Understanding Levers, Types, How They Work, Formulas and Examples
Education. Co. ID – This opportunity we will discuss about Levers or Levers, a full explanation of this Lever will be described as follows:
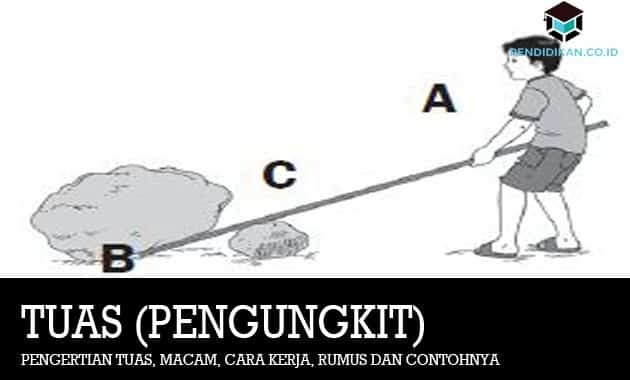
Definition of Lever or Lever
The lever or lever is a simple machine whose age is the oldest when compared to other simple machines. This lever has been used since the life of our ancestors. At that time, levers were used to be able to move heavy objects so that the work would be light.
For example, moving large stones to make temples and pyramids.
How the Lever Works
Point A in the figure below is called the power point, which is the place to do business (work). Point B is called the load point, is where the load is placed. This point C is called the fulcrum, where the plane is supported. The distance from the power to the fulcrum (AC distance) is called the power arm (lk).
The distance from the load point to the fulcrum (distance BC) is called the load arm (lb). The mass of power is mA and for the mass of the load it is mB. The mass of the load and the mass of this power are inversely proportional to the length of each arm.
So,
mA: mB = lb: lk or mA lk = mB lb
When both sides are multiplied by g then
mA g lk = mB g lk
wA lk = wB lb
The magnitude of wA = F = power, is the applied force, while for wB = w = the load lifted.
F lk = w lb
Information:
F = force acting (N)
w = load (N)
lk = power arm (m or cm)
lb = load arm (m or cm)
The ratio of the load to the power is called the mechanical advantage (KM) of the aircraft. So,
KM = W/F = Ik/Ib
Types of Levers or Levers
Based on the fulcrum, these levers are grouped into 3 types, including:
a. first type lever,

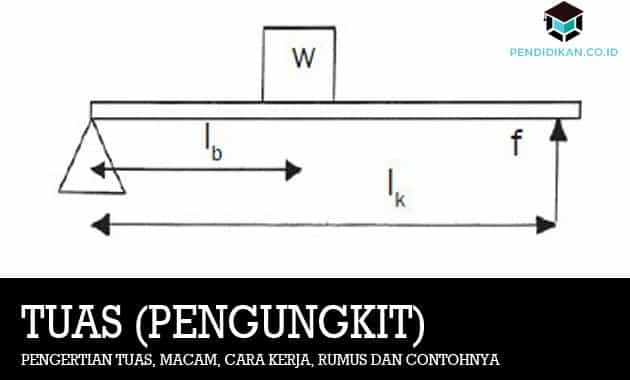
The location of the fulcrum of this type of lever is between the load point and the power point. Examples of the first type of lever, namely pliers and balance.
b. levers of the second type;
In the second type of lever, the load point is between the fulcrum and the power point. Examples are bottle openers and wheelbarrows.
c. third type lever.
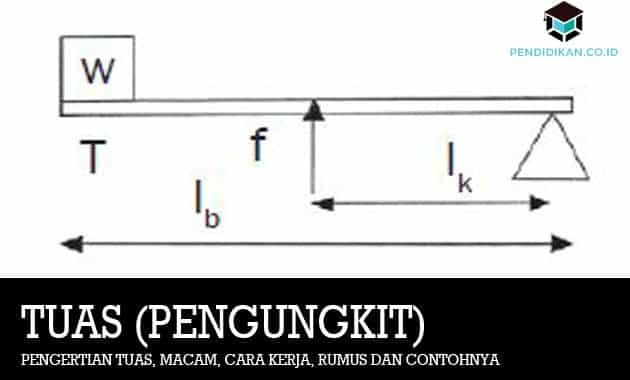
The point of force in this type of lever is between the fulcrum and the load point. This third type of lever is found on the arm that is being used to hold objects. For example, the hand holding a drinking water glass.
Examples of Lever or Lever Problems
A person is carrying two objects, each weighing 200 N and 300 N. Both objects were carried by using a stick. The object weighing 200 N is located at a distance of 150 cm from the fulcrum at one end of the stick. What is the minimum length of the stick needed so that the two objects carried are in equilibrium?
Discussion
Is known:
w1 = 200 N
w2 = 300 N
l1 = 150 cm = 1.5 m
Asked: l = …?
Answer:
w1 l1 = w2 l2
l2 = w1 l1/w2
= (200 N x 1.5 m)/ 300 N
= 1m
I = 11+12
= 1.5 m + 1 m = 2.5 m
So, the minimum length of the stick is 2.5 m.
Thus the explanation of the Definition of Lever, Kinds, How it Works, Formulas and Examples, hopefully what is described can be useful for you. thank you
See AlsoDefinition of Family, Functions, Types, Characteristics, and Duties
See AlsoUnderstanding Vendors, Functions, Duties, Responsibilities and Types
See AlsoInternational Law: Definition, Principles, Rules, Form, Purpose, and Classification According to Experts
