Metagenesis: Definition, Process, Examples and Explanations
Metagenesis: Definition, Process, Examples and Explanations – What is meant by metagenesis? On this occasion About the knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things that also cover it. Let's look at the discussion together in the article below to better understand it.
Metagenesis: Definition, Process, Examples and Explanations
Alternation of descent or metagenesis is the life cycle experienced by organisms where each phase or the stages involve individuals with different genetic content, usually the haploid (n) stage and the diploid stage (2n).
Another definition of metagenesis, namely, metagenesis is the alternation of offspring from the asexual phase to the sexual phase and vice versa. In metagenesis, there is a life cycle in which organisms will periodically carry out sexual and asexual phases. Not all organisms experience metagenesis, examples of metagenesis are metagenesis in mosses, metagenesis in ferns, and metagenesis in seed plants.
In plant metagenesis, there is an alternation of generations between gametophyte and sporophyte generations. The gametophyte generation is the generation that produces gametes or sex cells (haploid generation), while the sporophyte generation is the generation that produces spores (diploid generation).
The term from the word metagenesis is used to be able or able to explain the echoes of changes that occur occurs in living things in the essence of life, which occurs in two ways of reproduction in the cycle his life. The two ways of reproduction are by means of marriage (sexually) and also asexually (not married) as well as forming spores.
The term metagenesis in a complex sense is a shift from a multicellular diploid form as well haploid within an organism's life cycle, regardless of whether the organism is freely living or not colonize.
With the understanding of metagenesis above, there is a lot of debate going on among researchers about metagenesis occurring in multicellular animals. One example of Cnidarian, Cnidarian in several junior and senior high school books, it is explained that as an example of metagenesis in animals, however, if you use the definition of metagenesis described above, it turns out that the two sexual and asexual phases of Cnidarian are diploid. Then it is not referred to as metagenesis but referred to as heterogamy.
But if you are asked about or about a process of metagenesis in animals, you can or can provide an example of metagenesis from jellyfish (Obelia), because for some researchers they still think metagenesis occurs in jellyfish animal. Even if according to Barnes (2001) and Scott (1996) metagenesis does not occur in multicellular animals.
Process of Metagenesis
This process of metagenesis occurs in plants. This process of metagenesis is the basis of metagenesis (there are many variations in the future and it also depends on the organism, such as mosses and ferns).
Two single haploid gamete cells, each of which contains n chromosomes (haploid), which after merging become one diploid single-cell zygote (fuse to form a single-celled diploid zygote), which contains n pairs of chromosomes (2n / diploid).
The diploid zygote then undergoes germination or division by mitosis, so that the chromosomes in the cell remain 2n (diploid). The result is a multicellular diploid organism called a sporophyte. It is called a sporophyte because when it matures it produces sporophytes).
When the sporophyte matures, the sporophyte then produces one or more sporangia (singularly called a sporangium). This sporangium is a diploid organ that produces sporocytes (diploid single cells). The process of producing a sporocyte is carried out by means of meiotic division after which the spore cells that produce only half of the chromosomes will be reduced to n (haploid).
After these single spore cells (which are haploid / n) it germinates by mitosis so it will multicellular organisms are formed which are called gametophytes (ie gamete producers when mature). Because the method used is mitosis, the chromosomes in the gametophyte must remain haploid or also n chromosomes.
When the gametophyte matures, it produces one or more gametangia (when singular it is called the gametangium). This gametangium is the organ that produces haploid gametes in plants. Each of these gametangia has a mechanism so that the resulting gametes can or can reach a different type of gamete to be able to fuse into a zygote (and return to the first step of metagenesis).
It needs to be remembered that this is not a re-life cycle that keeps repeating itself, so don't assume that this is something the method of being able to re-make plants young, this is purely as two changes from the method of reproduction for survival kind.
