√ Definition of Heat, Type, Formula, Capacity and Displacement
Definition of Heat, Type, Formula, Capacity and Displacement – In this discussion, we will explain about heat. Which includes the definition of heat, specific heat, heat formula, heat capacity and heat transfer which are discussed in full and lightly. For more details, please see the review below carefully.
Definition of Heat, Type, Formula, Capacity and Displacement
Let's discuss the definition of heat first carefully.
Definition of Calor
Heat is a form of energy that can be transferred from one object to another because there is a temperature difference. When two objects that have different temperatures are brought together, heat will flow or move from the object with a higher temperature to the object with a lower temperature.
An example is when we mix cold water with hot water, we will get warm water. Many do not know the difference between temperature and heat. Temperature is a measured value on a thermometer, while heat is energy that flows from one object to another.
Calorie Formulas and Units
The formula and unit of heat, namely, the unit of heat is the calorie (cal) or joule (J). Calories are the number of calories needed to heat 1 gram of water to 1 oC. 1 calorie = 4.2 joules. 1 Joule = 0.24 calories
The Calor formula is:
Q = m. c. ∆T
With description:
Q = Heat (J)
M = Mass of object (kg)
c = Specific Heat (J Kg oC)
∆T= temperature change (oC)
Heat and Changes in Matter
Heat can change the temperature of a substance
Basically, every object whose temperature is more than absolute zero, then the object has heat. This content will determine the temperature of the object. If the object is heated, then the object receives additional heat making its temperature increase or increase. Meanwhile, if the object is cooled, then the object releases heat making its temperature decrease.
Heat can change the state of matter
Some objects if given heat in a certain unit, then the object will experience a change in form. An example is ice being heated (given heat), the ice (solid form) will turn into liquid (gas form), and if the heating continues, the water will also turn into gas. The point at which a substance will change form to become a liquid point substance or the melting point of an object.
Specific Heat And Heat Capacity

According to the research, it was found that if heat is applied to two different objects, they will also get different temperatures. For example, when oil and water are heated to the same temperature, the oil will have a temperature change that is twice as large as water.
This is due to differences in the specific heat of an object. The specific heat of an object is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of the object's mass to 1 oC, the unit of specific heat is heat/gram oCelsius or in the international system is defined by Joulse / kgoCelsius. Heat can be written in the following equation:
Information:
Q = Heat (J)
m = Mass of object (kg)
c = Specific Heat ( J Kg oC)
ΔT= Change in temperature (oC)
While the heat capacity is the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of a certain substance by 1 degree Celsius. If the heat Q produces t, then the heat capacity can be formulated as follows
Heat Transfer
Heat transfer occurs from a high temperature object to a low temperature object. There are three types of heat transfer that can occur, including:
Heat Transfer By Conduction
Transfer of heat by passing an intermediate substance (metal) without being accompanied by permanent displacement of the particles of that substance. For example, when heating one end of the metal, the other end of the metal will also heat up, this is because heat transfer occurs from high temperature to low temperature.
When heating one end of the metal, the particles on the metal end will cause vibrations to occur in other particles that are connected to it. So that all the metal particles will vibrate even though only one end of the metal is heated, this will stimulate heat transfer.
Heat Transfer By Convection
Heat transfer by convection is the transfer of heat through a substance accompanied by the movement of parts of the substance. Convection can occur in liquids or gases. There are two types of heat transfer by convection, including:
-
Scientific Convection
Natural convection is convection that is influenced by buoyant forces without external factors, and is caused by the presence of different types of objects. For example, when heating water, the density of hot water particles will rise away from the fire and be replaced by other water particles with a lower temperature. This process makes all the particles of the substance will be perfectly hot -
Forced Convection
Forced convection, namely convection that occurs due to the influence of external factors (eg pressure), and heat transfer is carried out by force or deliberately. Which means heat is forced to go where it wants to go with the help of external factors such as pressure, for example on a fan that will bring cold air to a hot place, and like a radiator on a car that has a cooling system machine.
Radiation Heat Transfer
Radiation heat transfer is a heat transfer process that does not use an intermediary substance. Radiation heat transfer is not the same as conduction and convection. In radiation, for heat transfer to occur, the two objects do not always have to meet because heat can move without an intermediary substance. Which means that heat will be emitted in all directions by the heat source, and will flow in all directions. For example, when we are with a bonfire from any angle, we will still feel the warmth from the source of the fire. Another example is the sun's heat that reaches the earth and other planets.
