Sound Is: Definition, Terms, Speed, Characteristics and Types
Sound Is: Definition, Terms, Speed, Characteristics and Types - On this occasion About Knowledge will discuss about Sound. Which in this discussion explains the meaning of sound, terms, speed, nature, type and formula for the speed of its propagation. For more details, see the following article.
Sound Is: Definition, Terms, Speed, Characteristics and Types
Sound is part of one type of wave that can be heard by the sense of hearing (ears). Sound or sound is a mechanical compression or longitudinal wave that propagates through the medium. The medium (intermediate substance) can be a liquid, solid or gas. So, sound waves can propagate in water, coal, air and so on.
Definition of Sound
The definition of sound is a type of wave in physics, namely longitudinal waves which can be felt by the sense of hearing (ears). In physics, the definition of sound is something that is produced by a vibrating object. An object that can produce a sound is called a sound source.
The source of the vibrating sound will also vibrate the air molecules around it. Therefore, the condition for the occurrence of sound is the existence of two vibrating objects. In this sound propagation also requires a medium, you can hear the sound if there is a medium that can propagate the sound.
Sound Occurrence Process
Quoted from the book Arif Smart Elementary School Grade 4, sound comes from vibrating objects. Examples are like, the human vocal cords, the harmonica that is blown, the drum that is beaten, the guitar that is plucked, and many more.
The vibrations will also cause sound waves in the air. The stronger the object vibrates, the stronger the sound it produces. Conversely, if the weaker the object vibrates, the weaker the sound that will be generated by the object.
The sound that is in the air will be caught by the earlobe. Furthermore, this sound will enter the ear canal and then hit the eardrum to vibrate. The vibrations will be transmitted to the hammer, anvil, stirrup and move towards the cochlea.
This vibration will also make the cochlea vibrate and the hair cells curl. Next, namely, the auditory nerve sends signals to the brain. Next, the brain will interpret the signal as sound.
Sound can also be recognized by certain characteristics, including:
- This is a longitudinal wave.
- Cannot propagate in a vacuum.
- Disa experiences resonance and reflection.
- The propagation speed is affected by the density of the propagation medium.
Sound Terms
The following are conditions for the occurrence and sound of sound, namely:
- There is a vibrating object (source of sound).
- There is a medium that propagates sound.
- There is a receiver within range of the sound source.
Speed of Sound
Sound has a limited propagation speed, sound also requires time to move from one place to another. Fast sound propagation is actually not too big. The speed of sound is much smaller when compared to the speed of light. Even now people have also been able to make planes that can fly several times faster than the speed of sound.
Sound Formulas
The speed of sound is also often formulated as follows:
v=s/t
v = speed of sound (m/s), s = distance from source to observer (m), t = time interval (s)
However, if the frequency, wavelength or period are known, the wave propagation formula that can be used is:
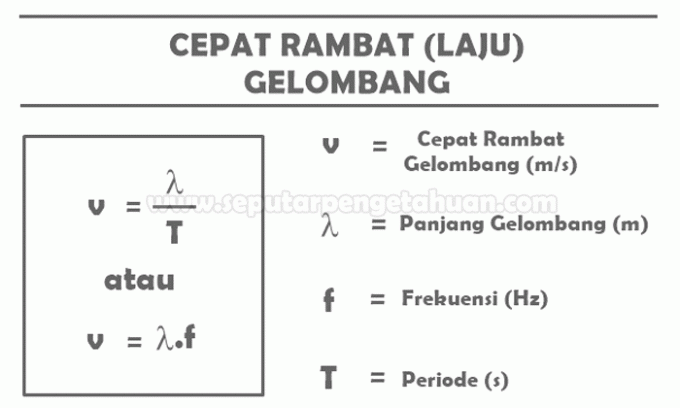
Notes:
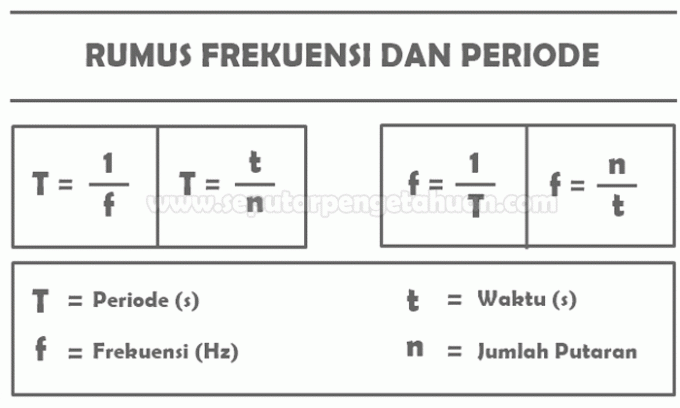
- Frequency (f), is the number of sound waves that pass a certain point in one second. This frequency is denoted by the letter f and the unit of frequency is Hertz (Hz).
- Period (T), Is the time needed to go through one wave. This period is denoted by the letter T and the unit for the period is seconds or seconds (s).
