a process that requires energy while catabolism is a process that releases energy.
- This anabolism is a reduction reaction while for catabolism it is an oxidation reaction.
Often the end product of anabolism is the starting compound for the catabolism process. (Wiradikusumah, 1985).
Characteristics of Anabolism
The characteristics of anabolism include the following:
- It is a rearrangement reaction
- The substrate is a simple compound
- The product of the reaction is a complex compound
- Requires energy
- Endothermic
- Can or can be exemplified by the reactions of photosynthesis or also chemosynthesis
Functions of Anabolic Reactions in the Body
This anabolism allows the body to be able to build or also grow new cells and maintain body tissues. This process then uses the energy produced by catabolic reactions, and then influenced by all kinds of hormones and enzymes to be able to form and repair cells and cells also network. Examples of anabolic processes include the growth and mineralization of bone, as well as the increase in muscle mass.
The Role of Hormones in Anabolic Reactions
The hormones below are categorized as anabolic hormones.
Growth hormone.
This hormone is made in the pituitary gland (a small gland at the bottom of the brain). Its function is to regulate body growth. Too much growth hormone in childhood can or can cause a person to grow taller than average (gigantism). Meanwhile, if too little can or can cause height less than average (dwarfism).
Insulin-like growth factors (IGF-1 and IGF-2).
These insulin-like growth factors stimulate the production of protein and fat. IGF-I and IGF-2, which work together with growth hormone, have an important role in growth and development bones and also all kinds of body tissues, including the mammary glands and in the occurrence of a reproductive process (procreation). This hormone then controls the production of growth hormone by the pituitary gland (pituitary), as well as sugar levels in the blood.
Insulin.
This hormone is made by the pancreas gland. This insulin has the task of regulating glucose (sugar) levels in the blood, helping the body convert the food consumed into energy, and also helping to store energy reserves. The body's cells cannot or can use glucose without insulin.
Testosterone.
Testosterone is a male hormone produced in the testes. Testosterone causes the formation of sperm and the development of male sex characteristics, such as: For example, a deeper voice, larger muscles, as well as facial hair growth and also body. The hormone testosterone also plays an important role in all bodies due to its impact on the brain, bone and muscle mass, vascular system, fat distribution, organs, energy levels, and function sexual. Not only in men, the hormone testosterone is also produced in a woman's body, but the amount is less. In women, this hormone is produced in the ovaries.
Estrogen.
Estrogen is a female hormone produced in the ovaries (as well as the placenta during pregnancy). The hormone estrogen is responsible for strengthening bone tissue, then developing the characteristics of body shape Women, such as the breast, play a role in thickening the tissue in the uterus (endometrium), and also regulate the cycle menstruation. In small amounts, estrogen is also produced in fat tissue and muscle. It is the main source of estrogen in women who have gone through menopause. Men also produce the hormone estrogen, but the amount is less.
Examples of Anabolic Reactions
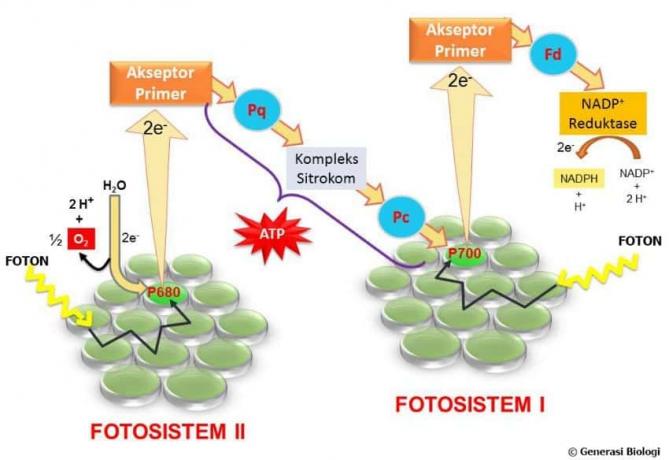
The anabolism occurs when simple compounds and elements are reacted in living things to produce more complex organic compounds. This anabolism uses energy sources such as sunlight or chemicals, so that these compounds and elements can or can be combined into complex compounds.
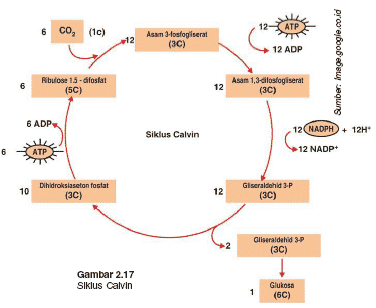
An example of anabolism is photosynthesis that occurs in plants.
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants in which energy from sunlight is used to produce energy converts carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) into molecules of sugar or glucose (C6H12O6) which are needed as growth. The process is then assisted by enzymes and chlorophyll. Chlorophyll is a green leaf pigment found in chloroplasts, organelles in plant cells.
The chemical reactions of photosynthesis include:
6 CO2 (Carbon dioxide) + 6 H2O (water) + sunlight –> C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6 O2 (oxygen)
Example of Anabolism
Anabolism is a metabolic process that converts simple compounds into complex compounds. For example like
- formation of glycogen from glucose
- the formation of proteins from amino acids,
- formation of triglycerides from fatty acids and
- glycerol
Thus the explanation of the definition of anabolism, characteristics, functions, roles, reactions, stages and examples, hopefully what is described can be useful for you. thank you
See AlsoUnderstanding Abstract, Function, Type, According to Experts
See AlsoUnderstanding Social Relations
See AlsoUnderstanding Nerve Cells, Structure, Parts, Functions and Types