Prevention of Heat Transfer
Heat transfer by convection, conduction and radiation can be prevented by isolating the room. Like for example a thermos is used to keep the water temperature hot by preventing heat transfer.
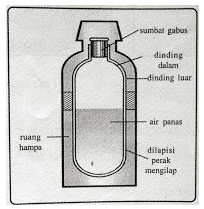
Calorimeter

The calorimeter is composed of two vessels of copper and copper whose heat type is unknown. The small vessel is placed in another larger vessel. So that the two vessels do not come into contact, an insulator is placed on the two vessels as a heat insulating material, for example cork. This insulating material is useful for holding back the heat that is in the calorimeter so it doesn't come out and also no heat enters from the outside.
Generally the lid used is made of wood which can also be used as a good insulator. In general, there are two holes whose function is to place the thermometer and stirrer. When a metal sample is introduced into the calorimeter, the water in it does not have to be stirred so that the system can reach thermal equilibrium quickly. This stirring rod is made of the same material as the calorimeter vessel.
Thus has been explained about Definition of Heat, Type, Formula, Capacity and Displacement, hopefully can add to your insight and knowledge. Thank you for visiting and don't forget to read other articles.
List of contents
Recommendation:
- √ Definition of the Solar System, Theory Formed and Its Structure… Definition of the Solar System, Formed Theory and Structure (Complete) - In this discussion we will explain about the solar system. Which includes the understanding of the solar system, the theory of the formation of the solar system, and the arrangement of the solar system...
- √ Definition of Islamic Banks, History, Functions, Purpose, Characteristics,… Definition of Islamic Banks, History, Functions, Purpose, Characteristics, Types and Products - In this discussion we will explain about Islamic Banks. Which includes the meaning, history, function, characteristics, types and products of…
- Ijarah Law: Definition, Legal Basis, Requirements, Pillars, Types of… Ijarah Law: Definition, Legal Basis, Terms, Pillars, Types and Terms - What is Ijarah law and basically?, On this occasion Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about it other…
- Physical Fitness: Definition, Components, Concepts, Elements,… Physical Fitness: Definition, Components, Concepts, Elements, Purpose, Benefits and Forms of Exercise - What's in What do you mean by physical fitness? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss fitness Physical and…
- Where Does Solar Energy Come From?: Geographic Layers… Where Does the Sun's Energy Come From?: Geographic Layers of the Sun and Thermonuclear Fusion Reactions - How Does the Sun Produce Energy? On this occasion, Around the Knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course things which also…
- Islamic Words of Wisdom Islamic Words of Wisdom - On this occasion, SeputihKnowledge.co.id will discuss Islamic Words of Wisdom and examples. Let's look at the discussion together in the article below to get more...
- Sharia Accounting: Understanding According to Experts, Basic… Syari'ah Accounting: Understanding According to Experts, Legal Basis, Characteristics, Purpose, Principles, Characteristics And The advantages - What is sharia accounting and its advantages? discuss it and...
- √ Definition of Expansion in Length, Formula, Area and Volume of Substance… Definition of Long Expansion, Formulas, Area and Volume of Solids - In this discussion we will explain about long expansion. Which includes the notion of long expansion, long expansion formulas, area, volume of matter...
- Indonesia's Geographical Conditions: Location, Land Condition, System… Geographical Conditions of Indonesia: Location, Land Conditions, Drainage Systems, Weather, Population Conditions and Flora Distribution Fauna - How is the Geographical Condition in Indonesia? Condition…
- Types of Drones, Terms, Parts, Basic Principles And… Types of Drones, Terms, Parts, Basic Principles and Movement - What are the types of drones and function?, On this occasion Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course other things Also…
- LHO Text: Definition, Characteristics, Characteristics, Purpose, Functions,… LHO Text: Definition, Characteristics, Characteristics, Purpose, Function, Structure, Linguistic Rules and Examples - What is what do you mean by LHO Text or Observation Report Text? On this occasion About knowledge.co.id…
- Vector: Definition, Material, Formulas and Example Problems Vector: Definition, Material, Formulas and Example Problems - What is meant by Vector in operation mathematics? On this occasion, Around the Knowledge.co.id will discuss vectors and other matters about it.…
- Factors Inhibiting Social Mobility: Definition, Factors… Inhibiting Factors of Social Mobility: Definition, Driving Factors and Explanations - What is the meaning of social mobility and What are the inhibiting factors? On this occasion, about the knowledge of Knowledge.co.id will discuss it, including nutritional content and naturally…
- Specific Gravity: Definition, Formula, Use and Difference… Specific Gravity: Definition, Formula, Use and Difference with Density - What is meant by Specific Gravity and What is the Unit Formula? discuss it...