Nature of Sound
Sound has certain properties, the nature of the sound wave, among others, namely:
- This is a longitudinal wave.
- Cannot propagate in a vacuum.
- The speed of the propagation is influenced by the density of the propagation medium (solid, liquid and gas). The highest speed is in a medium that has a high density as well.
- Can experience resonance as well as reflection.
- Requires a medium in its propagation or cannot propagate in a vacuum.
Sound also has the same properties as waves, including:
-
Sound Can Be Reflected
Sound can bounce when it hits an object or obstacle. After bouncing, the sound will produce an echo or echo. Echo is a sound that comes from reflections that sound clear. Meanwhile, echo is a sound produced from reflections that is heard together with the original sound, so that the sound that is heard is not clear or faint. -
Defractionable Sound
Sound can be refracted or refracted. This property makes the sound that will be produced not as loud as the original sound. For example, the sound of thunder sounds louder at night than during the day. -
Sound can Travel
Sound can be heard by the ear because of the process of sound propagation. Sound travels through mediums such as gases, liquids and solids. The process of sound propagation has a different speed in each medium. Sound is the fastest to propagate through solids and the slowest to propagate through gases such as air. An example is like when we dive in water, the sound can still be heard.
Sound Resonance
Resonance is an event or event in which an object vibrates due to the vibration of another object because the frequency is the same. Sound can also experience reflection, which in the sound reflection process is used as:
- Sound velocity determination
- Detection of defects and cracks in metal pipes
- Geophysics survey
- Metal plate thickness measurement
- Spot depth measurement.

Sound Type
Sounds can be grouped into several types, including the following:
Infrasound sound
Infrasound is a sound that has a frequency of less than 20 Hz, which dogs, crickets, geese and horses can hear.
Audiosonic sound
Audiosonic sound is a sound that has a frequency between 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz and can be heard by humans.
Ultrasound sound
Ultrasonic sound is a sound that has a frequency of more than 20,000 Hz, which bats and dolphins can hear.
Tone
Tone is a sound that has a regular frequency.
Sigh
Wheezing is a sound that has an irregular frequency.
Reverberation or rumbling
Reverberation or crackling is a reflected sound that partially comes along with the original sound, so that this disturbs the original sound.
Echo
Echo is a reflected sound that comes after the original sound is issued, so this will strengthen the original sound.
Thus the explanation about Sound Is: Definition, Terms, Speed, Characteristics and Types. Hopefully it can be useful and add to your insight. Thank You.
List of contents
Recommendation:
- Definition of Sublimation and Examples (Full Discussion) Definition of Sublimation and Examples of Sublimation (Full Discussion) – Many processes occur in a chemical substance. There are processes that change solids into liquids, change matter...
- Definition of Groundwater and its Types (Full Discussion) Definition of Groundwater and its Types (Full Discussion) - Water and soil are two different elements, but it turns out that there are terms where these two elements are combined in one meaning. What does…
- Friendship Short Stories: Definition, Writing Tips and Examples Friendship Short Stories: Definition, Writing Tips and Examples - What are Friendship Short Stories like? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss whether it is the Short Story of Friendship and other things about it. Let's see together…
- Swimming Material: History, Understanding According to Experts, Style,… Swimming Materials: History, Expert Definition, Styles, Benefits, Basic Principles and Techniques - Anything what needs to be learned in swimming material? discuss…
- Kingdom Animalia: Definition, Characteristics, Classification and Examples… Kingdom Animalia: Definition, Characteristics, Classification and Examples of Phylums - Is that what Kingdom means Animalia?, On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course other formulas as well covered it. Let…
- √ Effective Ways to Handle Solid Waste (Full Discussion) Effective Ways of Handling Solid Waste (Full Discussion) - Before discussing how to deal effectively with solid waste. We need to know that waste is divided into two namely, solid waste and…
- Precipitation is: 12 Definitions According to Experts, Types,… Precipitation is: 12 Definitions According to Experts Types, and Factors - In this discussion, Around Knowledge will explain about Precipitation. Precipation is a climatic event that is natural,...
- Chemical Equilibrium: Definition, Laws, Formulas, Example Problems Chemical Equilibrium: Definition, Laws, Formulas, Example Problems - In this discussion we will explain about chemical equilibrium, formula law and equipped with examples of chemical equilibrium with complete and...
- Vertical Downward Motion: Definition, Characteristics, Physical Quantities,… Vertical Downward Motion: Definition, Characteristics, Physical Quantities, Formulas and Example Problems - On this occasion Around the knowledge.co.id will discuss Vertical Downward Motion, formulas and of course other things Also…
- Uniformly Changing Circular Motion: Definition, Magnitude… Uniformly Changing Circular Motion: Definition, Physical Quantity, Formulas and Examples of Problems - What is Motion Circular Changes Regularly and Examples? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about...
