Newton's Law 1 2 3
Formula.co.id – Back again with Formula.co.id, the discussion this time is very interesting from the field of physics, namely Newton's laws. You need to know that there are three newton's laws are usually called newton's law 1, newton 2 and newton 3. Check out the following explanation.
Table of contents :
Understanding Newton's Laws
Newton's laws are the three laws of physics as the basis of classical mechanics describing the relationship between the forces acting on an object in motion. Almost all physics formulas relate to motion ranging from distance or height. So Newton's law is very important to study.
Newton's law is one of the rules applied in physics. An object in motion cannot be explained logically, but if you use Newton's laws you can calculate its speed and distance.
Objects fall from top to bottom, or the movement of objects from one point to another can mean that the object is moving or changing places.

Newton's Laws
Newton's 1st Law
If the resultant force acting on an object is equal to zero, then the object that was initially at rest will remain at rest. An object that initially moves in a straight line will remain in a straight line at a constant speed.
Newton's 1st Law Formula
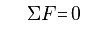
Newton's 1st Law Example
- When riding in a fast-moving car, the passenger will then be pushed forward on the brake.
- The car runs slowly then suddenly steps on the gas so the passengers will lean back.
- If you put, for example, a coin on a cloth and then the cloth is pulled quickly, the coin will stay.
Newton's 2nd Law
The acceleration of an object will be proportional to the amount of force (the resultant force) acting on the object and inversely proportional to its mass.
Newton's 2nd Law Formula
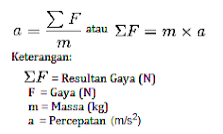
Newton's 2nd Law Example
- Pulling carts transporting fertilizer from house to fields
- If pulled with the same force, the cars with a larger mass (with a load) have a smaller acceleration, while on the same car (same mass) if pulled with a greater force will experience a greater acceleration also.
- Dribbling the ball on a flat surface
Newton's 3rd Law
If one object exerts a force on another object, the object that is subjected to the force will exert a force equal in magnitude to the force received from the first object but in the opposite direction.
Newton's 3rd Law Formula
Newton's 3rd law formula there are three, namely friction, gravity and similar forces.
Friction
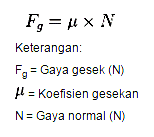
Gravity

Similar Style

Newton's 3rd Law Example
- When sitting on a foam chair, your body weight will press the chair down, while the chair will hold your weight up.
- Throw the ball at the wall then the ball will turn with the same force
- If someone puts on roller skates and pushes against a wall, the wall will push the same amount with the force you put out but in the opposite direction, so the person is pushed away Wall.
Problems example
1. A block of mass 5 kg (weight w = 50 N) is suspended by a rope and attached to the roof. If the block is at rest, what is the tension in the string?
Answer:
The forces acting on the block are as shown below, because the block is at rest, Newton's first law applies as follows.
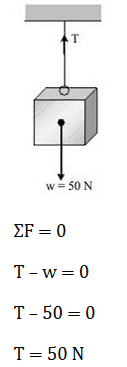
So, the tension in the string acting on the block is 50 Newtons.
2. An object with a mass of 10 kg is tied to a rope and formed a system as shown in Figure (a) below. If the system is at rest and the acceleration due to gravity is g = 10 m/s2 then determine the tension in the ropes T1 and T2!

The weight of the object is as follows.
w = mg
w = 10 kg × 10 m/s2
w = 100 N
By using the same analytical method as in the previous example problem where the force diagram is shown in figure (b), then the resultant force acting on this system is as follows.
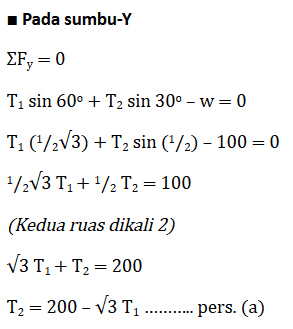
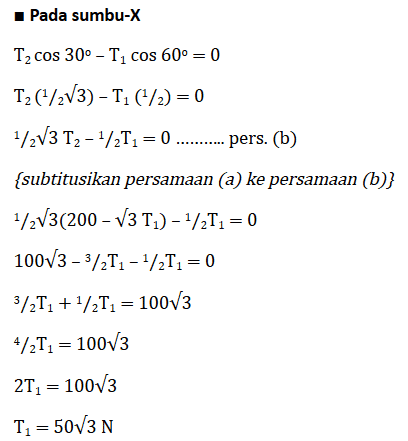

Also Read:
Formula for Average Speed, Distance and Time, Example Problems
Fast Wave Propagation Formulas and Example Problems
Thus an explanation of Newton's laws 1 2 3, explanations, sounds, and examples. Hopefully this article can add to your insight and information. Hopefully this article can help and bring a lot of benefits to all of you who read it. See you in the next article, continue to visit Formula.co.id, there are many interesting articles there.