Example of Metagenesis
-
Moss Plant Metagenesis
In mosses, such as mosses, the spores grow into protonema. Protonema grows into a moss plant. Moss plants will produce anteridium or male breeding tools and archegonium or female breeding tools. This organ can be in one plant (one house) or it can be in different plants (two houses). The anteridium will produce sperm, and the archegonium will produce ova (egg cells). That is why, moss plants are called gametophytes or gamete-producing plants. Moss plants are haploid (n).

The meeting of sperm and ovum will produce a zygote which eventually develops into a sporophyte or spore-producing plant. The sporophyte is diploid (2n). In mosses, the sporophyte remains attached to the end of the plant (gametophyte). Spore formation in the sporophyte occurs through division of the spore mother cell within the spongarium.
Fern Metagenesis
Fern spores will grow into prothallium. The prothallium grows to produce male (anteridium) and female (archegonium) reproductive organs. Therefore, the prothallium is referred to as the gametophyte. If the antheridium and archegonium are produced in one prothallium they are called monoecious and if the antheridium and archegonium are produced in different prothallium they are called two-homed.
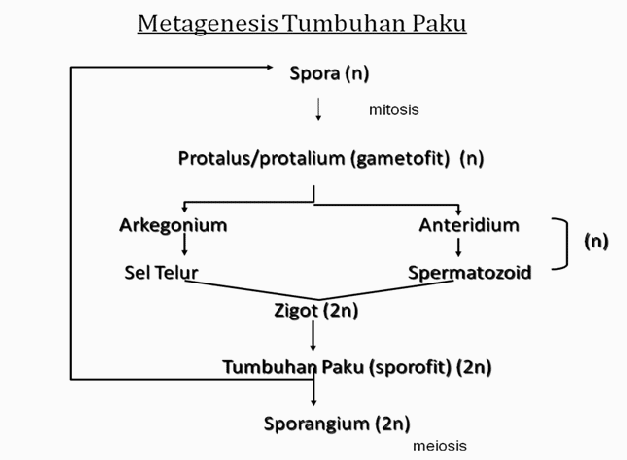
Sperm and ovum produced from the reproductive organs will experience fertilization to become a zygote. The zygote develops into a fern. Mature ferns will have leaves that produce spores called sporophylls. Therefore, ferns are called sporophytes.
Metagenesis of Seed Plants
Seed plants are the sporophyte generation. The female gametophyte generation develops within the ovule and attaches to the parent plant. The development of the male gametophyte begins with the formation of microspores and continues after pollination. The difference between seed plants and ferns is that the gametophyte generation of seed plants is smaller. development is more protected, and life dependence on the mother plant is more tall.

Microspores develop into pollen grains after leaving the spore box. During pollination, pollen that falls on the stigma will develop to form pollen reeds. In the pollen reeds will form sperm cells. In angiosperms, the so-called microgametophyte generation is the pollen tube. Meanwhile, the megagametophyte generation (macrogametophyte) is an institutional bag (embryonic bag).
After fertilization of the ovum by the sperm cell, a zygote is formed which then develops into an embryo in the seed. When the seeds germinate, the embryo will develop into sprouts, then into young plants and mature plants. Mature plants produce flowers, and so their life cycle begins again.
Metagenesis in Jellyfish
Several types of invertebrate animals experience alternation of generations, for example jellyfish. In its life cycle, jellyfish undergo alternation of generations, namely the polyp phase which settles on the bottom of the water and the medusa phase which can swim freely.
Stages of jellyfish metagenesis are as follows.
- Spermatozoids emerge from the mouth of the male medusa and enter the intestines of the female medusa to fertilize the eggs.
- The result of fertilization is a zygote which will develop into a blastula followed by a ciliated larva called a planula.
- The larval planula is formed by external fertilization and will settle on the substrate in a polypoid form known as a scyphistoma.
- The planula grows into a polyp, then the polyp reproduces asexually by forming a medusa and so on.
Jellyfish polyp is a vegetative generation that reproduces asexually by forming buds. Medusa is a generative generation that reproduces sexually by fusion of male and female sex cells.