- √ Definition of Ocean Waves, Theories, Benefits and… Definition of Sea Waves, Theories, Benefits and Classifications - On this occasion Around Knowledge will discuss Sea Waves. Which in this discussion explains the meaning of sea waves, theory, benefits,…
- Adsorption: Definition, Working Principle, Types, Factors That… Adsorption: Definition, Working Principle, Types, Influencing Factors and Examples - What is Adsorption?, On this occasion, about the knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course other things as well covered it. Let's see…
- √ Definition of the Solar System, Theory Formed and Its Structure… Definition of the Solar System, Formed Theory and Structure (Complete) - In this discussion we will explain about the solar system. Which includes the understanding of the solar system, the theory of the formation of the solar system, and the arrangement of the solar system...
- What is the high and low sound called? Definition of Tone, History… What is the high and low sound called? Definition of Tone, History of Scales and Terms in Tone - What is the high and low sound called? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and the things that surround it.…
- Papers: Definition, Characteristics, Functions, Types, Structures, Methods… Papers: Definition, Characteristics, Functions, Types, Structure, How to Make and Examples - What is meant by Papers and how to write them properly and correctly? On this occasion Seputarknowledge.co.id will…
- Thermochemistry: Definition, Equation, Reaction, Benefits and… Thermochemistry: Definition, Equation, Reaction, Benefits and Enthalpy Change - What is meant by Thermochemistry?, On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things as well covered it. Let…
- 4 Nature of Waves and Definition of Waves (Discussion… 4 Nature of Waves and Definition of Waves (Complete Discussion) – Waves without us realizing it happen automatically around us whether naturally or artificially. The waves will continue to occur and can't...
- √ Definition of Molarity, Formula, Preparation, Dilution… Definition of Molarity, Formulas, Preparation, Dilution of Solutions & Examples - In this discussion we will explain the meaning of molarity. Which includes the definition of molarity, molarity formula, examples of molarity questions, manufacture and dilution...
- √ Definition of Communication Media, Theories, Functions, Types,… Definition of Communication Media, Theory, Functions, Types, Characteristics & Forms - In this discussion we will explain about Communication Media. Which includes the notion of communication media, communication media theory, communication media functions,…
- Boyle's Law: Definition, Formulas, Applications and Examples… Boyle's Law: Definition, Formulas, Applications and Examples of Problems - In this discussion we will explain about Boyle's law. Which includes the meaning of Boyle's law, the Boyle's law formula, the application of…
- √ Definition of the Five Senses, Types, Kinds and Functions Definition of the Five Senses, Types, Kinds and Functions - On this occasion, Around Knowledge will discuss the meaning of the five senses. Which in this discussion explains the meaning of the five senses, types,…
- Standby Scout Material: Ranks, Honor Codes and Requirements… Standby Scout Materials: Ranks, Honor Codes and General Proficiency Requirements - What are the materials for alert level scouts? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it, including the level of alert scouts,…
- Electromagnetic Waves: Definition, Properties, Formulas,… Electromagnetic Waves: Definition, Properties, Formulas, Benefits, Spectrum - In this discussion we will explain about electromagnetic waves. Which includes the understanding of electromagnetic waves, the nature of electromagnetic waves, the formula for electromagnetic waves, the benefits of…
- Specific Gravity: Definition, Formula, Use and Difference… Specific Gravity: Definition, Formula, Use and Difference with Density - What is meant by Specific Gravity and What is the Unit Formula? discuss it...
- Purpose of Explanatory Text: Definition, Structure, Characteristics, Rules,… Purpose of Explanatory Text: Definition, Structure, Characteristics, Rules, Examples - In this discussion we will explain about explanatory text. Which includes the understanding of explanatory text, the purpose of explanatory text, the structure of the text...
- √ Natural Gas: Definition, Composition, Types, Benefits and… Natural Gas: Definition, Composition, Types, Benefits and Properties - On this occasion, Around Knowledge will discuss Natural Gas. Which in this discussion explains the meaning of natural gas,…
- Example of Cultural Arts Questions for Class 10 (X) SMA/MA/SMK Semester 1… Examples of Class 10 (X) Cultural Arts Questions for SMA/MA/SMK Semesters 1 and 2 (2019 and 2020) - On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss Multiple Choice Class 10 Cultural Arts Questions and Essay…
- Parts of the Ear and Their Functions: How They Work and… The Parts of the Ear and Their Functions: How they Work and the Problems - What are the Parts of the Ear and Their Functions? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss this and of course other things as well covered it. Let…
- √ Hydrosphere: Definition, Branches, Cycles, Types and Elements Hydrosphere: Definition, Branches, Cycles, Types and Elements - On this occasion, Around Knowledge will discuss the Hydrosphere. Which in this discussion explains the meaning of the hydrosphere, branches, cycles, types...
- Covalent Bonds: Definition, Characteristics, Types, Formulas… Covalent Bonds: Definition, Characteristics, Types, Chemical Formulas and Properties of Compounds - What is a covalent bond? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things as well covered it. Let…
