Understanding the Thalamus, Function, Structure, How it Works and Factors
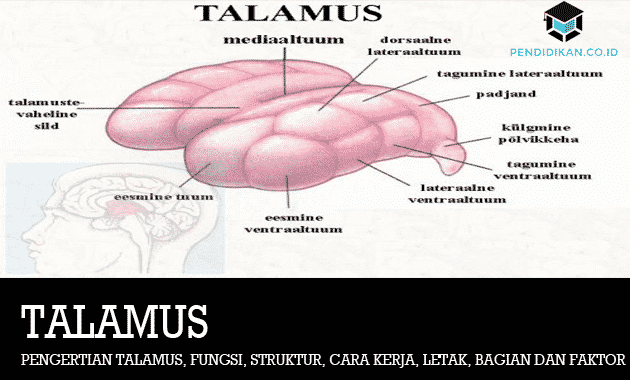
What is Thalamus?
Thalamus (thalamus) is derived from the Greek language which means the inner space. The thalamus is a structure located in the middle of the brain. More precisely it is located between the cerebral cortex and the midbrain. The thalamus is the largest structure found in the diencephalon, or a part of the brain that is located between the midbrain (mesencephalon) and the forebrain (telecephalon).
The function of the thalamus gland is to transmit sensory and motor signals related to consciousness, sleep and alertness to the cortex of the brain. Or to put it simply, the function of the thalamus is as a relay of sensory messages from the body to the brain and also regulates the level of consciousness. The thalamus is a sub organ of the diencephalon.
Another definition for this thalamus is a part of the limbric system as well as a connecting area of the cerebral cortex that has responsibility, namely as the control of movement and also sensory perception with other parts of the brain that are related or related in the function that is involved same.
Function of the Thalamus (Thalmus)
The main function of the thalamus gland is as a transmitter of information related to awareness, sleep cycles and alertness. In addition to the above, the thalamus also has a function as a transmitter and also a transmitter of information about sensory receptors such as sight, hearing, touch and taste except smell.
The thalamus is usually described as a relay station. This is because almost all sensory information (except smell) that is transmitted to the cortex first stops at the thalamus before being sent to its destination.
The thalamus is divided into several nuclei that are functionally specialized in handling certain types of information. This sensory information travels to the thalamus and is routed to the nucleus according to its role in the type of sensory data.
Then, the information is then sent from that nucleus to the appropriate area in the cortex where it will be further processed.
Structure and Parts of the Thalamus (Thalamus)
The location of the thalamus is at the top of the brainstem, near the center of the brain. The thalamus consists of a bulb-shaped mass which is divided into 2 (two) with a length of about 5.7 vm and symmetrical between the left and right.
The thalamus receives nutrients and oxygen from the 4 branches of the posterior cerebral blood vessels. The thalamus gland contains lamellae, which are myelinated nerve fibers.
This thalamus is one part of the complex nuclear system, which is together with the Prethalamus (Ventral Thalamus), Hypothalamus, Epithalamus, and also Dorsal Thalamus. Some of the nuclei found in the thalamus include the following:
- Anterior Thalamus Nucleus. Enter the limbric system which transmits the stimulus to the cingulate cortex.
- Anterior Ventral Nucleus. It is associated with the corpus striatum.
- Lateral Ventral Nucleus. has a function in receiving nerves from the globus pallidus and the cerebellum as well as secreting fibers that travel to the cerebral cortex.
- Posterolateral ventral nucleus. it is the station where the spinothalamic tract and medial lemniscus synapse, which then travel to the cerebral cortex.
- Centrum Medianum. It is associated with the corpus stratum.
- Medial Nucleus. It communicates with the hypothalamus as well as the frontal lobe
- Pulvinar Nucleus. It corresponds to the occipital lobe as well as the parietal lobe.
- Medial Geniculate Corpus. This is a connecting station that conducts auditory stimuli.
- Reticular Formation. This is the anatomical substrate of consciousness.
The thalamus is directly connected to the hippocampus (a part of the cerebrum which is located in the temporal lobe) by way of the mammillio thalamic pathway. and also communicates with the cerebral cortex by way of the thalmocortical tract.
Location of the thalamus (thalamus)
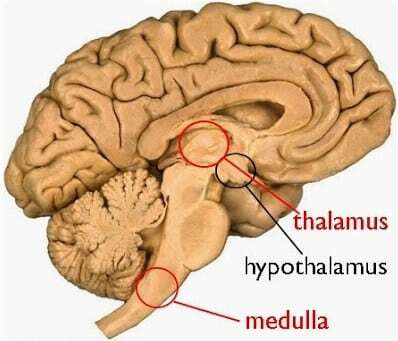
The location or also the location of the thalamus in humans is at the top of the brain stem. The average human brain weighs about three pounds. The top is also divided into two halves. The lower part of the brain is connected to the spinal cord by the brain stem. The thalamus is located above the brainstem which consists of two parts, also known as lobes.
