The Human Movement System: Bones, Joints, Muscles, Functions, Disorders And Disorders
The Human Movement System: Bones, Joints, Muscles, Functions, Disorders and Disorders – What are the motion systems in the human body? On this occasion, Seputartahuan.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things that also cover it. Let's take a look at the discussion in the article below to better understand it.
Table of contents
-
The Human Movement System: Bones, Joints, Muscles, Functions, Disorders And Disorders
-
Bone
- Bone Function
- Bone Type
- Bone Shape
- Abnormalities in Bones
-
Joint
- Types of Joints
- Disorders and Diseases of the Joints
-
Muscle
- Muscle Types
- Movement and Muscle Work
- Musculoskeletal Disorders And Disorders
- Disorders and Diseases of the Human Movement System
- Share this:
- Related posts:
-
Bone
The Human Movement System: Bones, Joints, Muscles, Functions, Disorders And Disorders
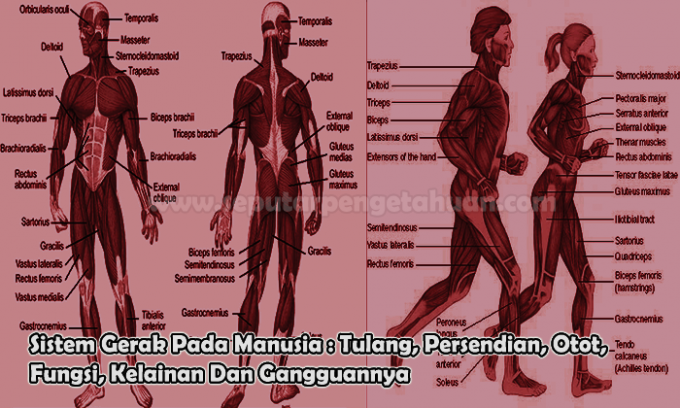
Moving is one of the characteristics of living things, moving means moving or changing places or positions, either part or all of the body. Supporting the movement of the human body is called a motion system consisting of a number of organs such as the skeleton or bones, joints and muscles.
Passive locomotion in humans are bones and active locomotion in humans are muscles and joints as a liaison between bones so that they can be moved.
The human skeleton consists of ± 206 bones that vary in size and shape. The bones that make up the skeleton are grouped into the skull, the bones that make up the body and the bones of the limbs.
The limbs are grouped into the upper and lower limbs. The bones of the upper limb consist of the arm, the ulna, the lever bone, the wrist bone, the palm bone and the finger bones. The bones of the lower limbs consist of the femur, shin bone, calf bone, ankle bone, foot bone and toe bone.
The arrangement and shape of the bones of the upper limbs correspond to the function of the arm, for example to lift, throw, hit, hold, grasp, pick up, and pick up. The bones of the lower limbs have the shape and arrangement of the bones of the lower limbs that are more adapted for walking, running, and bearing body weight.
Bone
Bone is the support and shaper for the body in vertebrates and without it the body cannot stand. Bones in humans are formed from in the womb to the second decade in an orderly arrangement.
In the motion system in humans, bones are passive means of movement, because bones cannot move without the help of muscles.
Bones that are arranged in such a way with a certain system are called skeletons or skeletons.
Bone formation occurs due to the presence of calcium in the form of salt attached with the help of collagen.
-
Bone Function
Functions of the bones or skeleton, including:
- Passive locomotion.
- Support and support so that the body can stand upright.
- Body shaper.
- Provides protection for tools or soft body parts.
- Where skeletal muscles are attached.
- Site of blood cell formation and mineral storage.
-
Bone Type
Human bone structure is composed of 0-20% water, about 60-70% bone mineral and the rest is collagen (protein). the main fiber in the body), but bones also contain other substances such as protein and inorganic salts in large quantities small.
Based on the constituent tissue, there are 2 types of bone, namely cartilage (cartilage) and hard bone (osteon).
-
Cartilage (Cartilage)
-
Cartilage structure consists of cartilage cells called chondrocytes. Chondrocytes are composed of young cartilage cells (chondroblasts). The chondrocytes are located in spaces called lacunae. Chondroblasts produce a matrix in the form of chondrins. Generally, chondrins are homogeneous and clear hyaline. The fibrous chondrins contain a lot of collagen (bone adhesive substance).
The nature of cartilage is flexible and composed of cartilage cells that produce a matrix in the form of chondrins. In children, cartilage is formed from mesenchymal cells and contains many chondroblasts. Whereas in adults, cartilage contains a lot of matrix and is formed by the perichondrium (cartilage membrane) which contains chondroblasts.
There are three types of cartilage including:
- Hyaline cartilage, which is a type of cartilage that has strong and elastic properties and is bluish-white in color. Examples of hyaline cartilage are in the nasal bones, trachea, larynx and the ends of the ribs.
