Esophageal Function: Definition of the Esophagus, Structure and Its Parts
Esophageal Function: Definition of the Esophagus, Structure and Its Parts – What is the function of the esophagus? At this time About the knowledge.co.id will discuss what Esophageal Function is and other factors. Let's look at the discussion together in the article below to better understand it.
Esophageal Function: Definition of the Esophagus, Structure and Its Parts
The esophagus or esophagus is a part of the digestive organ, which is a tube that connects the pharynx (throat) to the stomach. The esophagus is located between the trachea (windpipe) and the spine. The esophagus passes below the neck, pierces the diaphragm just to the left of the midline, and joins the heart (above) to the end of the stomach.
In adults, the esophagus is between 25 cm (10 inches) long. When a person swallows, the muscular walls of the esophagus contract to push food into the stomach. Glands in the lining of the esophagus produce mucus, which keeps the passageway moist and facilitates swallowing.
When food moves down the esophagus, the soft palate along with a tuft-like tissue at the back of the mouth (uvula) lifts up and closes the passage. nose, and when food moves toward the tracheal lid, the epiglottis will close so that food does not enter the trachea and lungs but food still enters esophagus.
The functions of the Esophagus in Humans include the following:
Passing Food From Mouth To Stomach
This is the basic function of the esophagus or esophagus, in the human neck there are two types of channels, namely the esophagus and throat. The esophagus in this case functions as a pipe for food from the mouth to the stomach, and meanwhile the throat is the respiratory tract that connects the mouth to the lungs.
Produces Peristalsis
In the esophagus alone food is not simply channeled. There are muscles that produce peristalsis so that the walls contract and slowly food is pushed into the stomach.
Prevents Gastric Fill And Fluid Rate
In the stomach during the digestive process, it will produce strong acids, namely hydrochloric acid and various enzymes that are in charge of helping the digestive process. The mixture of the two is called stomach acid. With a narrowing of the sphincter in the esophagus, this can prevent stomach fluids from entering the esophagus due to increased stomach acid levels.
Food Swallowing Phase
Swallowing is the process of carrying food from the mouth to the stomach with a combination of muscle and reflex movements from 3 (three) organs of the digestive system including the esophagus.
There are 3 phases of swallowing in humans, namely:
- Oral Phase, in this phase the food that is chewed in the mouth will be pushed to the back of the pharynx by the movement of the tongue muscles
- Pharyngeal phasel, in the phase where food enters, it stimulates the uvula to cover the nasal cavity and the epiglottis will close the respiratory tract so that food does not enter the lower pharynx and go to the esophagus.
- Esophageal Phase, the entry of food stimulates the occurrence of esophageal peristalsis which will carry food to the gastric sphincter and enter the stomach. After that, the food will be digested and temporarily stored in the stomach.
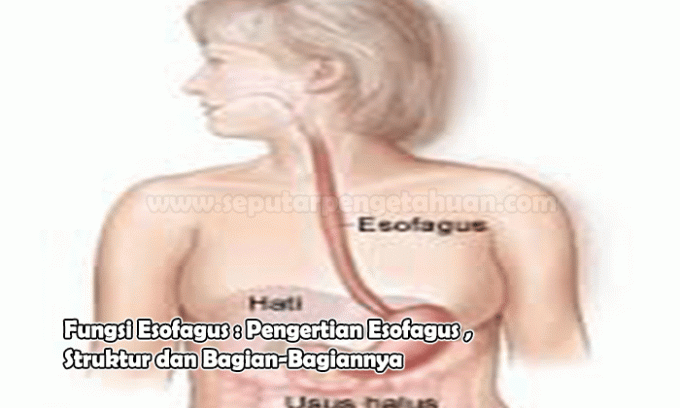
Esophageal Structure
The esophagus is composed of 4 (four) layers of walls, including:
Serous Layer
Is the outermost layer of the esophagus which consists of blood vessels, lymph and nerves. The serosa lining in the esophagus is a connective tissue. The serous layer has small cavities through which serous fluid escapes, which serves as a lubricant for muscle movement.
Muscle Layer
Is a layer of smooth muscle that works involuntarily. There are 2 (two) types of muscle fibers, namely longitudinal (elongated) and circular (circular) muscle fibers. The combination of the contractions of these two types of muscles will produce intestinal peristalsis which functions to break down food and carry it to the next digestive organs.