The difference between metagenesis and metamorphosis
Metagenesis and metamorphosis are two terms related to the growth and life cycle of organisms. Metagenesis is defined as the alternation of sexual and asexual generations of an organism in the life cycle. Metamorphosis is defined as the process in which an organism exhibits a different structural form or different structural stages from the adult organism during normal development.
This is the main difference between metagenesis and metamorphosis. There are two alternative sexual and asexual generations in the life cycle of organisms which show metagenesis whereas there are four different structural forms in the life cycle of organisms that show metamorphosis
Thus the review from About the knowledge.co.id about Metagenesis: Definition, Process, Examples and Explanations, hopefully can add to your insight and knowledge. Thank you for visiting and don't forget to read other articles.
List of contents
Recommendation:
- Definition of Plastids: Function, Structure, Characteristics, Types,… Definition of Plastids: Function, Structure, Characteristics, Types, Classification and Differences with Mitochondria - What is what do you mean by plastids?, On this occasion Se regarding the knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about matters other…
- √ Hydrosphere: Definition, Branches, Cycles, Types and Elements Hydrosphere: Definition, Branches, Cycles, Types and Elements - On this occasion, Around Knowledge will discuss the Hydrosphere. Which in this discussion explains the meaning of the hydrosphere, branches, cycles, types...
- Scope of Psychology: Definition, Kinds, Tasks and… Scope of Psychology: Definition, Kinds, Tasks and Methodology of Psychological Research - What is the scope psychology? On this occasion, Around the Knowledge.co.id will discuss what psychology is and what it is covered it. Let us…
- Moral Intelligence: Understanding According to Experts, Purpose,… Moral Intelligence: Understanding According to Experts, Purpose, Aspects, Components and How to Develop It - What is it what do you mean by moral intelligence and how to build it? discuss it...
- Ant Metamorphosis: Definition, Types of Metamorphosis and Phases… Ant Metamorphosis: Definition, Types of Metamorphosis and Its Stages - What are the stages of Ant Metamorphosis? In the previous discussion, Seputarknowledge.co.id has discussed Metamorphosis, namely: Definition, Phases, Types and For example…
- Respiratory Plant Plants: Definition, Types, Process… Respiratory Organs of Plants: Definition, Types, Respiration Process and Relationship of Respiration with Photosynthesis – Anything and how does the process of breathing plants? Of course…
- Definition of Hydrology and the Hydrological Cycle (Complete) Definition of Hydrology and the Hydrological Cycle (Complete) - The existence of water on Earth is relatively constant, because water is always circulating. This circulation of water is called hydrology. Sometimes somewhere water is available in large quantities,...
- Computer Hardware: How it Works, Types, Examples and… Computer Hardware: How it Works, Types, Examples and Functions - In today's computerized era, we are definitely familiar with computers and their devices. However, some may not know...
- Difference between Spermatogenesis and Oogenesis: Definition and… The Difference between Spermatogenesis and Oogenesis: Definition and Influencing Factors - What are the Differences between Spermatogenesis and Oogenesis? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss Spermatogenesis and Oogenesis along with…
- Example of Cultural Arts Questions for Class 10 (X) SMA/MA/SMK Semester 1… Examples of Class 10 (X) Cultural Arts Questions for SMA/MA/SMK Semesters 1 and 2 (2019 and 2020) - On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss Multiple Choice Class 10 Cultural Arts Questions and Essay…
- Humans As Individual Beings and Social Beings Humans As Individual Beings and Social Beings - Why is that, humans are the most perfect creatures in this universe, because they have reason to think. The word Human comes from…
- Enculturation Is: Understanding According to Experts, Functions,… Enculturation Is: Understanding According to Experts, Function, Media, Impact, Process and Examples - What is it What is the meaning of enculturation? On this occasion, Se regarding the knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course things other…
- Friendship Short Stories: Definition, Writing Tips and Examples Friendship Short Stories: Definition, Writing Tips and Examples - What are Friendship Short Stories like? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss whether it is the Short Story of Friendship and other things about it. Let's see together…
- 74 Definition of Education According to Experts 74 Definition of Education According to Experts – Humans have been educated since they were born into the world until they enter school. The word education is no longer foreign to our ears, because all...
