Definition of APBN, Structure, Cycle, Mechanism, Function, Principle

Definition of APBN (State Revenue and Expenditure Budget)
Based on Article 23 of the 1945 Constitution paragraph 1, this APBN is an embodiment of state financial management which is ratified every year in accordance with the law and also carried out in an open manner in which the government is fully responsible for prosperity people. APBN is the annual financial plan of the government of the Republic of Indonesia that has been or has been approved by the House of Representatives (DPR). This APBN has been or has been stipulated in the Law covering a period of 1 year starting from January 1 to December 31.
Based on the official website of the Ministry of Education and Culture, the Directorate General of Culture, this APBN is a part of state finances. Described in Law No. 17 of 2003 concerning State Finances, what is meant by APBN are:
- An annual financial plan of the state government approved by the DPR (Article 1, Paragraph 7).
- Consists of revenue budget, expenditure budget, and financing (Article 11, Paragraph 2).
- Covers a period of one year, starting from January 1 to December 31 (Article 4).
- Stipulated annually by law (Article 11 Paragraph 1).
- It has the functions of authorization, supervision, allocation, planning, distribution, as well as stabilization (Article 3, Paragraph 4).
Elements of the State Budget

When referring to Article 23 Paragraph 1 of the 1945 Constitution (amendment), there are 5 elements of the APBN, including:
- This state budget is the management of state finances
- The state budget is determined every year and is valid for 1 year
- This state budget is determined by law
- The state budget is carried out in an open and responsible manner
- APBN is intended for the prosperity of the people
The source of this APBN is the people, so its existence must be carried out in a law. The determination and ratification of the APBN is carried out jointly with the DPR. The DPR itself is an institution that represents the people (sovereignty). This APBN is a series of planning, implementation, and realization. So it is determined by law.
State Budget Structure and Components

1. State Revenue and Grants
This state income is an addition to the value of net worth in a country. Some of these sources of state revenue include the following:
a. Tax Revenue, including:
- Domestic Tax Revenue
- International Trade Tax Revenue
b. Non-Tax State Revenue or PNBP, including:
- Natural Resources Receipt
- SOE Profit Income
- Revenue of Public Service Agency (BLU)
- Other Non-Tax State Income
2. State Shopping
This State Expenditure is a reduction in the net worth of a country by the government within a certain period. Some of these state expenditures include the following:
- Employee Shopping
- Goods Shopping
- Capital Expenditure
- Interest Shopping and Loans
- Subsidies (Energy and Non-Energy)
- Grant Shopping
- Social Assistance Shopping
- Miscellaneous Shopping
3. State Budget Primary Balance
This primary balance is the total state revenue minus state expenditures excluding debt interest payments. The government is then considered successful if the total state revenue is greater than state spending.
4. State Budget Surplus/Deficit
This budget surplus is a condition in which the state's revenue is greater than the state's expenditure.
This budget deficit is a condition where the state expenditure is greater than the state revenue.
5. State Budget Financing
Financing is each receipt that must be repaid as well as expenses incurred then it will be accepted again, be it in the relevant fiscal year or also in the budget year next.
Budget Cycle

In the management of the state budget, the cycle of the state budget is known as well as the financial relationship of the state budget. The APBN cycle, namely as a manifestation of the management of the APBN, all activities or activities The APBN management activities will include planning, implementation, supervision and also accountability. This series of state budget management can then be referred to as the state budget cycle. So, 1 cycle of the APBN will consist of:
- Preliminary Talks (including the preparation of a work plan).
- Discussion and determination of the RAPBN.
- Discussion of Semester I Report and Prognosis for the following 6 months.
- Discussion of the bill regarding the amendment of the current year's APBN.
- Discussion of Accountability for the Implementation of the State Budget.
The scope of the state budget
The scope of this APBN includes all revenues and expenditures. The revenue comes from taxes or non-tax, as well as grants. This expenditure or expenditure is the expenditure of the central and regional governments. If expenditure is greater than income (deficit), then look for financing from domestic or foreign sources. All receipts and expenses are accommodated in one account called the State General Treasurer (BUN) at Bank Indonesia. Regarding the management of the state budget, all revenues and expenditures must be included in the state budget. So that when the APBN is accounted for, all realized revenues and expenses in the special account must be consolidated into the BUN account.
State Budget Functions

