Definition of Cambium: Characteristics, Functions, Types and Structures
Definition of Cambium: Characteristics, Functions, Types and Structures – What is the Cambium in plants and its functions? On this occasion, Seputardinding.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things that also cover it. Let's look at the discussion together in the article below to better understand it.
Definition of Cambium: Characteristics, Functions, Types and Structures
Cambium is a layer of meristematic tissue in plants whose cells are actively dividing and is responsible for plant secondary growth. The cambium structure in this plant is found in the stems and roots.
The cambium is an active cell layer that separates the xylem (wood) and phloem transport vessels (bark) is a tissue that is responsible for secondary growth in plants, especially roots and stem. This secondary growth occurs in the first season and causes an increase in girth.
The theoretical definition of the cambium is a layer of cells called the starting cells; practically, it is difficult to distinguish from the still-differentiated daughter cells, and collectively the number of cell layers is called the cambium or the zona cambial.
The form of cambium is in the form of mucus in the skin (xylem) and wood (phloem). The function of the cambium in woody stems is as a medium or pathway for nutrients from the soil to the leaves.
Cambium can only be found in dicots and gymnosperms (open seed plants) and cannot be found in monocots. Because monocot plants do not have a cambium, monocot stems do not undergo secondary growth or thickening or increasing the diameter of the stem.
In short, the notion of secondary growth is defined as the activity of the cambium in the formation of xylem and phloem. Secondary growth in plants causes the stem to grow wide as well as annual rings and pith radii are formed. Between the xylem and phloem there is a cambium whose cells are actively dividing.
Cambium growth outward will form secondary phloem and cambium growth inward will form secondary xylem so that the diameter of the plant stem will increase.
The tissue that is inside the cambium is called wood, while the outer part of the cambium is called papagan or skin. The formation of secondary transport bundles in the stem occurs due to the activity of the cambium which is influenced by the seasons.
Cambium features
The following are the characteristics or characteristics of the cambium in plants, including:
Cambium can only be found in dicot plants and open seed plants (gymnosperms), where its activity can produce cork tissue (cork or phellem, felem) outwards.
The function of the cork network is to control the entry and exit of water, to prevent attacks from pests as well as other mechanical functions.
Cambium function
Cambium is a plant structure that is hard, while the functions of cambium in plants include:
Forms wood vessels (xylem) and sieve tubes (phloem).
Transporting the results of photosynthesis in the form of glucose, oxygen and water vapor from the leaves to all parts of the plant.
Transport water and nutrients from roots to leaves for photosynthesis.
Types of Cambium in Plants
The following types of cambium in plants include:
Primary Cambium
Primary or intervascular cambium, namely the type of cambium that is located between the xylem and phloem of dicot plants and open seed plants.
Secondary Cambium
Secondary cambium, which is a type of cambium that is located on the surface of roots and stems that break due to secondary growth. The function of the secondary cambium or cork cambium is to form cork cells as a substitute for the epidermis (to the outside) and to form living feloderm cells (into).
Based on the fixed network it forms, the cambium is divided into:
Cork Cambium
Cork cambium is a type of cambium that is included in the cortex. Cork cambium activity forms cork tissue (phelem, phellem or cork) outwards. The function of the cork network is to control the entry and exit of water, preventing pest attacks, and other mechanical functions. While the activity of cork cambium in some plant species forms phelloderm (phelloderm).
Vascular Cambium
Vascular cambium or vascular cambium or commonly called cambium is a type of cambium that generally becomes a barrier between the bark (bark) of the wooden column on a tree trunk. The growth of the cambium inwards will form xylem vessels and the outer growth of the cambium will form sieve tubes (phloem, phloem).
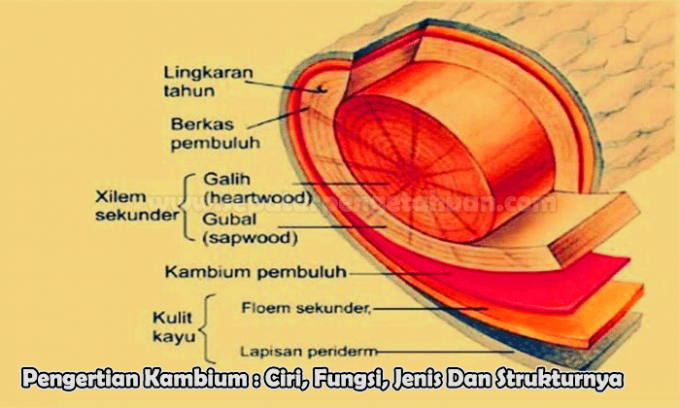
Structure of the Cambium
Cambium is a lateral meristem because it is located in the outer region of stems and roots. For most shrubs and trees, the cambium region is a multilayered cylinder whose cross section forms a continuous ring. When the cadmium is active, it types from many layers to cells, but when it is quiescent (inactive).
