√ Definition of Particle Dynamics, Types of Forces and Mass Relations
Definition of Particle Dynamics, Types of Forces and Mass Relations – In this discussion we will explain about particle dynamics. Which includes the understanding of particle dynamics, the types of particle dynamic forces and the mass relationship of particle dynamics which are discussed in detail and lightly. For more details, please see the review below carefully.
Definition of Particle Dynamics, Types of Forces and Mass Relations
Let's discuss the notion of particle dynamics first carefully.
Understanding Particle Dynamics
Particle dynamics is a science that discusses the forces that make a particle that was originally stationary to move, or that speed up or slow down the motion of a particle.
Types of Particle Dynamics
The types of particle dynamics are:
Style
If we push or pull an object, it can be said that we exert a force on the object. But force can also be exerted by inanimate objects. A spring on a stretched spring will exert a force on the objects it is connected to ends, or a locomotive will exert force on the middle row of cars he pulled.
A force has both direction and magnitude, so it is a vector which obeys the rules of vector addition. Force can be expressed by a line that has an arrow at the end as the direction of the force, while the length of the line indicates the magnitude of the force. In International Standard units, the unit of force is Newton (N) or kg.m/s2.
Gravity
Objects dropped near the surface of the earth will fall with the same acceleration, namely the acceleration due to gravity (g = 9.8 m/s2 = 9.8 N/kg in SI units), if air resistance is negligible. The force that causes this acceleration is called the gravitational force (FG). So it can be said that the gravitational force is the force exerted by the earth on every object around it
The law of gravity states that the force between two particles having mass m1 and M2 and separated by a distance r is an attractive force along the line connecting the two particles and has a magnitude:
Information:
F = The force of attraction between the two objects (N)
G = Gravity constant (6.673 x 10-11 Nm2/kg-2)
m1, m2 = Mass of object 1 (kg)
r = distance between the two objects (m)
If M1, is represented by the mass of the earth (M) and m2 as the mass of an object m that is around the earth and has a distance r from the center of the earth, then the gravitational force by the earth on the object is:
Gravity acting between the earth and objects. The direction of gravity is always downward towards the center of the earth (looks like the picture above). The force of gravity on an object of magnitude:
W = mg
So the acceleration due to gravity g can be expressed as:
g =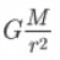
Normal Style
The normal force (N or FN) is a force that arises when two objects touch each other. The direction of the normal force remains perpendicular to the surface in contact (the tangent plane) with the object (see figure below). The size of the normal force depends on the magnitude and size of the pressure force on the contact surface (the tangent area). So if our hands press the surface of a table with a large compressive force, the normal force generated will also be large. Meanwhile, if we press gently, the normal force generated will also be small.
Friction
An object launched from above a horizontal or flat surface, its speed will decrease and eventually stop. It is very clear if a force in the horizontal direction acts on the object, which direction is opposite to the object's motion. This force is often called the frictional force (f) acting on the object and is caused by the surface.
Friction can occur when two objects rub together, that is, the surfaces of the two objects touch each other when one object moves with respect to another object and is parallel to the surfaces that are in contact with each other the.
The direction of the frictional force is always opposite to the direction of motion of a moving object (can be seen in the image below). So if a block moves from left to right over a floor, then a frictional force with a direction to the left will act on the block.
A frictional force acting between two surfaces that are at rest relative to one another is called the static frictional force (Fs). The maximum static frictional force is the smallest force that makes an object move. For dry, unlubricated surfaces, it is found that the maximum static frictional force between the two surfaces does not depend on the area of the contacting surfaces that rub against each other. But it is proportional to the magnitude of the normal force between the two objects that touch each other (note in figure c above).
fs ≤ μs N
With μs = static friction coefficient. The same sign as on the surface above applies if s reach maximum size. Once an object begins to move, the frictional force acting on it will decrease so that a smaller force is required to maintain uniform straight motion. The force acting between two surfaces that are moving relative to each other is called the kinetic frictional force (fk).
