Example of a Molality Problem: Mole Fraction, Formula and Solution
Example Molality Problem: Mole Fraction, Formula and Solution – On this occasion About the knowledge.co.id will discuss molality with several examples of questions and of course about other things that also cover it. Let's look at the discussion together in the article below to better understand it.
Example of a Molality Problem: Mole Fraction, Formula and Solution
Molality or molal concentration is a measure of the concentration of a solute in a solution in terms of the amount of substance in a certain mass of the solvent. This is different from the definition of molarity which is based on a certain volume of solution.
The common unit of molality in chemistry is mol/kg. A solution with a concentration of 1 mol/kg is also sometimes expressed as 1 molal. The term molality is formed in analogy to molarity which is the molar concentration of a solution.
The molality of a solution can be tested by adding some solvent. More simply, the Molality (m) of a solution is the moles of solute divided by the kilograms of solvent. Molality or molality is the concentration of a solution which states the number of moles (n) of solute in 1 kg or 1000 grams of solvent.
The difference between molality and molarity is that if molality is molality or molal concentration (m) expresses the number of moles solute in 1000 grams of solvent while molarity is a statement of the number of moles of solute in every one liter solution. Molarity is represented by the notation M and the units are moles/liter.
Molality Formula
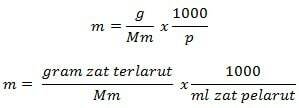
Information
m = molality (mol/kg)
g = grams of solute (g)
Mm = molar mass of substance (g/mol)
P = mass of solvent (g)
Molality Relationship with Mass Percent
Mass percent is a unit of concentration commonly used in chemical solutions. Examples of solutions that we can find everyday are 75% alcohol solution and 24% acetic acid solution. Mass percent is the number of grams of solute in 100 grams of solution mass. The equation that shows the calculation of the mass percent is as follows:

Relationship Molality With Molarity
Molarity expresses the number of moles of solute in one liter of solution. Molarity can be converted to molality by converting the volume of the solution into the mass of the solution. Converting volume to mass requires data on the density of the solution (p), which can be formulated as follows:

Mole Fraction
The mole fraction is a measure of the concentration of a solution which expresses the ratio of the number of moles in a part of a substance to the total number of moles present in the components of the solution. The mole fraction is divided into 2 parts:
Solute mole fraction (Xt)
The formula for the mole fraction of the solute (Xt), namely:

Information:
Xt = mole fraction of solute
Nt = number of moles of solute
Np = number of moles of solvent
Solvent mole fraction (Xp)
The formula for the mole fraction of the solvent (Xp), namely:

Information
Xp = mole fraction of solvent
Nt = number of moles of solute
Np = number of moles of solvent
The sum of the mole fractions of solute and solvent is 1
Xt + Xp = 1
Examples of Molality Problems and Solutions
Problem 1
What is the molality of a solution containing 4 g of NaOH (Ar Na = 23 g/mol, Ar O = 16 g/mol, and Ar H = 1 g/mol) dissolved in 250 g of water?
Completion:
Is known:
mass of NaOH = 4 gr
ArNa = 23 gr/mol
ArO = 16 g/mol
ArH = 1 gr/mol
mass of water = 250 gr = 0.25 kg
Asked: m = ?
Answer:
Mr. NaOH = 40 gr/mol
number of moles of NaOH = mass/Mr
number of moles of NaOH = 4 gr/(40 gr/mol)
number of moles of NaOH = 0.1 mol
m = number of moles/p
m = 0.1 mol / 0.25 kg
m = 0.4 m
Problem 2
What is the molality of a 37% (w/w) HCl solution? (Ar H = 1 g/mol, Ar Cl = 35.5 g/mol)
Completion:
Is known:
mass of HCl = 37%
ArH = 1 g/mol
ArCl = 35.5 g/mol
Asked: m = ?
Answer:
Mr. HCl = 36.5 gr/mol
suppose the mass of the solution is 100 grams then the mass of HCl is:
HCl mass = 37% x 100 gr
mass of HCl = 37 gr
mass of solvent = mass of solution – mass of HCl
mass of solvent = 100 gr – 37 gr
mass of solvent = 63 gr = 0.063 kg
number of moles of HCl = mass/Mr
number of moles of HCl = 37 gr /(36.5 gr/mol)
number of moles of HCl = 1.01 moles
m = number of moles/mass of solvent
m = 1.01 mol /0.063 kg
m = 16.03 m
Problem 3
Determine the molality of the solution prepared by dissolving 12 grams of urea CO(NH2)2 in 250 grams of water.