The layer is considered a two-sided layer because it can generate gradients in many directions. Following perlicinal division, the cells develop into cells that remain on the outside of the agar active as a change or external cells develop so internal cells remain valid as cells exchange.
The most convincing evidence is that parallel xylem and secondary phloem are mirror images of one another. At some point, the change creates new empiric fingers which can be found in xylem and phloem. While the gearbox is ejected inside together with the thickening of the xylem cylinder.
The cell will divide into anticline fission plane so that it can enlarge the tangential area. Therefore, the gear area compensates for the breadth of the xylem cylinder. It was mentioned above that the transmission is completely cylindrical. However, small amounts of wood occur in most plants e.g. Euphorbiaaceae, succulents and most dicots, including papaya.
Here the cambium will look like a series of thin bands bounded by the original vascular bundle bundles. The limited activity of the cambium means that the files are in the form of wooden posts or wooden nets.
Thus the review from Seputarknowledge.co.id about Definition of Cambium: Characteristics, Functions, Types and Structures ,hopefully can add to your insight and knowledge. Thank you for visiting and don't forget to read other articles.
List of contents
Recommendation:
- √ Definition of Hard Bones, Functions, Characteristics, Types, Structures &… Definition of Bones, Functions, Characteristics, Types, Structures & Examples - On this occasion we will explain about bones. The discussion includes the definition of bones, functions, types, characteristics, bone structure...
- Plant Strengthening Tissues: Definition, Collenchyma,… Plant Strengthening Tissues: Definition, Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma, Characteristics, Types and Structures - What are the tissues plant boosters and the differences? other thing…
- √ Definition of Hair and Hair Structure (Full Discussion) Definition of Hair and Hair Structure (Full Discussion) - There are so many parts of the human body and all of that is important for the human body because one with the other will be interrelated and interrelated help.…
- The Political Life of the Majapahit Empire: Early History and… The Political Life of the Majapahit Kingdom: Early History and Legacy - How was the Political Life of the Kingdom Majapahit? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss the Majapahit Kingdom and other things covered it. Let's look at the discussion together...
- √ Definition of Mature Tissues in Plants, Characteristics, Functions &… Definition of Adult Tissues in Plants, Characteristics, Functions & Structures - In this discussion we will explain about adult tissues in plants. Which includes the understanding of mature tissue in plants, function, structure...
- Moss Life Cycle: Definition, Structure and Benefits of Moss Moss Life Cycle: Definition, Structure and Benefits of Moss - How is the life cycle of a moss plant?, On this occasion, about the knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course other things too covered it. Let…
- Lymph Circulatory System Functions: Constituent Components And… Functions of the Lymph Circulatory System: Composing Components and Their Anatomy - What is the Function of the Lymph Circulatory System Bening?, On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things that also…
- Bacteria and Their Role: Types, Beneficial and… Bacteria and Their Role: Types, Beneficial and Harmful Roles - What are bacteria? Bacteria are single-celled or unicellular organisms, prokaryotes or prokaryotes, microscopic or very small in size. Bacteria contribute...
- Erythrocytes: Definition, Characteristics, Functions, Structures and Processes… Erythrocytes: Definition, Characteristics, Functions, Structure and Formation Process - What are the types of yang energy there? Also…
- Example of historical story text in Indonesia Examples of historical story texts in Indonesia – What are examples of historical stories like? This time around the knowledge.co.id will discuss examples of historical stories and their structure. Let's take a look at the discussion in the article on…
- Ovarian Function: Definition and Anatomical Structure Function of the Ovaries: Definition and Anatomical Structure - In this discussion we will explain about the Ovaries. Which includes the definition, anatomical structure, function and influence of age on the growth and development of the ovaries…
- DNA and RNA: Definition, Characteristics, Differences and… DNA and RNA: Definition, Characteristics, Differences and Discussion of the Process - What are the meanings and differences of DNA and RNA? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course other things that...