For dry and unlubricated surfaces, it is found that the kinetic frictional force does not depend on the contact surface area or on the velocity relative between the two rubbing surfaces, but proportional to the magnitude of the normal force between the two rubbing objects (see fig on). Where is µk = kinetic friction coefficient.
fk = μkN
In figure a it can be seen that a beam of a beam is at rest on a horizontal surface in a state of equilibrium under the influence of the weight W and the upward force P exerted on the surface against him.
If a rope is tied to one side of the block (as in picture b above), then a force is applied to the rope but not too large so that the block remains still. The force P exerted by the surface on the block is inclined to the left. Because the forces P, T, and W must be concurrent, the component of the force P that is parallel to the surface is called the static frictional force fs) and the component perpendicular to the surface is called the normal force (N) that the surface exerts on the beam (see figure b on).
Based on the equilibrium conditions, then fs equals t and N equals W. If T continues to be enlarged, then the beam will start moving at a certain T value and in other words fs is located at the maximum value (see figure c above). If T is enlarged again so that the beam is no longer in balance, but is already moving. Then the frictional force will decrease (see figure b above).
μ constants and µk is a unitless quantity. Generally µs > μkb for two specific surfaces. The value of each of the two coefficients depends on the properties of the two friction surfaces. The rougher a surface, the greater the coefficient value and the smaller the value if the surface is smooth. Often the value is less than 1, although it may be greater than 1.
Thus has been explained about Definition of Particle Dynamics, Types of Forces and Mass Relations, hopefully can add to your insight and knowledge. Thank you for visiting and don't forget to read other articles.
List of contents
Recommendation:
- Pencak Silat: Definition, History, Characteristics, Purpose, Techniques,… Pencak Silat: Definition, History, Characteristics, Purpose, Techniques, and Levels - Does anyone know what it is Pencak Silat? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss Pencak Silat and other things other…
- 9 Kinds of Wind: Definition and Explanation 9 Types of Wind: Definition and Explanation - On this occasion we will explain about Wind. Which includes the meaning of wind, types of wind and explanations with complete and easy-to-understand discussion.
- Badminton Game: History, Techniques, Rules, Means… Badminton Game: History, Techniques, Regulations, Facilities and Infrastructure - On this occasion About the knowledge.co.id will discuss the game of badminton and of course about other things as well covered it. Let's see…
- 12 Definitions of Motion According to Experts and Its Types (Complete) 12 Definitions of Motion According to Experts and Its Types (Complete) - After we discussed understanding physics, then we will discuss the meaning of motion and the types of motion that are internal matter physics…
- Motivational short stories: definition, writing tips and examples Motivational Short Stories: Definition, Writing Tips and Examples - What is a Motivational Short Story?, On On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss whether it is the Short Story of Friendship and other matters about it. Let's see…
- Movement System in Humans: Bones, Joints, Muscles,… Movement System in Humans: Bones, Joints, Muscles, Functions, Abnormalities and Disturbances - What are the systems motion in the human body?, On this occasion, Se regarding the knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about…
- Vertical Downward Motion: Definition, Characteristics, Physical Quantities,… Vertical Downward Motion: Definition, Characteristics, Physical Quantities, Formulas and Example Problems - On this occasion Around the knowledge.co.id will discuss Vertical Downward Motion, formulas and of course other things Also…
- 74 Definition of Education According to Experts 74 Definition of Education According to Experts – Humans have been educated since they were born into the world until they enter school. The word education is no longer foreign to our ears, because all...
- Specific Gravity: Definition, Formula, Use and Difference… Specific Gravity: Definition, Formula, Use and Difference with Density - What is meant by Specific Gravity and What is the Unit Formula? discuss it...
- Inclined Plane: Definition, Formulas, Mechanical Advantage And… Oblique Plane: Definition, Formulas, Mechanical Advantages and Examples of Problems - What is meant by plane oblique and how to calculate the physics? naturally…
- Chromatography: Definition, Types and Explanations Chromatography: Definition, Types and Explanations - In this discussion we will explain about chromatography. An explanation that includes the meaning of chromatography, types of chromatography and explanations that will be presented in full...
