Plant Strengthening Tissues: Definition, Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma, Characteristics, Types and Structures
Plant Strengthening Tissues: Definition, Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma, Characteristics, Types and Structures – What are the plant reinforcement tissues and their differences?, On this occasion About the knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things that also cover it. Let's look at the discussion together in the article below to better understand it.
Plant Strengthening Tissues: Definition, Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma, Characteristics, Types and Structures
Reinforcing network or often referred to as supporting network is one of the constituent networks Plants that function to strengthen or support the plant body so that plants can stand upright.
Based on the shape and nature, there are 2 (two) plant supporting tissues, namely collenchyma tissue and sclerenchyma tissue.
Collenchyma Network
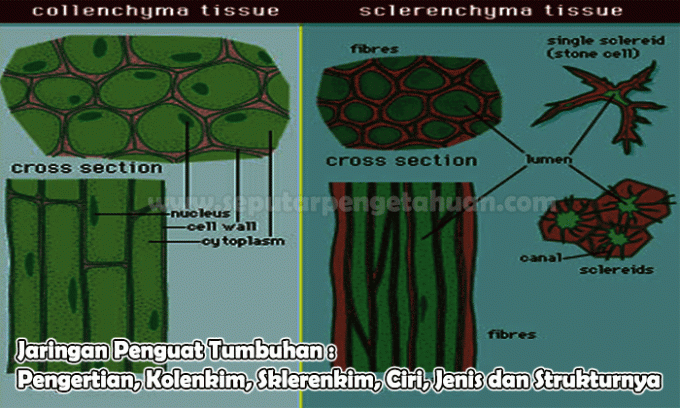
The definition of collenchyma tissue is a network that functions as a strengthening or supporting tissue in plant organs that are still actively growing and developing.
Collenchyma tissue is composed of living cells, has an elongated shape and generally has walls with irregular thickening. The thickening of the walls mainly occurs at the corners and consists of a thick cellulose material.
Collenchyma tissue only has a primary wall which is soft, flexible and not lignified. The cell contents may contain tannins and chloroplasts. Collenchyma can be found on stems, leaves, flowers, and fruits and roots that are exposed to sunlight.
Characteristics of Collenchyma Network
Characteristics or features of collenchyma tissue, namely:
- Has an elongated shape parallel to the center of the organ where the collenchyma is located.
- Collenchyma cell walls are not lignified, but contain cellulose, pectin and hemicellulose.
- Some collenchyma cells have chloroplasts so they can function to support photosynthesis.
- Usually collenchyma cells experience local thickening.
-
Kinds of Colenchyma Network
Based on the shape of the thickening and its location, the types of collenchyma tissue can be divided into:
- Angular collenchyma
Angular collenchyma (corner) is collenchyma tissue that is thickened at the corners. This collenchyma tissue can be found in leaves, for example the leaves of the celery plant. - Lamellar collenchyma
Lamellar collenchyma (tangential) is collenchyma tissue that is thickened in the tangential or spreading part of the cell wall. This tissue supports the strength of the outer layers of plant structures, such as stems or leaves. - Annular collenchyma
Annular collenchyma is collenchyma tissue whose cell walls are evenly thickened. This type of collenchyma is rarely found because it is only found in carrot leaves and some vines. - Lacunar collenchyma
Lacunar collenchyma (lacunate) is collenchyma tissue that has thickened on the surface of the space between cells.
- Angular collenchyma
-
Location of collenchyma in plants
Collenchyma tissue can be found in stems, leaves, as well as in flower and fruit parts. In stems, collenchyma may form fully cylindrical or arranged into bundles that extend parallel to the axis of the stem. In leaves, collenchyma is found on both sides of the main leaf vein or on one side only, and is also present along the edge of the leaf.
Rarely found on the roots that are in the ground. Only occasionally are plants whose roots rise above the ground to find collenchyma tissue, because the formation of collenchyma tissue occurs when exposed to sunlight. And usually there is collenchyma directly under the epidermis.
Collenchyma structure
Sizes and shapes vary. It can be short prisms or long elliptical like fibers with tapered ends and there is an intermediate form between the two forms.
