Rutherford's Atomic Definition, Theory, Strengths and Disadvantages
Education. Co. ID – On this occasion we will discuss the retherford atomic theory, a full explanation of the retherford atom will be described as follows:
Understanding Atom
This atom is a basic unit of matter, which consists of an atomic nucleus and a negatively charged electron cloud that will surround it. The nucleus of this atom consists of positively charged protons, or neutrons which have a neutral charge.
The electrons in an atom can be bound to the atomic nucleus by electromagnetic forces. From several sets of such atoms can also relate to each other, and can also form a molecule. Atoms containing the same number of protons and electrons are neutral, then those containing Different numbers of protons or electrons are positive or negative and are often referred to as ions. These atoms are also grouped based on the number of protons and neutrons contained in the atomic nucleus. The number of protons in the atom determines the chemical element of the atom, and the number of neutrons determines the isotope of a particular element.
Ernerst Rutherford's Atomic Theory
After John Dalton's Atomic Theory was refuted and later corrected by Jj. Thomson states that The atom is like Raisin Bread, then it's Rutherford's turn to disprove the atomic theory Thomsom.
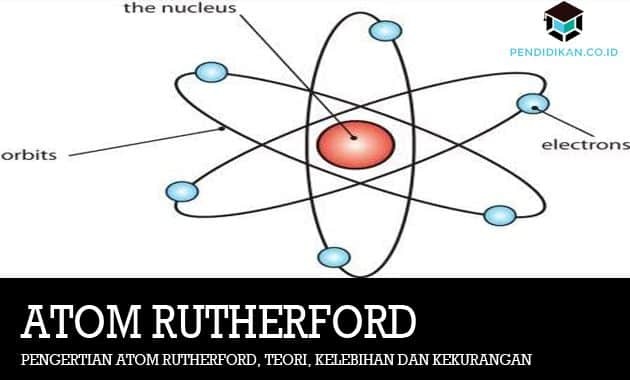
At that time Rutherford said that the atom has a central nucleus or often called a nucleus surrounded by a cloud of electrons having a negative charge.
Rutherford's atomic theory was based on the experiment of bombarding the atomic nuclei of gold plates on alpha particles which is often known as the Geiger-Marsden experiment. In that stone, Rutherford will design an experimental design for the bombardment of gold atoms by alpha particles that have been partikel emitted by radioactive elements. Well, it turns out, there are radioactive rays that have been reflected, deflected, or also forwarded. Rutherford then explained that when the alpha particle hits the atomic nucleus, there will be a collision that causes the deflection or reflection of the alpha particle. This is due to the mass and also the charge of the atom which is concentrated in the nucleus. Rutherford then suggested that the charge on the atomic nucleus would be proportional to the atomic mass in SMA / atomic mass units. Alpha particles hitting the electron cloud will not be deflected or reflected.
From the results of his understanding through these experiments, Ernerst Rutherfordutherford finally concluded and stated that:
- Most of the volume of the atom is a vacuum.
- The atomic mass will be concentrated in the atomic nucleus (nucleus).
- The atomic charge can be concentrated in the center of the atom with a fairly small volume. The multiple of the charge is proportional to the atomic mass.
By means of his statement E. Rutherford could deny that the atom was not like a raisin bread but also like an arrangement of planets orbiting the sun. Which the sun will be likened to is as a positively charged central core (nucleus) or also a planetary arrangement that has a positive charge it is described as a negative charge, therefore, Dalton and Thomson's atomic theory has its advantages or disadvantages, Atomic theory E. Rutherford also has its strengths and weaknesses. Below are the advantages and disadvantages of the atomic theory E. Rutherford.
Ernerst Rutherford's Atomic Theory Strengths and Disadvantages.
The advantages and disadvantages of Ernerst Rutherford's atomic theory are as follows:
Ernerst Rutherford's Atomic Theory
- Easy to understand to be able to explain very complicated atomic structure
- Can explain the shape of an electron orbit around the atomic nucleus
- Can describe the motion of electrons around the nucleus
Disadvantages of Ernerst Rutherford's Atomic Theory
- Rutherford's atomic model has not been able to explain where the electrons are located and also how they are rotated about these atoms.
- These electrons can emit energy when they move, so the atomic energy becomes unstable.
- Cannot explain the line spectrum on the hydrogen atom (H).
That's all and thank you for reading about Rutherford's Atomic Understanding, Theory, Strengths and Weaknesses, Hopefully what is described can be useful for you.
See AlsoDefinition of Campaign, Elements, Types, Forms, Functions, Objectives, & Media
See AlsoDefinition of Holding Company, Characteristics, Functions, Benefits, Objectives and Examples
See AlsoJJ Thomson's Atomic Definition, Theory, Strengths and Disadvantages