- Moment of Inertia: Definition, Factors, Equations of Forms… Moment of Inertia: Definition, Factors, Equations in Forms of Objects and Example Problems - What is meant with the Moment of Inertia?, On this occasion, Se regarding the knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about matter…
- Islamic Words of Wisdom Islamic Words of Wisdom - On this occasion, SeputihKnowledge.co.id will discuss Islamic Words of Wisdom and examples. Let's look at the discussion together in the article below to get more...
- Renaissance Age Renaissance Period: Definition, History, Background and Characters - What is meant by the Renaissance era? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things that also…
- Law of Conservation of Mass: Definition, History, Sound Law And… The Law of Conservation of Mass: Definition, History, Sound of the Law and Experimental Examples - What does the law of conservation sound like mass?, On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things Also…
- Purpose of Explanatory Text: Definition, Structure, Characteristics, Rules,… Purpose of Explanatory Text: Definition, Structure, Characteristics, Rules, Examples - In this discussion we will explain about explanatory text. Which includes the understanding of explanatory text, the purpose of explanatory text, the structure of the text...
- History of Islamic Education: Definition and Scope History of Islamic Education: Definition and Scope - Here we will discuss what history is and what is the meaning of the history of Islamic education itself and its scope. And explain what...
- Standby Scout Material: Ranks, Honor Codes and Requirements… Standby Scout Materials: Ranks, Honor Codes and General Proficiency Requirements - What are the materials for alert level scouts? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it, including the level of alert scouts,…
- Physical Fitness: Definition, Components, Concepts, Elements,… Physical Fitness: Definition, Components, Concepts, Elements, Purpose, Benefits and Forms of Exercise - What's in What do you mean by physical fitness? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss fitness Physical and…
- Resultant Force: Definition, Formulas, Newton's Laws, Example Problems… Resultant Force: Definition, Formulas, Newton's Laws, Example Problems and Discussion - What is meant by resultant force? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it, including formulas and of course…
- Elements of the Art of Music: Definition, History, Types, Genres… Elements of the Art of Music: Definition, History, Types, Flow and Functions of Music - What are the Elements Is the Art of Music? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss what are the elements from…
- √ Economics: Definition and its Division (Complete) Economics: Understanding and its Division (Complete) - On this occasion, Around Knowledge will discuss Economics. Which in this discussion explains the meaning of economics and its division ...
- Free Falling Motion: Definition, Characteristics, Physical Quantities, Formulas… Free Falling Motion: Definition, Characteristics, Physical Quantities, Formulas and Example Problems - What is meant with free fall motion and how to calculate the physics? will…
- The Collapse of the Kediri Kingdom: History and Legacy The Fall of the Kediri Kingdom: History and Legacy - The Kediri Kingdom or the Kadiri Kingdom or the Panjalu Kingdom was a kingdom that existed in East Java between 1042-1222. The kingdom is in the city…
- Computer Hardware: How it Works, Types, Examples and… Computer Hardware: How it Works, Types, Examples and Functions - In today's computerized era, we are definitely familiar with computers and their devices. However, some may not know...
- √ Definition of Hard Bones, Functions, Characteristics, Types, Structures &… Definition of Bones, Functions, Characteristics, Types, Structures & Examples - On this occasion we will explain about bones. The discussion includes the definition of bones, functions, types, characteristics, bone structure...
- Example of historical story text in Indonesia Examples of historical story texts in Indonesia – What are examples of historical stories like? This time around the knowledge.co.id will discuss examples of historical stories and their structure. Let's take a look at the discussion in the article on…
- Uniformly Changing Circular Motion: Definition, Magnitude… Uniformly Changing Circular Motion: Definition, Physical Quantity, Formulas and Examples of Problems - What is Motion Circular Changes Regularly and Examples? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about...
- Example of Cultural Arts Questions for Class 10 (X) SMA/MA/SMK Semester 1… Examples of Class 10 (X) Cultural Arts Questions for SMA/MA/SMK Semesters 1 and 2 (2019 and 2020) - On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss Multiple Choice Class 10 Cultural Arts Questions and Essay…
- √ Review Text: Definition, Purpose, Structure and Examples Review Text: Definition, Purpose, Structure and Examples - On this occasion, Around Knowledge will discuss review text. Which explains the meaning of review text, purpose, characteristics, structure, types and…