Submucosa Layer
It is a layer of loose connective tissue that contains blood vessels, lymphatics, nerves and mucous glands. Blood vessels in the submucosa lining of the esophagus play an important role in circulating the food that is absorbed.
Mucosa Layer
Composed of stratified squamous epithelial cells and thin connective tissue. This layer has goblet cells which produce mucus. Under normal circumstances, the esophagus is not resistant to stomach acid so it will feel like pain or burning when there is an abnormality of stomach acid rising to the esophageal mucosa.
Esophageal Parts
The structure of the esophageal tissue is divided into 3 (three) parts, namely:
- Superior Section (upper 1/3 of Esophagus), most of the constituent muscles in this section are skeletal muscles, where these muscles work consciously / can be controlled.
- Mid section (middle 2/3 of esophagus), composed of mixed muscles of skeletal and smooth muscles.
- Inferior Section (lower 3/3 of esophagus), the constituent muscles are smooth muscles that work without us realizing it or cannot be controlled.
Thus the review from About the knowledge.co.id about Esophageal Function, Hope it is useful.
List of contents
Recommendation:
- Nemathelminthes: Definition, Characteristics, Classification, Physiology… Nemathelminthes: Definition, Characteristics, Classification, Physiology and Role - What is Nemathelminthes? In general, nemathelminthes are animals whose entire members consist of various roundworms with an elongated cylindrical body shape, not segmented.
- 13 Anatomy of the Human Body and Its Functions 13 Anatomy of the Human Body and Its Functions - In the branch of biology, there are those who study anatomy, namely biology which studies the internal structure of living things. For this discussion, About Knowledge…
- Explain Trachea Structure: Definition, Function, and Disorders… Explain the structure of the trachea: definition, function, and disorders of the trachea - What is the trachea? The trachea or windpipe is part of the respiratory system in the form of a tube. For more details, on this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id…
- Human Respiratory Organs and Respiratory Mechanisms… Human Respiratory Organs and Respiratory Mechanisms (Complete) - Here we will discuss what are the respiratory organs in the human body complete with their respiratory mechanisms. For those of you who are still in school...
- Human Digestive System: Definition, Anatomy of Organs and… Human Digestive System: Definition, Anatomy of Organs and Disorders - How is the Human Digestive System?, On On this occasion, Seputar Knowledge.co.id will discuss it, including the anatomy of organs and of course other things as well covered it. Let…
- Meristem Network Functions, Definition, Types, Characteristics, Types &… Meristem Network Functions, Definition, Types, Characteristics, Types & Locations - In this discussion we will explain about meristem networks. An explanation that includes the definition of meristem tissue, meristem tissue functions, characteristics...
- Papers: Definition, Characteristics, Functions, Types, Structures, Methods… Papers: Definition, Characteristics, Functions, Types, Structure, How to Make and Examples - What is meant by Papers and how to write them properly and correctly? On this occasion Seputarknowledge.co.id will…
- √ Definition of Joints, Functions, Parts, Structures and Types Understanding Joints, Functions, Parts, Structures and Types - On this occasion, Around Knowledge will discuss the Definition of Joints. Which in this discussion explains the meaning of joints, functions, parts, structures…
- Examples of Flat Shapes: Types, Characteristics and Formulas of Flat Shapes Examples of Flat Shapes: Types, Properties and Formulas of Flat Shapes - What are the examples of Flat Shapes?
- Kingdom Animalia: Definition, Characteristics, Classification and Examples… Kingdom Animalia: Definition, Characteristics, Classification and Examples of Phylums - Is that what Kingdom means Animalia?, On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course other formulas as well covered it. Let…
- Indonesia's Geographical Conditions: Location, Land Condition, System… Geographical Conditions of Indonesia: Location, Land Conditions, Drainage Systems, Weather, Population Conditions and Flora Distribution Fauna - How is the Geographical Condition in Indonesia? Condition…
- Bone Formation Process: Process Differences Each Age and… Bone Formation Process: Differences in the Process of Each Age and Decline in Bone Function -How is the process of formation What is the bone? On this occasion, Around the Knowledge.co.id will discuss what the Reinforcement Process is and other explanations about it. Let us…
- Friendship Short Stories: Definition, Writing Tips and Examples Friendship Short Stories: Definition, Writing Tips and Examples - What are Friendship Short Stories like? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss whether it is the Short Story of Friendship and other things about it. Let's see together…
- Optical Instruments: Definition, Functions, Types and Parts Optical Instruments: Definition, Functions, Types and Parts - What are optical devices and what are their types? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course other things that...