According to Muller, there are three main forms due to thickening of the collenchyma cell walls:
- Angle collenchyma or angular collenchyma. with longitudinal thickening at the corners of the cells. In cross sections, corner thickening is seen where three or more cells meet. For example on the stems of Solanum tuberosum and on Salvia.
- Plate or plank collenchyma, with thickening especially on the tangential walls. For example, in the cortex of the trunk of Sambucus nigra
- Lacunar collenchyma, which is similar to corner collenchyma, but contains many intercellular spaces around which wall thickening occurs. For example on Ambrosia stems.
- Duchaigne (1955 in Fahn, 1982) provides an additional type of collenchyma, namely ring (annular) collenchyma.
-
Collenchyma cell arrangement
Can be found on stems, leaves and on the flowers, fruits and roots, especially if the roots are exposed to light. The collenchyma cell wall is an example of a primary wall that expands and thickens as the cell grows larger.
The collenchyma walls are mainly composed of cellulose and pectin compounds and contain a lot of water. The fresh material of the collenchyma walls contains about 67% water. Fahn (1982) stated that according to Roelofsen collenchyma cell walls contain 45% pectin, 35% hemicellulose and about 20% cellulose.
Collenchyma cells have active protoplasts which are capable of eliminating wall thickening when the cells are stimulated to divide as when the cells form cork cambium. Collenchyma such as parenchyma can contain chloroplasts so that it can carry out photosynthesis.
Sclerenchyma Network
Sclerenchyma tissue is a network of reinforcement or supporting tissue with a thick secondary wall because it contains lignin. This sclerenchyma tissue is only found in plant organs that no longer carry out growth and development.
Sclerenchyma tissue consists of sclerenchyma fibers (sclerenchyma fibers) and sclereids (stone cells). Sclerenchyma fibers are long, slender, and are found in strands or circles. Sclerenchyma fibers can be found in flax, Agave, and Hibiscus sabdariffa fibers.
Meanwhile, sclereids are shorter in size and have an irregular shape. Actually sclereids can be found in all parts of the plant, especially the bark, sieve tubes and seeds. The coconut shell is almost entirely composed of sclereids.
Stone cells in fruit can provide characteristics, for example a sandy structure on the skin of the fruit and pear flesh or sandy grains on the flesh of a guava.
The function of the sclerenchyma tissue is to strengthen the parts of plants that are mature or not undergo growth and development as well as protect the parts or soft organs that are in inside. For example in coconut shells, castor seed shells and walnuts.
Sclerenchyma tissue is a supporting tissue found in plant organs that are no longer experiencing growth and development or in mature plants. Sclerenchyma tissue consists of fibers (sclerenchyma fibers) and sclereids (stone cells).
Sclerenchyma tissue is a mechanical tissue that is only found in plant organs that no longer carry out growth and development or fixed plant organs. Sclerenchyma functions to withstand all pressures so that it can protect weaker tissues.
Sclerenchyma does not contain protoplasts, so the cells are dead. The cell wall is thick due to the previous secondary thickening which consists of lignin.
-
Characteristics of cells in sclerenchyma tissue
- The cells are dead with thick cell walls
- Thick secondary wall, generally composed of lignin
- It is rubbery, generally no longer contains chloroplasts
- The cells are more rigid than collenchyma, sclerechyma cells cannot elongate
-
Types of Sclerenchyma Tissue
-
Sclerenchyma Fibers (Fibers)
-
The sclerenchyma fibers consist of cells that are ± 2 mm in length and the sides are pointed at the ends. Sclerenchyma fibers are dead cells. The cell wall is thickened from wood and contains cellulose lamellae so that the cell lumen is narrow.
These fibers are in the form of polygons, namely pentagons or hexagons. The nooks are narrow which are shaped like narrow sloping channels. Sclerenchyma fibers in plants are formed at the same time when the growth of organs in plants stops.
Sclerenchyma fibers are found in separate strands or in whorls in the cortex and phloem, in scattered groups in the xylem and phloem. In Gramineae, the sclerenchyma fibers are arranged in a circular, squiggly system connected to the epidermis.