How the Thalamus Works
This thalamus can or can work with several stages of the process that occurs starting from the signal received by the thalamus. after that the thalamus sends it to 2 (two) places, namely the amygdala and the prefrontal cortex. The amygdala and the prefrontal cortex are the main locations that have a function for the human psyche and intellect. This signal from the thalamus will be received first by the amygdala due to the path traversed the amygdala is faster by passing through a pathway of neuronal parts in a nervous system in human. The pathway through which the amygdala is directly connected to the thalamus.
Hearing
After that, the signal sent to the prefrontal cortex will produce a distant neocortex. The location which is far from the center of the signal it receives turns out to have an unusual role. In the neocortex can or can recognize the name of a reaction that is not spontaneous. So if for example we play a tone, the amygdala will then play first spontaneously, then the neocortex will follow.
Vision
The workings of the thalamus when viewing starts from the image that is seen, it sends a signal to the thalamus. after that the thalamus will direct sensory messages to the visual area.
smell
Meanwhile, when we are using the sense of smell, it is through the way the nose works, with the working system on the sense of sight almost the same as when the thalamus receives sensory messages when seeing, it's just that the signal captured by the sense of smell is nose. Another difference when the brain is working using the sense of smell the signals that are captured we can call the olfactory bulb. The location of the olfactory bulb is near the area associated with emotions. Thus, when we smell something, there must be some hidden memories that we will remember.
Diseases Associated with the Thalamus
Fatal Familial Insomnia
This very rare neurodegenerative disease is that a person will experience symptoms of insomnia. The condition of people who experience it will certainly not be able to or be able to sleep during the day and at night sleep can not sleep or also sleep for a short period of time. This is because the thalamus can actually be a sleep regulator. Unfortunately when this Fatal Familial Insomnia occurs, neurons and astrogliosis in the thalamus will be lost due to selective atrophy. If this goes on for a long time it will cause short-term death.
Thalamus Stroke
This thalamus stroke can occur in someone because the brain is bleeding so that the blood components may be disrupted. Thalamic strokes are common in young adults. Sometimes the disease often cannot be determined why it occurs. Several measures to overcome thalamic stroke by doing this therapy using oxygen and infusion, namely as a tool to facilitate the process of fluids and substances entering. The act of removing the blockage due to bleeding in the thalamus is necessary to reduce the risk of stroke.
Tremor
This tremor occurs because the brain cannot or can control and control its function so that it often experiences an unconscious movement, especially in the hands.
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia can or can be caused by damage to the thalamus. This is because the thalamus has many connections to the prefrontal cortex. Abnormalities in the thalamus can or can be associated with symptoms that occur in someone who has schizophrenia.
Factors Affecting Thalamus Work
Of course, when the condition of the thalamus is healthy or has several diseases related to the thalamus, there are several factors that can or can affect the work of the thalamus. Some of these factors are as follows:
Stimulation of brain cells
Stimulation of brain cells can or can help the workings of the brain including the thalamus brain. Activities or activities that can or can stimulate brain cells by carrying out activities or activities such as listening, writing, music, counting, speaking, and memorizing.
Nutrition
Nutrients consumed by the brain are very important and not only for brain health but can also increase the function and work of the brain so that it is optimal.
Nervous system drugs
There are several drugs that can or can affect the nervous system in humans. Therefore, the use of the drug should not be consumed often if it is not needed. In addition to disturbing the nervous system, excessive drug use can cause damage to human organs such as the kidneys and liver.
Environment
Environmental conditions can also affect the nervous system, such as social life at school, work or other places.
Psychological
One's psychology should not be underestimated. It turns out that these psychological problems can also help someone in dealing with something. If someone makes a decision on the actions they take, the brain function will be stimulated.
Sports
Sports activities can certainly increase the strength of human bones but can also make the human brain work. when we do exercise the brain plays an important role in regulating the balance of the body. If these activities are carried out regularly, the function of the brain in maintaining the balance of the body can run well.
Thus an explanation of the understanding of the thalamus, its function, structure, workings, location, parts and factors, hopefully what is described above can be useful for you.
See AlsoUnderstanding Logistics
See AlsoUnderstanding the bronchioles, characteristics, functions, location and structure Struktur
See AlsoUnderstanding HR, Functions, Factors, Examples and According to Experts