- Fibrous cartilage (fiber), which is a type of cartilage that is hard and white in color. Examples of fibrous cartilage are found in the kneecap and vertebrae.
- Elastic cartilage, which is a type of cartilage that has flexible and elastic properties and has a yellow color. Examples of elastic cartilage are found in the auricle and epiglottis.
-
Bones (Osteon)
-
Bone structure is composed of bone cells called osteocytes. The function of hard bones is as a constituent of various skeletal systems. Hard bone cells (osteocytes) are formed from osteoblasts (young bone cells). The bone cells are located in spaces called lacunae. The lacunae are connected by canaliculi which contain cytoplasm and blood vessels. The function of the canaliculi is to meet the nutritional needs of osteocytes.
There are 2 types of hard bone, namely compact bone (solid bone) and spongy bone (hollow bone). Examples of compact bone are the tubular bones and examples of spongy bones are the epiphyses of the tubular bones. In the hard bone matrix (compact bone) there is a content of lime, phosphate, and collagen fibers. While the spongy bone matrix contains bone marrow or fat cells.
Bone Shape
Bones are divided into 3 types based on their shape, namely as follows:
- Pipe Bone
The shape of this bone is long and round with a cavity in the middle like a pipe. Examples of pipe bones are finger bones, femur, and upper arm bones. - Flat Bone
The shape of this bone is flat or flat. Examples are the sternum, shoulder blades, and ribs. - Short Bone
The bones are round and short. Examples are: vertebrae, ankle bones, and wrist bones. Flat bones have a function as a place for the process of formation of red and white blood cells.
- Pipe Bone
-
Abnormalities in Bones
The following are some examples of bone disorders:
- Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a disorder of the spine that causes its position to be bent to the right or left side. this can occur due to lifting weights on one shoulder or arm too often. or it can also be caused by the habit of sitting in an inclined position so that the weight of the body rests on one arm. - Kyphosis
Kyphosis is a spine disorder that is too bent towards the back, this disorder is usually caused by: the habit of sitting in a position that is too bent or often carrying heavy loads using the back. - Lordosis
The opposite of kyphosis, which is a spine disorder that is too bent forward, a sitting position with outstretched chest can be the cause of this disorder. - Polio
This disorder is caused by polio virus infection, the sufferer will experience a bone condition that is getting smaller and smaller, leading to paralysis. - Rickets
Abnormalities that occur due to lack of vitamin D intake, so that his leg bones are shaped like the letter X or O.
- Scoliosis
Joint
Joints are the link between the bones so that the bones can be moved. The connections between bones are called joints or articulations. The function of the joint is to provide flexibility and movement in its place, as well as the axis of the limb. There are about 360 joints in the human body.
The components that form or support the joints consist of ligaments, joint capsules, synovial fluid and hyaline cartilage.
-
Types of Joints
Based on the nature of the movement, the types of joints are divided into:
- Diarthosis (moving joints), which is a type of joint that allows movement in one direction, two directions or in all directions. Examples of movable joints such as the knee joint (one way), the palm joint (two directions) and the shoulder joint (in all directions).
- Amphiarthrosis (stiff joint), which is a type of joint that allows only a small amount of movement. An example of a rigid joint is the joint between the ribs.
- Synartosis (dead joints), which is a type of joint that can not be moved. One example of a dead joint is a joint between the bones of the skull.
Based on the direction of movement, joints are divided into:
- Hinge joints, which are types of joints that allow only one direction of movement, generally can only be bent or straightened. Examples of hinge joints include the joints in the knees and elbows.
- Saddle joints, which are types of joints that allow two-way movement. An example of a saddle joint is the joint in the palm of the hand.
- Bullet joints, which are types of joints that allow movement in all directions. Examples of ball joints include the joints in the femur and shoulder.
- Rotary joints, which are types of joints that allow movement of one bone that rotates against another bone. Examples of rotary joints include joints in the atlas bone.
- Sliding joint, which is a type of joint that allows movement of one bone to slide on another bone. Examples of sliding joints include the joints between the carpal bones.
- Glide joints or arthrodial joints, which are types of joints in which the surfaces of the joints involved are flat or only slightly curved. An example of a gliding joint is the wrist.
- Rolling joint, which is a type of joint that allows only a little movement and can rotate around an axle. Examples of rolling joints as in the joint with a cubit.
- Condyloid joints, which are types of joints that can be moved sideways and back and forth, but do not surround the shaft. An example of a condyloid joint is the palm of the hand.
Based on the structure, the types of joints include:
- Fibrous joints, which are types of joints that do not have cartilage, one bone to another is connected by fibrous connective tissue. So much to move. Examples of fibrous joints are found in the sutures of the skull.
