Definition of Food Chain, Web, Components, and Examples
Education. Co. ID – An explanation of the Food Chain is a topic that we will discuss this time, an explanation of this Food Chain will be described in full below:
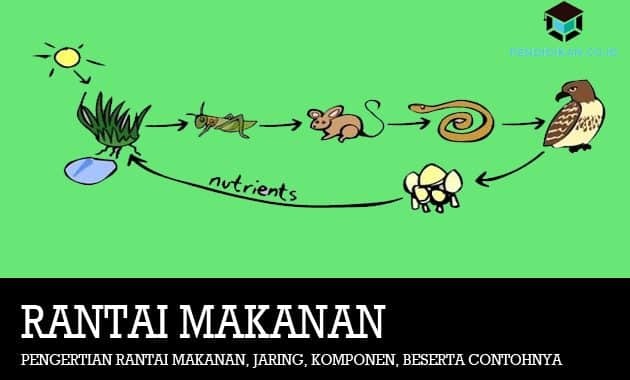
Definition of Food Chain
The definition of a food chain is an event / occurrence of eating and being eaten between every living thing in certain sequences.
In the event of eating and being eaten, there are those who act as producers, consumers, and decomposers (decomposers). Each level of the food chain in an ecosystem is called a trophic level.
A food chain always starts from living things that produce food or also those that produce food which are called producers, for example green plants. The food chain that begins with plants is called a grazing food chain.
The plant will then be eaten by herbivorous animals, namely as level I consumers. After that, the herbivorous animals will be eaten by carnivorous animals that act as level II consumers. Furthermore, these carnivores will be eaten by other carnivores whose role is as level III consumers.
And so on until the last living being is not eaten by another living being. The last animal will die and be eaten by decomposing bacteria.
Components in the Food Chain
In the food chain pyramid we will find the words producers, consumers and decomposers. Producers are living things that can / can produce their own food such as plants. These plants can produce their own food which can be used as a source of energy for consumers.
Consumers are living things that cannot/can make their own food. Therefore, to be able to get this consumer energy, it depends on producers or other creatures. Consumers themselves are divided into three parts, namely primary consumers, secondary consumers and tertiary consumers.
- 1. The primary consumer is the first consumer where he gets the energy directly from the producer. Examples are living things that include herbivores such as cows, buffalo, rabbits and others.
- 2. Secondary consumers are second consumers who get a source of energy or food from the first consumer. For example, animals that eat meat or are called carnivores. Examples such as cats, dogs, snakes and others.
- 3. Tertiary consumers are consumers who get energy sources by eating second consumers. Examples are such as eagles, peregrines, tigers, lions and others.
Decomposers are organisms that play a role in breaking down organic substances into inorganic substances. The decomposers decompose carcasses and dead plants and the nutrients contained in them will be used by producers or also plants as a source of nutrition.
Example of a Food Chain
Below are some examples of food chains that occur in rice and marine ecosystems.
Food Chain in Rice Field Ecosystem
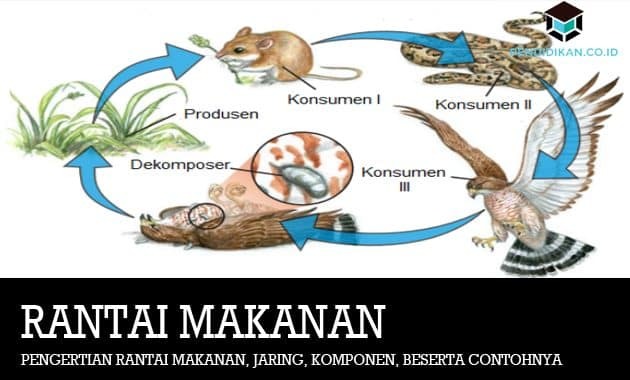
Based on the picture above, it can be concluded that:
The plant acts as a producer. These plants use sunlight to produce food in the form of starch and stored in seeds, stems, and other parts.
The rat acts as a level I consumer. The rat eats the plant (rice), after which the rat converts a number of rice plants into energy for their life activities.
The snake then acts as a level II consumer. This snake is a source of food for the eagle to stay alive.
Meanwhile, eagles themselves act as top consumers because there are no more living things that eat eagles. After that the eagle will die and then rot due to the presence of decomposing bacteria.
Food Chain in Marine Ecosystem
Look at the following picture.
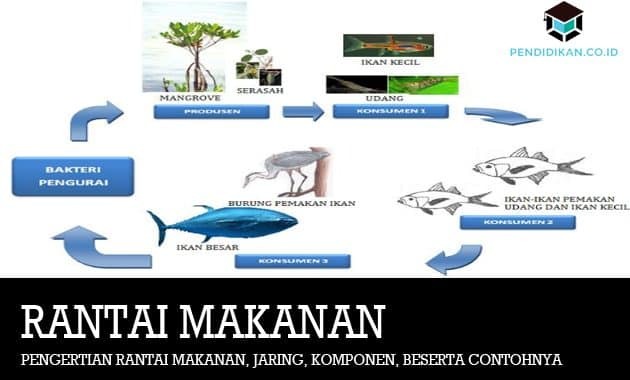
Based on the picture above, it can be concluded that:
The Mangrove tree acts as a producer.
Shrimp and small fish act as level I consumers. Shrimp and fish also eat the roots and trunks of mangrove trees in their survival.
Furthermore, the shrimp and small fish will then be eaten by fish whose size is larger than the size of level I consumers. These fish act as second-level consumers.
Fish-eating birds and large fish act as top consumers. Birds are the top consumers because the birds will not be eaten by other consumers.
Then the birds and large fish will die and will rot as a result of decomposition by decomposing bacteria.
Definition of Food Web
The definition of a food web is a combination of several food chains whose cycles are interconnected.
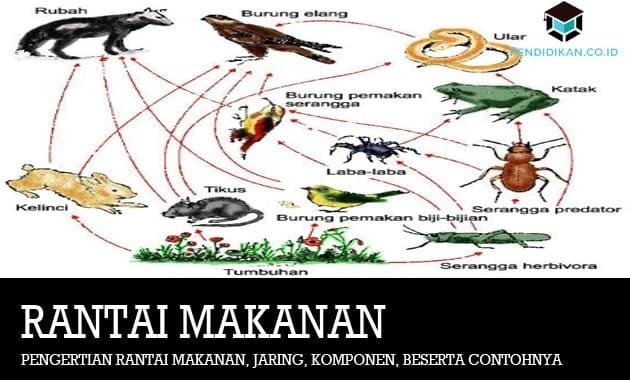
Events of eating and being eaten in an ecosystem, it turns out that one consumer does not depend on one producer or one consumer. Likewise, one (1) type of producer can be eaten by different consumers.
This causes the direction of the food chain to be branched or not only in one direction. Some of these food chains will form a food web. The food web consists of several interconnected food chains in an ecosystem.
Well, that's the explanation of the Definition of Food Chain, Web, Components, and Examples, hopefully what is described can be useful for you. thank you
See AlsoDefinition of Diastropism
See AlsoUnderstanding Parasitism Symbiosis
See AlsoCritical Understanding, Benefits, Characteristics, Goals & Ways of Thinking According to Experts