- The Collapse of the Kediri Kingdom: History and Legacy The Fall of the Kediri Kingdom: History and Legacy - The Kediri Kingdom or the Kadiri Kingdom or the Panjalu Kingdom was a kingdom that existed in East Java between 1042-1222. The kingdom is in the city…
- Preface: Definition, Structure and Examples Preface: Definition, Structure and Examples - How to write a good Preface ?On this occasion, Around the Knowledge.co.id will discuss what is the Preface and other things about it. Let's see…
- Boyle's Law: Definition, Formulas, Applications and Examples… Boyle's Law: Definition, Formulas, Applications and Examples of Problems - In this discussion we will explain about Boyle's law. Which includes the meaning of Boyle's law, the Boyle's law formula, the application of…
- Three Variable Linear Equation System: Features, Components,… System of Three Variable Linear Equations: Features, Components, Solving Methods and Example Problems - What is in what do you mean by a system of three-variable equations? On this occasion, Se regarding the knowledge.co.id will discuss it...
- Computer Hardware: How it Works, Types, Examples and… Computer Hardware: How it Works, Types, Examples and Functions - In today's computerized era, we are definitely familiar with computers and their devices. However, some may not know...
- √ Definition of Black Body Radiation, Heat Radiation, Formulas &… Definition of Black Body Radiation, Heat Radiation, Formulas & Example Problems - In this discussion we will explain about black body radiation. Which includes the notion of black body radiation, heat radiation, the formula...
- √ Definition of Electric Current, Formulas, Examples of Current Strength Problems… Definition of Electric Current Strength, Formulas, Examples of Electric Current Strength Problems - In this discussion we will explain about electric current strength. Which includes the definition of strong electric current, strong current formula…
- √ Tanjung: Definition, Benefits, Characteristics and Examples Tanjung: Definition, Benefits, Characteristics and Examples - On this occasion, About Knowledge will discuss Tanjung. Which in this discussion explains the meaning of the cape, the benefits of the cape, the characteristics and...
- Alternative Energy: Understanding According to Experts, Characteristics,… Alternative Energy: Understanding According to Experts, Characteristics, Benefits, Terms and Types - What is energy alternative?, On this occasion Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things Also…
- Characteristics of Planets: Types of Planets and Their Characteristics Characteristics of Planets: Types of Planets and Their Characteristics - What are the characteristics that a planet must have Planet?, On this occasion, Around the Knowledge.co.id will discuss it, including objectives, examples and naturally…
- Examples of Flat Shapes: Types, Characteristics and Formulas of Flat Shapes Examples of Flat Shapes: Types, Properties and Formulas of Flat Shapes - What are the examples of Flat Shapes?
- √ Definition of the Sun, Structure, Layers, Spectrum &… Definition of the Sun, Structure, Layers, Spectrum & Benefits - In this discussion we will explain about the sun. Which includes the meaning of the sun, the composition of the elements of the sun, the layers of the sun, the sun's light spectrum and the benefits...
- Short Recount Text Example: Definition, Characteristics, Types and… Short Recount Text Example: Definition, Characteristics, Types and Structure of Recount Text - What is meant with recount text and what kind of example? discuss…
- Exhibition Purpose: Definition, Functions, Benefits, Types, Elements… Exhibition Purpose: Definition, Functions, Benefits, Types, Elements and Principles of Exhibition - What is meant by an exhibition or exhibition? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss what an exhibition is and what…
- 31 Benefits of Tomatoes for Skin Health & Beauty 31 Benefits of Tomatoes for Health & Facial Skin Beauty - Tomatoes are one of the plants found in South America, tomatoes are in the family of green or red peppers, potatoes. Amongst the community…
- √ Definition of Chemical Subatomic Particles, Parts and Types… Definition of Chemical Subatomic Particles, Parts and Types (Complete) - In this discussion we will explain Chemical Subatomic Particles. Which includes the understanding of chemical subatomic particles, parts of subatomic particles and types of particles...