- Parts of the Skin: Epidermis, Dermis, Structure And… Parts of the Skin: Epidermis, Dermis, Structure and Functions - On this occasion, Se regarding the knowledge.co.id will discuss the parts of the skin and of course about other things that also cover it. Let's see together…
- Differences in Cardiac Striated Smooth Muscle, Shape, Working System and… Differences in Cardiac Striated Smooth Muscles, Shape, Working System and Location - What are the Differences in Smooth Muscles Lurik Hati?, On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course other things Which…
- Papers: Definition, Characteristics, Functions, Types, Structures, Methods… Papers: Definition, Characteristics, Functions, Types, Structure, How to Make and Examples - What is meant by Papers and how to write them properly and correctly? On this occasion Seputarknowledge.co.id will…
- √ Definition of Binary Fission and Its Phases in Bacteria… Definition of Binary Fission and Its Phases in Bacteria (Complete) - In this discussion we will explain about binary fission. Which includes the understanding of binary fission and binary fission phases in bacteria that...
- Metamorphosis Is: Definition, Phases, Types and Examples Metamorphosis Is: Definition, Phases, Types and Examples - What is Metamorphosis? Metamorphosis is defined as the process of development of living things that was originally an egg to mature perfectly and experience something…
- √ Definition of Veins, Functions, Characteristics and… Definition of Veins, Functions, Characteristics and Types - In this discussion we will explain about veins or also called Veins. An explanation that includes the meaning of veins,…
- Collenchyma Network: Definition, Structure, Characteristics, Functions and… Collenchyma Network: Definition, Structure, Characteristics, Functions and Types - Collenchyma tissue is also called reinforcing or supporting tissue, is one of the constituent tissues of plants. To understand more, let's follow the discussion...
- Transformer: Definition, Functions, Types, Parts, Principles… Transformer: Definition, Functions, Types, Parts, Working Principles, Weaknesses and Winding Formulas - What is it transformers and their functions? On this occasion, Se regarding the knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about it others that…
- Metagenesis: Definition, Process, Examples and Explanations Metagenesis: Definition, Process, Examples and Explanations - What is meant by metagenesis? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things that also cover it. Let's see…
- √ Definition of the Five Senses, Types, Kinds and Functions Definition of the Five Senses, Types, Kinds and Functions - On this occasion, Around Knowledge will discuss the meaning of the five senses. Which in this discussion explains the meaning of the five senses, types,…
- Large Blood Circulation: Definition, Types, Components and… Great Blood Circulation: Definition, Types, Components and Functions - What is large blood circulation?, On On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it, including types, components and of course other things which also…
- Cell Transport: Definition, Active, Passive, Endocytosis &… Cell Transportation: Definition, Active, Passive, Endocytosis & Exocytosis - On this occasion we will discuss cell transportation. Want to know more details? see the discussion below in full.
- 6 Functions of Roots in Plants and Their Types 6 Functions of Roots in Plants and Their Types - Friends, all of you must already know the shape of the roots that we will discuss on this occasion. Where the root is an important part apart from...
- Definition of White Blood Cells (Leukocytes), Functions, Types and… Definition of White Blood Cells (Leukocytes), Functions, Types and Characteristics - This time we will discuss about blood. Blood is an important thing for humans, if you've ever heard that someone is...
- Mangrove Forests Are: Characteristics, Benefits, Causes of Damage And… Mangrove Forests Are: Characteristics, Benefits, Triggers of Damage and Countermeasures - What is meant by forest mangroves and their functions? On this occasion, Se regarding the knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about it other…
- Animal Cells: Definition, Parts and Functions Animal Cells: Definition, Parts and Functions - In this explanation, you will learn about Animal Cells. Which includes understanding, the parts of animal cells and their functions with complete and easy discussion...
- Meristem Network Functions, Definition, Types, Characteristics, Types &… Meristem Network Functions, Definition, Types, Characteristics, Types & Locations - In this discussion we will explain about meristem networks. An explanation that includes the definition of meristem tissue, meristem tissue functions, characteristics...
- Separating Funnel: Definition, Form, Function, Working Principle… Separating Funnel: Definition, Form, Function, Working Principle and How to Use it - What is a separatory funnel? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it, including functions, how it works and of course other things that...
