Physics Electric Power Formulas and Example Problems
Formula.co.id – On this occasion we will discuss the formula for electric power and in the previous discussion we have discussed the formula for infusion fluids. And in the electric power formula there is an electric power formula, examples of electric power, 3 phase electric power formulas, understanding of electrical energy, kinds of electric power, junior high school electric power formula, electric voltage formula and examples of questions, formulas electricity.
Table of contents :
Understanding Electric Power
Electric Power or in English yes Electrical Power which means the amount of energy absorbed or generated from within a circuit or circuit. The source of energy is like an electric voltage that will produce electrical power while the load connected to it will absorb the electrical power.
In other words, electric power is the level of energy use in a circuit or electrical circuit. We take the example of incandescent lamps and irons, incandescent lamps absorb the electrical power it receives and convert it into light while the iron converts the absorption of the electric power into heat.
The higher the wattage value, the higher the electrical power used.
Then based on the concept of business, what is meant by electric power is the amount of effort in electricity move charge per unit time or shorter, namely the amount of electrical energy used per unit time seconds. And based on the definition above we get a formula for electric power as below:
P = E/t
Information :
- P = Electrical Power (watts)
- E = Energy with ( joules )
- t = time with ( second )
And in the calculation formula, Electrical Power is usually symbolized by the letter (P) which means Power. Meanwhile, the international unit (SI) of electrical power is watts. Actually, watt is equal to 1 joule per second (watt = joule / second)
Then the watts derived units that are often used include:
1 milliWatt = 0.001 watt
1 kiloWatt = 1,000 watts
1 MegaWatt = 1,000,000 watts
Electric Power Formula
P = V x I
Or
P = I2 R
P = V2 / R
Information:
- P = Electrical Power ( W )
- V = Electrical Voltage ( V )
- I = Electric Current ( A )
- R = Resistance ( )
Electric Power Equation Daya
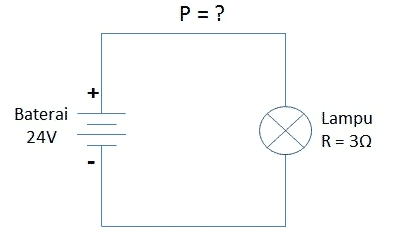
In the example picture above, the only known variables are voltage ( V ) and resistance ( R ), so we cannot use the formula the basis of electric power is P = V x I, but we can use an equation based on Ohm's law concept to simplify calculations his.
Ohm's Law
V = I x R
So, if only the electric current (I) and resistance (R) are known, then:
P = V x I
P = ( I x R ) x I
P = I2 x R You can use this formula to find electric power.
While the elaboration of the formula if only the voltage (V) and resistance (R) are known, then:
P = V x I
P = V x (V/R)
P = V2 / R You can use this formula to find electric power.
Horsepower (hp) relationship with Watt
Almost all electrical equipment uses watts as a unit of electrical power usage. But there are also certain equipment that does not use watts but uses units of Horsepower (hp). In the conversion that is, 1 hp = 746 watts.
In order to understand better I will give you all examples of the questions:
Examples of Electrical Power Problems
- An LCD tv requires a voltage of 220V and an electric current of 1.2A to activate it. So how much electric power should be used?
Answer:
Is known :
V = 220V
I = 1.2A
Asked:
electric power ( P )….?
Answered:
P = V x I
P = 220V x 1.2A
P = 264 Watt
So, the LCD TV will use 264 Watts of electrical power.
That's a complete explanation of the electric power formula along with its understanding, sample questions and formulas, hopefully useful...
Related Formulas:
- Potential Difference Formula
- Derivative Quantity Formula