Completion:
Is known:
mass of urea = 12 gr
Mr Urea = 60 g/mol
mass of solvent = 250 gr = 0.25 kg
Asked: m = ?
Advertisement
Answer:
number of moles of Urea = mass/Mr
number of moles of Urea = 12 gr /(60 g/mol)
number of moles of Urea = 0.2 moles
m = number of moles/mass of solvent
m = 0.2 mol / 0.25 kg
m = 0.8 m
Problem 4
What is the molality of an alcoholic solution containing 23 mass % ethanol (Mr = 46)?
Answer:
Is known:
mass of ethanol = 23%
Mr ethanol = 46 g/mol
Asked: m = ?
Completion:
for example the mass of the alcohol solution is 100 grams then the mass of ethanol is:
mass of ethanol = 23% x 100 gr
mass of ethanol = 23 gr
mass of solvent = mass of solution – mass of ethanol
mass of solvent = 100 gr – 23 gr
mass of solvent = 77 gr = 0.077 kg
number of moles of ethanol = mass/Mr
number of moles of ethanol = 23 gr /(46 g/mol)
number of moles of ethanol = 0.5 mol
m = number of moles/mass of solvent
m = 0.5 mol /0.077 kg
m = 6.49 m
Problem 5
Calculate the concentration (% by mass) of glucose in a 2 molal glucose solution.
Completion:
Is known:
m = 2 molal = 2 mol/kg = 0.002 mol/gr
Mr glucose = 180 gr/mol
Asked: mass of glucose (%) = ?
Answer:
moles of glucose = mass/Mr
moles of glucose = mass of glucose/(180 g/mol)
moles of glucose = mass of glucose x 0.005 mol/gr
Substitute the moles of glucose into the following equation:
m = moles of glucose/mass of solvent
0.002= mass of glucose x 0.005/mass of solvent
o, oo2/o, oo5 = mass of glucose/mass of solvent
2/5 = mass of glucose/mass of solvent
So the mass ratio of glucose: mass of solvent = 2:5, while the mass ratio of glucose: mass of solution = 2:7.
So,
% mass of glucose = (mass of glucose/mass of solution) x100%
% by mass of glucose = (2/7) x 100%
% glucose mass = 28.57 %
Problem 6
What is the molality of a solution containing 8 g of NaOH (Ar Na = 23 g/mol, Ar O = 16 g/mol, and Ar H = 1 g/mol) dissolved in 250 g of water?
Discussion
Is known:
Mass of NaOH = 8 gr
ArNa = 23 gr/mol
ArO = 16 g/mol
ArH = 1 gr/mol
mass of water = 250 gr = 0.25 kg
Wanted: Molality (m)….?
Answer:
Mr. NaOH = 40 gr/mol
The number of moles of NaOH = mass/Mr
Number of moles of NaOH = 8 gr/(40 gr/mol)
The number of moles of NaOH = 0.2 mol
m = number of moles/p
m = 0.2 mol / 0.25 kg
m = 0.8 m
Problem 6
Determine the molality of the solution prepared by dissolving 15 grams of urea CO(NH2)2 in 250 grams of water.
Discussion
Is known:
Mass of urea = 15 gr
Mr Urea = 60 g/mol
Solvent mass = 250 gr = 0.25 kg
Wanted: Molality (m)…. ?
Answer:
Number of moles of Urea = mass/Mr
Total moles of Urea = 15 gr / 60 g/mol
The number of moles of Urea = 0.25 mol
m = number of moles/mass of solvent
m = 0.25 mol / 0.25 kg
m = 1 m
Problem 7
What is the molality of a 37% (w/w) HCl solution? (Ar H = 1 g/mol, Ar Cl = 35.5 g/mol).
Discussion
Is known:
mass of HCl = 37%
ArH = 1 g/mol
ArCl = 35.5 g/mol
Wanted: Molality (m)…?
Answer:
Mr. HCl = 36.5 gr/mol
Suppose the mass of the solution is 100 grams, then the mass of HCl is:
HCl mass = 37% x 100 gr
mass of HCl = 37 gr
mass of solvent = mass of solution – mass of HCl
mass of solvent = 100 gr – 37 gr
mass of solvent = 63 gr = 0.063 kg
number of moles of HCl = mass/Mr
number of moles of HCl = 37 gr /(36.5 gr/mol)
number of moles of HCl = 1.01 moles
m = number of moles/mass of solvent
m = 1.01 mol /0.063 kg
m = 16.03 m

Problem 8
Determine the amount (grams) of NaOH that must be dissolved in 1 liter of water (water = 1.00 g/mL) to obtain 0.25 m NaOH.