1. Functions of the State Budget according to its Fiscal policy:
-
Allocation Function
This APBN has a function, namely as tax revenue which is allocated for expenditures of a public interest. Some of the allocations of funds include, among others, road construction, bridge construction, park construction, etc. -
Distribution Function
The APBN also has a function to be distributed to the public in order to realize income distribution and reduce economic disparities between social classes. Subsidies, scholarships and pension funds are some manifestations of the distribution function of the APBN. -
Stability Function
This state budget is also an instrument to be able to control the country's economic stability. If there are extreme economic problems that create imbalances in the country's economy, the APBN can then help to overcome these problems.
2. Functions of the State Budget When viewed from the Management Side
- Government guidelines to be able to carry out their duties in the coming period.
- As a means of public control of a government performance.
- Being an assessor of how well the government runs its country based on policies and programs that have been or have been implemented.
State Budget Preparation Process
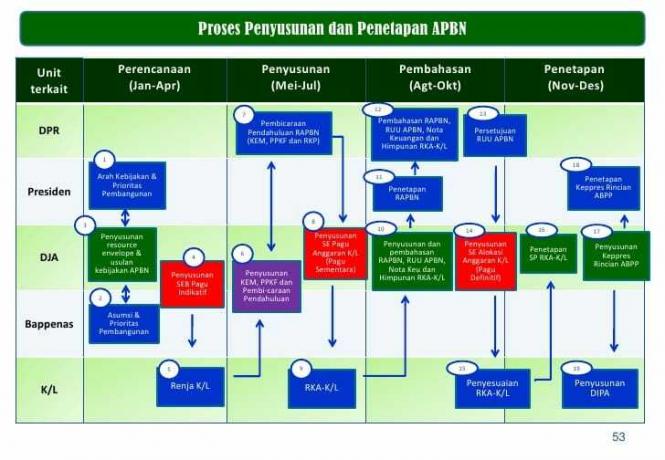
1. Preliminary Stage
-
Design Stage
The government compiles this RAPBN (Draft of the State Revenue and Expenditure Budget), namely by determining basic assumptions of the state budget, estimates of revenues and expenditures, priority scale, as well as budget preparation exercise. The basic assumptions of the APBN include:
- Country Economic Growth
- Inflation
- Currency Exchange Rate (Rupiah)
- National Oil Price
- Interest Rate for Bank Indonesia Certificates (SBI) for the last 3 months
- Lifting
- The stage of the inter-commission meeting with its partners to discuss a draft (technical department/institution)
- The stage of finalizing the preparation of the RAPBN by the government
2. Stages of Submission, Discussion, and Determination of the State Budget
- Starting with the president's speech as an introduction to the APBN Bill and Financial Notes.
- After that, it was continued with a good discussion between the Minister of Finance and also the budget committee of the House of Representatives
- People (DPR) or between commissions and related departments.
- The Minister of Finance and also the budget committee of the House of Representatives (DPR) or between commissions and related departments will determine the acceptance or rejection of the RAPBN.
- If the RAPBN is accepted, it will then be ratified into the APBN and then submitted to the government for implementation.
- But if the RAPBN is rejected, then the government must then use the previous APBN.
3. State Budget Implementation Supervision Stage
- The supervision stage is carried out by functional supervisors, whether they come from external (outside the government) or internal (within the government).
- Before the completion of the fiscal year, usually in November, the government through the Minister of Finance then makes a a report on accountability for an implementation of the state budget and also after that report it in the form of a draft Calculation
- The State Budget (RUU PAN) which is carried out no later than 15 months after the end of the implementation of the APBN for the relevant fiscal year. The report must also be prepared on the realization that has been or has been audited by the Supreme Audit Agency (BPK).
Principles of Preparation of the State Budget
a. Based on Aspects of State Revenue
- Intensification (efforts to increase) budget revenue in terms of the amount and speed of its deposit.
- Intensification (efforts to increase) collection and collection of state receivables.
- The claim for compensation for losses suffered by the state and the prosecution of fines.
b. By Expenditure Aspect
- Economical, efficient and also according to needs.
- Directed, controlled, in accordance with the program or activity plan.
- To the maximum extent possible, use domestically produced products by taking into account national capabilities and potential.
Principles of Preparation of the State Budget

- Independence, trying to increase state revenue as best as possible.
- Savings, increased efficiency and increased productivity.
- Sharpening development priorities.
- In accordance with the principles and laws of the State.
State Budget Preparation Mechanism/Process
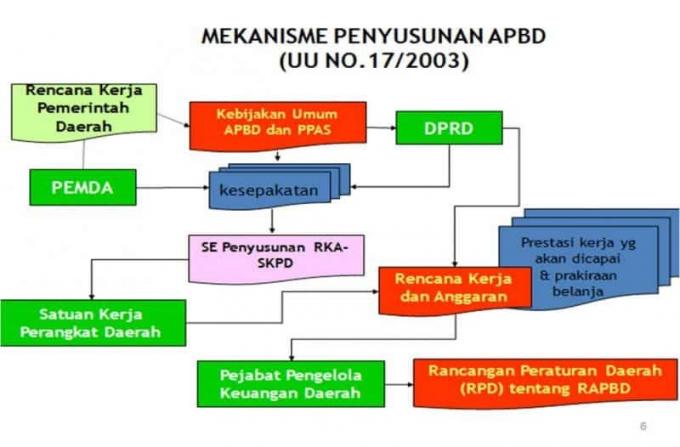
In preparing the APBN, the government does it in the form of a plan. The plan is submitted to the DPR, after which it is discussed by the DPR during the session.
After the RAPBN is approved by the DPR, the RAPBN after that will then be determined as the APBN through a law. If the RAPBN is not activated, the government will then use the APBN in the previous year. So that the implementation of the APBN is in accordance with the plan, a decision is made regarding the implementation of the APBN.
Thus the explanation of the Definition of the State Budget, Structure, Cycle, Mechanisms, Functions and Principles, hopefully what is described can be useful for you. thank you
See AlsoDefinition of Deficit, Causes, Impacts and How to Overcome It
See AlsoUnderstanding APBD, Types, Objectives, Functions, and Foundations
See AlsoDefinition of Achievement Work Behavior