- √ Definition of the Large Intestine, Its Structure, Functions and Parts… Definition of the Large Intestine, Structure, Function and Parts (Complete) - This time around the knowledge.co.id will again discuss the parts of the human body, namely the large intestine. The large intestine is an important organ for digestion…
- √ Definition of Echinodermata, Characteristics, Structure and… Definition of Echinodermata, Characteristics, Structure and Classification - On this occasion, Around Knowledge will discuss about Echinoderms. Which in this discussion explains the meaning of Echinodermata, characteristics, organ systems, structure, reproduction,…
- Motivational short stories: definition, writing tips and examples Motivational Short Stories: Definition, Writing Tips and Examples - What is a Motivational Short Story?, On On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss whether it is the Short Story of Friendship and other things about it. Let's see…
- Faith in Qada and Qadar: Understanding, Proof, Wisdom and… Faith in Qada and Qadar: Definition, Proposition, Wisdom and Their Functions - What is meant by Faith in Qada and Qadar?
- LHO Text: Definition, Characteristics, Characteristics, Purpose, Functions,… LHO Text: Definition, Characteristics, Characteristics, Purpose, Function, Structure, Linguistic Rules and Examples - What is what do you mean by LHO Text or Observation Report Text? On this occasion About knowledge.co.id…
- 74 Definition of Education According to Experts 74 Definition of Education According to Experts – Humans have been educated since they were born into the world until they enter school. The word education is no longer foreign to our ears, because all...
- Plant Strengthening Tissues: Definition, Collenchyma,… Plant Strengthening Tissues: Definition, Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma, Characteristics, Types and Structures - What are the tissues plant boosters and the differences? other thing…
- √ Stem Definition, Functions, Properties, Types & Stem Structures… Stem Definition, Functions, Properties, Types & Stem Structure (Complete) - In this discussion we will explain about stems. What is a stem? what are the functions, the types of rods, and the structure of the stem will be...
- √ Ribs: Definition, Number, Structure and Functions Ribs: Definition, Number, Structure and Function - On this occasion, Around Knowledge will discuss ribs. Which in the discussion this time explains the meaning of the ribs, the division...
- Calf Bone: Definition, Functions and Characteristics Calf Bones: Definition, Functions and Characteristics - On this occasion, Around the Knowledge.co.id will discuss the calf bones, their functions and of course other things that also cover them. Let's look at the discussion together in the article on…
- √ Left Brain: Definition, Function, Structure and How It Works Left Brain: Definition, Function, Structure and How It Works - On this occasion, Around Knowledge will discuss about the Left Brain. Which in this discussion explains the meaning of the left brain,…
- Ligaments Are: Definition, Anatomy, Structure, Functions,… What is a Ligament: Definition, Anatomy, Structure, Function, Types, Mechanism of Action - What is a Ligament? Ligaments are part of the fibrous connective tissue that allows joints and bones to join. To know more about it, let's…
- Definition of Floor Gymnastics: History, Types, Elements and… Definition of Floor Gymnastics: History, Types, Elements and Benefits of Floor Gymnastics - What is Floor Gymnastics and examples? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss Floor Gymnastics...
- Large Blood Circulation: Definition, Types, Components and… Great Blood Circulation: Definition, Types, Components and Functions - What is large blood circulation?, On On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it, including types, components and of course other things which also…
- Pencak Silat: Definition, History, Characteristics, Purpose, Techniques,… Pencak Silat: Definition, History, Characteristics, Purpose, Techniques, and Levels - Does anyone know what it is Pencak Silat? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss Pencak Silat and other things other…
- Islamic Words of Wisdom Islamic Words of Wisdom - On this occasion, SeputihKnowledge.co.id will discuss Islamic Words of Wisdom and examples. Let's look at the discussion together in the article below to get more...