Discussion
Is known:
1 L of water = 1000 mL = 1000 g (since ρ of water = 1.00 g/mL)
mNaOH = 0.25 m
Mr NaOh = 40
Asked: gr…?
Answer:
mNaOH = gr / Mr x 1,000 / P
0.25 = gr/40 x 1,000/1,000
0.25 = g/40
g = 0.25 x 40
g = 10 grams
So, the amount of NaOH needed is 10 grams.
Problem 9
Determine how many mL of water are needed to dissolve 4.9 grams of H2SO4 whose concentration is 0.25 M (Ar H = 1; S = 32; O =16)!
Discussion
Is known:
mH2SO4 = 0.25
Mr H2SO4 = 98
gr = 4.9 grams
Asked :p???
Answer:
m = gr/Mr x 1,000/P
0.25 = 4.9/98 x 1,000/p
p = 20 grams (20 mL)
So, the volume of water is 20 mL.
Problem 10
What mass of water is required to prepare a 1.2 m solution using 0.6 mol NaCl?
Discussion
molality (m) = 1.2 mm =
nP
1,2 =
0,6P
P=
0,61,2
= 0.5 kg
So the mass of water (mass of solvent) required is 0.5 kg
Problem 11
Suppose there are 2 moles of solute dissolved in 1 liter of solvent, what is the molality?
Discussion
dissolved moles (n) = 2 molm =
nP
m =
21
= 2m
Calculate the molality of 25 grams of KBr (Mr = 119) dissolved in 750 mL of pure water.
Discussion
solute = 25 grams
Mr = 119
solvent (P) = 750 mL = 750 grams (because ρ of water = 1.00 g/mL) = 0.75 kgn =
dissolved substanceMr
n =
25119
= 0.21 mol
m =
nP
m =
0,210,75
= 0.28 m
Thus the review from About the knowledge.co.id about Example of a Molality Problem , hopefully can add to your insight and knowledge. Thank you for visiting and don't forget to read other articles.
List of contents
Recommendation:
- Cellulose Is: Definition, Type, Structure, Properties and… Cellulose Is: Definition, Type, Structure, Properties and Functions - Cellulose is a fiber-like compound, and is found in the protective cell walls of plants. To understand better, of course we will discuss…
- √ Definition of Expansion in Length, Formula, Area and Volume of Substance… Definition of Long Expansion, Formulas, Area and Volume of Solids - In this discussion we will explain about long expansion. Which includes the notion of long expansion, long expansion formulas, area, volume of matter...
- Measures: Definition, Length Unit Conversion, How to… Measuring Ladder: Definition, Conversion of Length Units, How to Use and Example Questions - What's in what do you mean by size ladder and how to use it?, this time around the knowledge.co.id will discuss it...
- Covalent Bonds: Definition, Characteristics, Types, Formulas… Covalent Bonds: Definition, Characteristics, Types, Chemical Formulas and Properties of Compounds - What is a covalent bond? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things as well covered it. Let…
- Environmental Speech: Definition, Purpose, Characteristics and… Environmental Speech: Definition, Purpose, Characteristics and Examples - How is the text of environmental speech structured? what's good and right?, On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course things Which…
- Cone formulas, characteristics, properties, elements and examples of problems Cone Formulas, Characteristics, Properties, Elements and Examples Problem - How to calculate the area and volume of a shape cone space?, On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things Which…
- Viscosity Formula: Definition of Viscosity, Coefficient and… Viscosity Formula: Viscosity Definition, Coefficient and Influencing Factors - How is the Viscosity Formula is it? Viscosity is a measurement of the resistance of a fluid that is changed either by stress or by pressure. On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id…
- Unit of Weight: Definition, Conversion Ladder and Examples… Unit of Weight: Definition, Conversion Ladder and Example Problem - What is a Unit of Weight?, On this occasion About the knowledge.co.id will discuss it, including understanding and of course other things as well covered it. Let…
- Moment of Inertia: Definition, Factors, Equations of Forms… Moment of Inertia: Definition, Factors, Equations in Forms of Objects and Example Problems - What is meant with the Moment of Inertia?, On this occasion, Se regarding the knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about matter…
- Uniformly Changing Circular Motion: Definition, Magnitude… Uniformly Changing Circular Motion: Definition, Physical Quantity, Formulas and Examples of Problems - What is Motion Circular Changes Regularly and Examples? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about...
