The BEP Formula and Its Definition, Functions, and Formulas
Formula.co.id – On this occasion we will discuss the bep formula and in the previous discussion we have discussed the derivative quantity formula. And in the bep formula there are entrepreneurship bep formulas, pharmacy bep formulas, bep charts, bep benefits, examples of bep questions, how to calculate small business bep.
Table of contents :
Definition of BEP
Definition of bep or abbreviation of ( Break Even Point ) is the point where the entity or company or it can be a business in a state that has not yet made a profit, and has not suffered a loss either.
Break Even Point or BEP can be interpreted as an analysis to determine and find the number of goods or services that must be sold to consumers and at a certain price to cover the costs incurred and can also make a profit or profit.
BEP can also be interpreted as a situation where in the company's operations, the company does not make a profit and do not experience a loss or (the income generated will use the total cost ).
However, the BEP analysis is not only to find out whether the company's condition has reached the BEP point or not, but the BEP analysis is able to provide informational results. to the loan company regarding the various levels of sales volume, as well as their relationship to the possibility of making a profit according to the level of sales that is concerned.
Analysis Function From BEP
BEP formula or analysis break even point namely the analysis of return on investment that is used to determine things such as:
- First, the minimum amount of sales must be maintained so that the company does not suffer losses. And this minimum number of sales means also the minimum amount of production that must be made immediately.
- Both the number of sales that must be achieved to obtain the planned profit or it can be interpreted that the level of production must be fixed in order to make a profit that.
- Third, measure and maintain that sales and levels of production are not less than BEP.
- Fourth, analyze changes in selling prices, cost of goods and the amount of sales or production levels. So that the analysis of the BEP is a sales planning tool and at the same time a production level planning tool, so that a company does not experience minimal losses. Then because it has to make a profit means a company must produce above its BEP.
BEP formula
The following are some of the BEP formula models that can be used to analyze the Break Even Point:
1. Mathematical Approach
The first BEP formula is how to calculate the break even point that must be known, namely the number of total fixed costs, variable costs per unit or total variable, total sales results or selling price per units. Then the formula is like this:
-
Break even points in units.
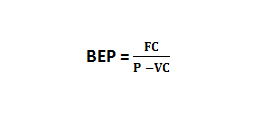
Information :
BEP = Break Even Point
FC = Fixed Cost
VC = Variable Cost
P = Price per unit
S = Sales Volume
- Break even point in rupiah.
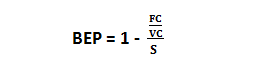
Information :
BEP = Break Even Point
FC = Fixed Cost
VC = Variable Cost
S = Sales Volume
2. Graphics Approach
Then the second BEP formula is a graphical approach describing the relationship between sales volume and costs incurred by the company and profits. In addition to knowing about fixed costs, variable costs and the level of loss of a company.
The assumption used in this basic opportunity analysis is that the selling price, variable costs per unit are constant.
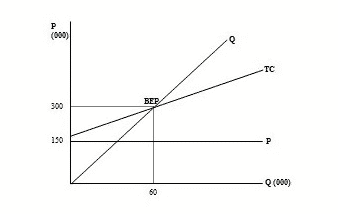
And from the graph above, it can be seen that for each sales unit there is a complete information on every rupiah of sales, fixed costs, variable costs, total costs and profits or loss.
So the management can see if it is going to produce a number of units, all of the components above will be seen. The BEP through the graph is very clearly shown both in terms of units and in terms of the rupiah that has been obtained.
Sample Questions and How to Calculate BEP
It is known that a PT. XYZ has a business engaged in electrical machine tools with complete data as follows:
- Production capacity that can be used is 100,000 units of electric machines.
- The selling price of the unit is estimated at Rp. 5000,- units
- Total fixed costs of Rp. 150,000,000,-
- The total variable cost is Rp. 250,000,000,-
The details of the data for each cost are as follows:
Fixed Cost
Factory Overhead = Rp. 60,000,000,-
Distribution fee = Rp. 65,000,000,-
Administration fee = Rp. 25,000,000,-
Total FC = Rp.150,000,000,-
Variable Cost
Material cost = Rp. 70,000,000,-
Labor cost = Rp. 85,000,000,-
Factory overhead = Rp. 20,000,000,-
Distribution cost = Rp. 45,000,000,-
Administration fee = Rp. 30,000,000,-
Total VC = Rp.250,000,000,-
Settlement to get the BEP value in units and rupiah.
Solution:
Production capacity 100,000 units
Selling price per unit Rp. 5000,-
Total Sales 100,000 units x Rp. 5000,- = Rp. 500,000,000,-
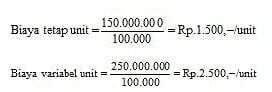
To get the BEP value in units as follows:

Note: So the company PT. XYZ must sell 60,000 Units of power machine tools in order to BEP.
Then, to find the BEP value in rupiah as follows:
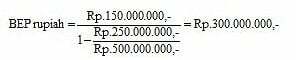
Note: So the company PT. XYZ must get a turnover of Rp. 300,000,000, - for BEP to occur.
That is a complete explanation of the bep formula along with its understanding, functions and examples of questions and calculations, hopefully it will be useful...
Also Read:
- Derivative Quantity Formula
- NPV Rumus formula
- ROA formula Rumus