- Historical Text: Definition, Characteristics, Structure, Language Rules… Historical Text: Definition, Characteristics, Structure, Linguistic Rules and Examples - What is meant by Historical Texts? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss what historical texts are and other things other…
- Faith in Qada and Qadar: Understanding, Proof, Wisdom and… Faith in Qada and Qadar: Definition, Proposition, Wisdom and Their Functions - What is meant by Faith in Qada and Qadar?
- Cloning is: Definition, Types, Benefits and Examples Cloning is: Definition, Types, Benefits and Examples - In this discussion we will explain about cloning. Which includes the meaning, types, benefits and examples of cloning with a complete discussion and...
- √ Main Characteristics of the Taxonomy and Life Cycle of Seed Kormophyta… Main Characteristics of the Taxonomy and Life Cycle of Seed Kormophyta (Complete) - Previously I posted a I will now write a related article about the main characteristics of the taxonomy and life cycle of the spore-forming Kormophyta discuss…
- √ Phylogenetic: Definition, Types, Classification and Examples Phylogenetic: Definition, Types, Classification and Examples - On this occasion, Around Knowledge will discuss Phylogenetics. Which in this discussion explains the definition of phylogenetics, types, classification and examples...
- Adsorption: Definition, Working Principle, Types, Factors That… Adsorption: Definition, Working Principle, Types, Influencing Factors and Examples - What is Adsorption?, On this occasion, about the knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course other things as well covered it. Let's see…
- Examples of Scientific Work: Functions and Rules of Language Examples of Scientific Papers: Functions and Rules of Language - What are examples of good and correct forms of writing scientific papers? Previously, Seputar the knowledge.co.id has discussed Scientific Work: Definition, Characteristics, Benefits,…
- Anabolic Reactions: Definition, Photosynthesis Process and… Anabolic Reactions: Definition, Photosynthesis and Chemosynthesis - The body's process of obtaining energy is called metabolism. Metabolism is still divided into 2 namely catabolism and anabolism. On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss what...
- Genetic Engineering: Definition, Process, Types, Benefits,… Genetic Engineering: Definition, Process, Types, Benefits, Strengths and Weaknesses - What is genetic engineering that?, On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things as well covered it. Let us…
- Pencak Silat: Definition, History, Characteristics, Purpose, Techniques,… Pencak Silat: Definition, History, Characteristics, Purpose, Techniques, and Levels - Does anyone know what it is Pencak Silat? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss Pencak Silat and other things other…
- Bacteria and Their Role: Types, Beneficial and… Bacteria and Their Role: Types, Beneficial and Harmful Roles - What are bacteria? Bacteria are single-celled or unicellular organisms, prokaryotes or prokaryotes, microscopic or very small in size. Bacteria contribute...
- √ Definition of Self-Esteem, Aspects, Sources, Components, Factors and… Understanding Self-Esteem, Aspects, Sources, Components, Factors and How to Grow It - In this discussion we will explain about self-esteem. Which includes the notion of self-esteem, the importance of self-esteem, aspects and...
- The Nitrogen Cycle: Definition, Process, Form and Examples The Nitrogen Cycle: Definition, Process, Forms and Examples - What is the nitrogen cycle?, On On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things as well covered it. Let's see together…
- Environmental Speech: Definition, Purpose, Characteristics and… Environmental Speech: Definition, Purpose, Characteristics and Examples - How is the text of environmental speech structured? what's good and right?, On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course things Which…
- Definition of Biotics, Components and Their Functions (Discussion… Definition of Biotics, Components and Their Functions (Full Discussion) – In the environment without us realizing it, there has been a relationship or interaction that occurs continuously every day. There are often changes...
- Factors Inhibiting Social Mobility: Definition, Factors… Inhibiting Factors of Social Mobility: Definition, Driving Factors and Explanations - What is the meaning of social mobility and What are the inhibiting factors? On this occasion, about the knowledge of Knowledge.co.id will discuss it, including nutritional content and naturally…