- Indefinite Integral: Definition, Formulas, Properties and Examples… Indefinite Integral: Definition, Formulas, Properties and Examples of Problems - What is meant by Indefinite Integral Of course and how to calculate the mathematical operations? will…
- Definition of Learning Methods: Characteristics, Purpose, Types and… Definition of Learning Methods: Characteristics, Purpose, Types and Discussion - What is meant by Method Learning?, On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things Also…
- Chemical Equilibrium: Definition, Laws, Formulas, Example Problems Chemical Equilibrium: Definition, Laws, Formulas, Example Problems - In this discussion we will explain about chemical equilibrium, formula law and equipped with examples of chemical equilibrium with complete and...
- Acid-Base Solutions: Definition, Acid-Base Theory, Properties and… Acid-Base Solutions: Definition, Acid-Base Theory, Properties and Types - Acid and base solutions are two groups of chemical compounds that are widely found and used in everyday life.
- Build Space – Definition, Formulas, and Various… Build Space – Definition, Formulas, and Its Various Types - On this occasion, we would like to review mathematical material about geometric shapes, both in terms of understanding and others. Immediately, let's discuss...
- √ Acid-Base Indicator: Definition, Types and Examples Acid-Base Indicators: Definition, Types and Examples - On this occasion, Around Knowledge will discuss Acid-Base Indicators. Which in this discussion explains the meaning of acid indicator...
- Boyle's Law: Definition, Formulas, Applications and Examples… Boyle's Law: Definition, Formulas, Applications and Examples of Problems - In this discussion we will explain about Boyle's law. Which includes the meaning of Boyle's law, the Boyle's law formula, the application of…
- Motivational short stories: definition, writing tips and examples Motivational Short Stories: Definition, Writing Tips and Examples - What is a Motivational Short Story?, On On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss whether it is the Short Story of Friendship and other things about it. Let's see…
- Definition of Pressure: Types of Pressure, Formulas and Example Problems Definition of Pressure: Types of Pressure, Formulas and Example Problems - What is Pressure? At On this occasion, around the knowledge.co.id, we will discuss what pressure is and what other elements are covered it. Let's see…
- Dynamic Fluids: Types, Features, Bernoulli Equation, Theorems… Dynamic Fluids: Types, Properties, Bernoulli's Equation, Toricelli's Theorem, Formulas And Examples of Problems - What is it dynamic fluids and their types? about…
- Density of Water: Definition, Formulas and Examples Density of Water: Definition, Formulas and Examples - What is the density of water? Let's see together…
- Definition of Quantity, Unit, Measurement and Examples… Definition of Quantity, Unit, Measurement and Examples (Complete) - In basic physics concepts, surely we have been introduced to something related to everyday life. Like measuring height, weighing mass, measuring width,...
- Examples of Scientific Work: Functions and Rules of Language Examples of Scientific Papers: Functions and Rules of Language - What are examples of good and correct forms of writing scientific papers? Previously, Seputar the knowledge.co.id has discussed Scientific Work: Definition, Characteristics, Benefits,…
- Examples of Flat Shapes: Types, Characteristics and Formulas of Flat Shapes Examples of Flat Shapes: Types, Properties and Formulas of Flat Shapes - What are the examples of Flat Shapes?
- Sample Physical Education Questions for Class 11 (XI) SMA/MA/SMK Semester 1 and 2 Examples of Class 11 (XI) Physical Education Questions for SMA/MA/SMK Semesters 1 and 2 (2019 and 2020) - On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss examples of Multiple Choice Class 11 Physical Education Questions and Essay…
- Precipitation is: 12 Definitions According to Experts, Types,… Precipitation is: 12 Definitions According to Experts Types, and Factors - In this discussion, Around Knowledge will explain about Precipitation. Precipation is a climatic event that is natural,...
- √ Definition of Chemical Compounds, Characteristics, Types & Nomenclature… Definition of Chemical Compounds, Characteristics, Types, Complete Nomenclature - In this discussion we will explain about Chemical Compounds. Covers the definition, characteristics, types and nomenclature of chemical compounds with discussion...
- Single Substances Are: Definition, Elements and Compounds Single Substances Are: Definitions, Elements and Compounds - What does a single substance mean? Let's look at the discussion together...
- Inclined Plane: Definition, Formulas, Mechanical Advantage And… Oblique Plane: Definition, Formulas, Mechanical Advantages and Examples of Problems - What is meant by plane oblique and how to calculate the physics? naturally…
- Unit Conversion: Definition, Factor, Length, Mass, Time,… Unit Conversion: Definition, Factor, Length, Mass, Time, Volume and Pressure - What is unit conversion?, On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it, including factors, types and of course other things Which…