There are two types of sclerenchyma fibers, namely as follows.
- Fiber Outside the Xylem (Extraxilaris)
Some extraxilaris fibers are lignified and some are not. This fiber can be used to make rope, jute sacks, and textile base materials for clothing.
- Xylem Fiber (Xilari)
This type of fiber is the main component of wood because its walls contain lignin which makes the walls hard and stiff.
-
Stone Cells (Sclereids)
-
Sclereids are found in plant parts, including in the cortex, phloem, fruit, and seeds. The sclereid wall is composed of cellulose which contains a thick and hard lignin substance. In some plants, suberin and cutin are sometimes found.
The cells have narrow nodules and the slits are round, forming a canal called a nodal canal. The cell lumen is very narrow due to thickening of the cell wall.
Sclereids may be found singly or in small groups between cells, such as granules such as sand on the guava fruit flesh or a continuous mass such as on a coconut shell hard.
Thus the review from About the knowledge.co.id about Plant Strengthening Network , hopefully can add to your insight and knowledge. Thank you for visiting and don't forget to read other articles.
List of contents
Recommendation:
- Definition of the Cytoskeleton, Function and Structure (Complete) Definition of the Cytoskeleton, Function and Structure (Complete) - Meeting again with Around Knowledge, now we will discuss the cytoskeleton. What is the cytoskeleton? So for those who don't know and who want to know, let's...
- Understanding Reptiles, Structure, Body Functions and Characteristics Definition of Reptiles, Structure, Body Functions and Characteristics - Living things that live on this earth have various types and their habitats. Some are in the water, in the air, on land, as for those who are...
- Faith in Qada and Qadar: Understanding, Proof, Wisdom and… Faith in Qada and Qadar: Definition, Proposition, Wisdom and Their Functions - What is meant by Faith in Qada and Qadar?
- Physical Fitness: Definition, Components, Concepts, Elements,… Physical Fitness: Definition, Components, Concepts, Elements, Purpose, Benefits and Forms of Exercise - What's in What do you mean by physical fitness? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss fitness Physical and…
- Lymph Circulatory System Functions: Constituent Components And… Functions of the Lymph Circulatory System: Composing Components and Their Anatomy - What is the Function of the Lymph Circulatory System Bening?, On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things that also…
- Class 6 Farewell Speech Text: Main Contents, Characteristics,… Farewell Speech Text for Class 6: Main Contents, Characteristics, Purpose and Examples of Speeches - What is the composition of the text of farewell speech for class 6 which is good and true and touching?
- Definition of White Blood Cells (Leukocytes), Functions, Types and… Definition of White Blood Cells (Leukocytes), Functions, Types and Characteristics - This time we will discuss about blood. Blood is an important thing for humans, if you've ever heard that someone is...
- Example of Cultural Arts Questions for Class 10 (X) SMA/MA/SMK Semester 1… Examples of Class 10 (X) Cultural Arts Questions for SMA/MA/SMK Semesters 1 and 2 (2019 and 2020) - On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss Multiple Choice Class 10 Cultural Arts Questions and Essay…
- The Political Life of the Majapahit Empire: Early History and… The Political Life of the Majapahit Kingdom: Early History and Legacy - How was the Political Life of the Kingdom Majapahit? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss the Majapahit Kingdom and other things covered it. Let's look at the discussion together...
- Morphemes Are: Classification, Morphs and Allomorphs and… Morphemes Are: Classification, Morphs and Allomorphs and Examples - What is a morpheme?, On On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things as well covered it. Let…
- Optical Instruments: Definition, Functions, Types and Parts Optical Instruments: Definition, Functions, Types and Parts - What are optical devices and what are their types? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course other things that...
- Pythagoras: History, Theorem Formulas and Example Problems Pythagoras: History, Theorem Formulas and Example Problems - Who is Pythagoras with his Theorem? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss what Pythagoras is with formulas and examples the question. Let us…
- 17 Benefits of Midnight Prayer and Its Miracles (Discussion… 17 Benefits of Midnight Prayer and Its Miracles (Full Discussion) – As Muslims, we certainly want to do a lot of good deeds and endeavor to Allah SWT. Everyone competes in fulfilling his desire to be able to...
