Sound: Definition, Terms, Speed, Properties, Types, and the Formula for Speed of Propagation
Education. Co. ID Sound is one of the types of waves that can be heard by the sense of hearing (ears). Sound is a mechanical compression or longitudinal wave that propagates through a medium. This medium can be liquid, solid, gas. So, these sound waves can propagate for example in water, coal, air and so on.
Definition of Sound
Understanding sound is one type of wave in physics, namely longitudinal waves that can be felt by the sense of hearing (ears). In physics, the definition of sound is something that is produced by vibrating objects. The object that produces a sound is said to be the source of the sound. The source of the vibrating sound will vibrate the air molecules around it. With this, the condition for the occurrence of sound is the presence of a vibrating object. The sound propagation also requires a medium. We can hear sound if there is a medium that can propagate sound. There are several conditions that must be met so that the sound can be heard.
Sound Conditions
The conditions for the occurrence and sound of the sound are:
- There is a vibrating object (sound source)
- There is a medium that propagates sound, and
- There is a receiver within range of the sound source
Sound Speed
Sound has a limited propagation speed. The sound takes time to move from one place to another. The speed of sound is actually not that great. The speed of sound is much smaller than the speed of light. Even now people have been able to make planes that can fly several times faster than the speed of sound.
See AlsoAxioms and Theorems: Definition, Conditions, and examples
Sound Formula
The speed of sound is often formulated as follows:
v = s/t
v = speed of sound (m/s), s = distance from source to observer (m), t = time interval (s)
However, if the frequency, wavelength or period is known, the formula for the speed of wave propagation that can be used is:
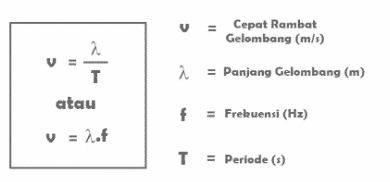
Notes:
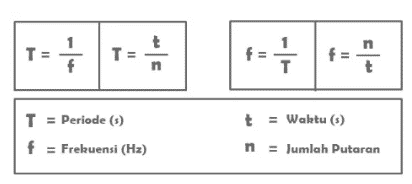
a. Frequency (f), which is the number of sound waves that pass a certain point in one second. It is denoted by the letter f and the unit of frequency is Hertz (Hz).
b. Period (T), which is the time it takes to travel one wave. It is denoted by the letter T and the period unit is seconds or seconds (s).
Properties of Sound
Sound has certain properties. The characteristics of these sound waves include:
- It is a longitudinal wave
- Cannot propagate in a vacuum
- The speed of propagation is influenced by the density of the medium of propagation (solid, liquid, gas). The highest speed is in a medium that has a high density as well.
- May experience resonance as well as reflection.
- Requires a medium in its propagation or cannot propagate in a vacuum.
Sound Resonance
Resonance is an event or occurrence where the vibration of an object is due to the vibration of another object, because the frequency is the same. The sound can be reflected, the sound reflection process is used in, among others:
- Determination of the speed of sound propagation
- Detection of defects and cracks in metal pipes
- Geophysical survey
- Metal plate thickness measurement
- Depth measurement.
Types of Sound
Sounds are grouped into several types. The types of sounds include the following:
Infrasound
that is, a sound with a frequency less than 20 Hz, which can be heard by dogs, crickets, geese, and horses.
Audiosonic sound
namely sound whose frequency is between 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz and can be heard by humans.
See AlsoConsular Representative: Definition, Functions, Main Duties, Devices and Rights
Ultrasonic sound
That is a sound whose frequency is more than 20,000 Hz, and can be heard by bats and dolphins.
Tone
i.e. sound with regular frequency.
sigh
It is a sound whose frequency is irregular.
Echo or kerdam
Namely the reflected sound which is partly coming together with the original sound, so that it interferes with the original sound.
Echo
namely the reflected sound that comes after the original sound is issued, so that it can amplify the original sound.
Thank you so much, above is a description of Sound: Definition, Terms, Speed, Properties, Types, and Formulas for Speed of Propagation, hopefully it can be useful for you.
Also read other interesting articles:
- Definition, Characteristics, Way of Life, Habitat, Reproduction and Classification of Fungi
- Understanding, Types and Functions of Traditional Music in General
- Understanding Physics, Benefits, Objectives, According to Experts