- Cartilaginous joints, which are types of joints in which the ends of the bones are connected by cartilage and supported by ligaments.
- Synovial joints, which are types of joints that have space between joints so that it allows for a lot of movement with the ends of the bones covered with thin hyaline cartilage to protect against impact and friction between the bones. An example of a synovial joint is the knee.
-
Disorders and Diseases of the Joints
The following disorders, disorders and diseases of the joints, including:
- Dislocation, which is a shift in the position of the joint due to a torn or pulled ligament.
Sprains / Sprains, which are conditions where the ligaments of the joint are pulled by sudden movements. - Ankylosis, which is a condition where the joints cannot be moved.
- Arthritis, or joint infection, is a condition in which the joints become inflamed. There are 3 types of arthritis, including:
- Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease of the connective tissue of the joints.
- Ostevartritis, which is a joint disease due to the thinning of cartilage.
- Gautarthritis, namely movement disorders due to failure of uric acid metabolism.
- Dislocation, which is a shift in the position of the joint due to a torn or pulled ligament.
Muscle
Muscle is an active tool in humans that can relax (lengthen) and contract (shorten). Without muscles, the body cannot move because there is nothing to move the bones.
There are 3 properties of human muscles including:
- Contractility (shortens when contracted)
- Extensibility (lengthens when relaxed)
- Elasticity (return to original size)
-
Muscle Types
There are 3 types of muscles in the human body, including:
- Skeletal muscle, which is a type of muscle that attaches to the body's skeleton and is used for movement, so this muscle is also called skeletal muscle. In addition, striated muscles are called voluntary muscles because they work subconsciously (volunteer).
- Smooth muscle, which is a type of muscle that works involuntarily (autonomous), smooth muscle can be found in the digestive tract such as the stomach.
- Cardiac muscle, which is a type of striated muscle that works involuntarily or reflexively and is found in the walls of the heart, especially the myocardium.
-
Movement and Muscle Work
Muscles move by contraction and relaxation. When the muscle contracts, it will shorten in size and become hard and will form a bubble in the middle. When the muscles contract, the bones are pulled. To return the bone to its initial position, relaxation is needed.
This means that another muscle has to contract in order to pull the bone back into its starting position. so to be able to move the bones at least it takes the cooperation of two kinds of muscles with different ways of working.
Based on how they work, muscles can be divided into two types, namely:
- Synergistic Motion
Synergistic motion is the harmonious movement of two or more muscles. In synergistic motion, these muscles will contract and relax simultaneously. An example is the movement of the back and neck muscles. - Antagonist Motion
Opposite movement between two or more muscles to move a part of the body. For example, when the forearm is raised, the biceps relax while the triceps relax.
- Synergistic Motion
-
Musculoskeletal Disorders And Disorders
- The following disorders, disorders and diseases of the muscles, including:
- Muscle spasms, which are conditions where the muscles are no longer able to contract because they run out of energy because they are used continuously.
- Atrophy, which is a condition in which muscles shrink so that the ability to contract is lost.
- Hypertrophy, which is a condition where the muscles are enlarged and strong due to frequent exercise, this condition can be seen in bodybuilders and others.
- Tetanus is a muscle spasm caused by a toxin produced by Clostridium tetani.
- Stiff or Neck Stiffness, which is a condition that occurs due to inflammation of the neck muscles due to wrong movements or obstacles so that the neck feels stiff.
- Abdominal hernia, which is a condition in which the weak abdominal wall muscles are torn so that the intestines sag into the abdominal cavity.
Disorders and Diseases of the Human Movement System
The following disorders, disorders and diseases that occur in the bones, among others:
- There are 4 types of fractures, including:
- Simple fracture, when the fractured bone does not injure the muscle.
- Greenstick, if the bone is only cracked and some of it does not separate.
- Closed fracture, when the bone is broken, the muscle is injured but the skin does not come out.
- An open fracture occurs when the bone is broken and the skin is exposed.
- Rickets is a disease of brittle bones caused by a lack of vitamin D. People with rickets have X or O-shaped leg bones.
- Osteoporosis, which is a disease of the bones where the condition of the bones become soft due to a lack of certain hormones that help calcium attachment or also due to a lack of calcium.
- Microcephaly, namely abnormalities in the bones of the head in the form of a smaller or disproportionate head size. This is because during pregnancy, the mother lacks calcium so that the formation of the baby's skull is not perfect.
That's the review from Seputardunia.co.id about Movement System In Humans ,Hopefully it can add to your insight and knowledge. Thank you for visiting and don't forget to read other articles.
Also Read:Upper Bone Function: Part, Structure and Discussion