- 74 Definition of Education According to Experts 74 Definition of Education According to Experts – Humans have been educated since they were born into the world until they enter school. The word education is no longer foreign to our ears, because all...
- Kutai Kingdom: Founder, Lineage, Heyday and… Kutai Kingdom: Founder, Lineage, Heyday and Fall and Legacy - What is the history of the kingdom Kutai, which is located in Kalimantan? On this occasion, Se regarding the knowledge.co.id will discuss the kingdom of Kutai And…
- Vacuoles Are: Characteristics, Functions, Structures and… Vacuoles Are: Characteristics, Functions, Structures and Types - Is that what is called a vacuole plants and animals?, On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about matter…
- Papers: Definition, Characteristics, Functions, Types, Structures, Methods… Papers: Definition, Characteristics, Functions, Types, Structure, How to Make and Examples - What is meant by Papers and how to write them properly and correctly? On this occasion Seputarknowledge.co.id will…
- Connective Tissue: Definition, Functions, Characteristics, Types, Location &… Connective Tissue: Definition, Functions, Characteristics, Types, Location & Composition - In this discussion we will explain about connective tissue. Which includes the understanding of connective tissue, function, characteristics, types, tissue constituents.
- √ Definition of Plant Tissue, Structure, Characteristics, Functions &… Definition of Plant Tissue, Structure, Characteristics, Functions & Types - On this occasion Around Knowledge will discuss Plant Tissues. Which in the discussion this time is one of the materials for…
- Network Topology: Definition, Types and Characteristics Network Topology: Definition, Types and Characteristics - What is a network topology? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss this and of course other things as well covered it. Let's take a look at the discussion on...
- √ Differences between Animal Cells and Plant Cells (Discuss Completely) Differences between Animal Cells and Plant Cells (Full Discussion) - On this occasion, Around Knowledge will discuss the differences between animal cells and plant cells. Which in this discussion explains the difference…
- Table Tennis: Definition, History, Techniques, Equipment,… Table Tennis: Definition, History, Techniques, Equipment, Rules, Types of Strokes and Scoring Systems - What do you know about Table Tennis? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss whether…
- Cartesian Coordinates: Definition, System, Diagram and Examples… Cartesian Coordinates: Definition, Systems, Diagrams and Example Problems - What do you mean by Cartesian coordinates ?On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss Cartesian coordinates and other things covers it.…
- Preface: Definition, Structure and Examples Preface: Definition, Structure and Examples - How to write a good Preface ?On this occasion, Around the Knowledge.co.id will discuss what is the Preface and other things about it. Let's see…
- Kingdom Animalia: Definition, Characteristics, Classification and Examples… Kingdom Animalia: Definition, Characteristics, Classification and Examples of Phylums - Is that what Kingdom means Animalia?, On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course other formulas as well covered it. Let…
- Standby Scout Material: Ranks, Honor Codes and Requirements… Standby Scout Materials: Ranks, Honor Codes and General Proficiency Requirements - What are the materials for alert level scouts? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it, including the level of alert scouts,…
- Prayer and Dhikr After Prayer Prayer and Dhikr After Prayer - How are the readings of Prayer and Dhikr after prayer? Let's look at the discussion together...
- Definition of Plastids: Function, Structure, Characteristics, Types,… Definition of Plastids: Function, Structure, Characteristics, Types, Classification and Differences with Mitochondria - What is what do you mean by plastids?, On this occasion Se regarding the knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about matters other…
- Nutrition: Definition, Types, Kinds and Benefits Nutrition: Definition, Types, Kinds and Benefits - In the body of living things there are lots of organs in it that work continuously with one another. And when someone…
- High Jump: Definition, History, Style, Technique, Rules… High Jump: Definition, History, Style, Technique, Rules, Stages and Forms of Course - Is it a sport High Jump? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss High Jump and other things Which…
