Polynomial: Definition, Value, Terms, Distribution and Example Problems
Polynomial: Definition, Value, Conditions, Division and Example Problems – What is meant by Polynomial? On this occasion About the knowledge.co.id will discuss about Polynomials and the things that surround them. Let's look at the article below to understand it better.
Polynomial: Definition, Value, Terms, Distribution and Example Problems
Polynomials or commonly referred to as polynomials are a form of terms with many values composed of variable variables and constants. The operations used are only addition, subtraction, multiplication and powers of non-negative integers.
The general form of this Polynomial, namely:
Polynomial General Form: an xn + an-1 xn-1 +... + a1 x + a
Information:
with an, an-1, …., a1, a0 € R coefficient or constant
Polynom an ≠ 0, and n are positive integers.
The highest power of x is the degree of the polynomial. While terms that do not contain a variable (a) are referred to as fixed (constant) terms.
A polynomial can look like the following:
25x2 +19x – 06
Another example of the polynomial form is:
- 3x
- x – 2
- -6y2 – (½)x
- 3xyz + 3xy2z – 0.1xz – 200y + 0.5
- 512v5+99w5
- 5 (Constants are coefficients whose variable has a power of 0, so a number is a polynomial.)
A polynomial can have:
- A variable (is a mutable value, like x, y, z in an equation; may have more than 1 variable)
- Coefficients (are constants accompanying variables)
- Constant (a fixed value that doesn't change)
- The exponent or power is the power of the variable; can also be referred to as degrees of a polynomial.
Polynomial Terms
There are also several conditions so that an equation can be called a 'polynomial', including the following:
- Variables cannot have fractional or negative exponents.
- Variables cannot be included in a trigonometry equation.
Polynomial and Non-Polynomial
Here are some forms that are not included in the polynomial form, including the following:
- 3xy-2, because the rank is negative. Exponents or powers can only be {0,1,2…}.
- 2/(x+2), because dividing by the variable is not allowed (the power of the denominator is negative).
- 1/x ,for the same reason ^.
- √x, because the root is a power of a fraction, which is not allowed.
- x cos x, because there is a variable x in trigonometric functions
Here are the things that are allowed or included in the polynomial form, pay close attention:
- x/2 is allowed, because it's okay to divide by a constant.
- √x2 yes, because after explaining the result there is no exponential fraction.
- √2 may be because the root is a constant, not a variable.
- ½ x5 – (cos∏)x3 – (tan 60°)x – 1 is possible because trigonometric functions are constants, and there are no variables in them
Polynomial Value
We can find the value of the polynomial f (x) for x=k or f (k) using the substitution method or using the Horner scheme. Here are the details:
Substitution way:
By substituting x = k into the polynomial, it will become:
f(x) = an kn + an-1 kn-1 +... + a1 k + a
-
How to horner scheme:
As an example:
(f(k) = x3 +bx2 +cx +d so: f(k) = ak3 + bk2 + ck + d
xa3 +bx2 + cx + d = (ak2 + bk + c) k+d
= ((ak + b) k + c) k+d
Polynomial Division
In general, division within a polynomial can be written as follows:
Formula: f(x) = g(x) h(x) + s(x)
Information:
- f (x) is the polynomial that is divisible.
- g (x) is the multiplier term.
- h (x) is the polynomial term of the quotient.
- s (x) is the remainder term.
Before we understand the polynomial division method, we must first know about the remainder theorem namely
Let F(x) be a polynomial of degree n,
If F(x) is divided (x-k) then the result is F(k)
If F(x) is divided (ax-b) then the result is F(b/a)
If F(x) is divided by (x-a)(x-b) then the result is:
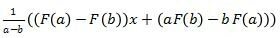
Ordinary Distribution Method
An example is if 2x3 – 3x2 + x + 5 divided by 2x2 – x – 1
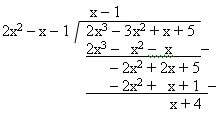
then the quotient and the remainder is the quotient = x-1 and the remainder = x+4
Horner's Division Method
We can divide polynomials f (x) by (x-k) using the Horner method.
We can use this method for degree 1 divisors or divisors that can be factored into degree 1 divisors.
The method is as follows:
- Just write down the coefficient → it has to be coherent or sequential starting from the x coefficientn, xn–1, … to constants (if there is a non-existent variable, then the coefficient is written 0)
For example: for 4x3 – 1, the coefficients are 4, 0, 0, and -1 (for x3, x2, x, and constants)
- If the coefficient of the highest degree P(x) ≠ 1, then we must divide the quotient again by the coefficient of the highest degree P(x).
- If we can factor the divisor, then:
- If the divisor can be factored to P1 as well as P2, then S(x) = P1.S2 + S1
- If the divisor can be factored to P1, P2, P3, then S(x) = P1.P2.S3 +P1.S2 + S1
- If the divisor can be factored into P1, P2, P3, P4, then S(x) = P1.P2.P3.S4 +P1.P2.S3 +P1.S2 + S1
- and so on.
Indefinite Coefficient Method
Basically, this method is done by substituting F(x) of degree m and P(x) of degree n into the general form of polynomial division, then filling H(x) and S(x) with
H(x) is a polynomial of degree k, where k = m – n
S(x) is a polynomial of degrees n-k
Examples of Polynomial Problems
question 1.
Is known
F(x) = 2x3 – 3x2 + x + 5
P(x) = 2x2 – x – 1
Determine the quotient and remainder
Answer :
F(x) = 2x3 – 3x2 + x + 5
P(x) = 2x2 – x – 1 = (2x + 1)(x – 1)
So p1: (2x + 1) = 0 -> x = -1/2 and p2: (x – 1) = 0 -> x = 1
Then the horner steps are shown in the following figure

So, the results are obtained and the remainder is as follows
H(x) = x-1
S(x) = P1×S2 + S1 = x + 4
Problem 2.
Tribe of many x4 – 3x3 – 5x2 + x – 6 divided by x² – x -2 the remainder equals …
a. 16x + 8
b. 16x – 8
c. -8x+16
d. -8x – 16
e. -8x – 24
Answer:
It is known that the divisor is: x² – x -2, so:
x² – x -2= 0
(x – 2) (x + 1) = 0
x = 2 and x = -1
Remember the formula: P(x) = H(x) + (px + q), so the remainder (px + q), then:
- x = 2
f(2) = 2p + q
24 – 3(2)3 – 5(2)2 + 2 – 6 = 2p + q
16 – 24 – 20 + 2 – 6 = 2p + q
-32 = 2p + q … (i)
- x = -1
f(-1) = -p + q
(-1) – 3(-1)3 – 5(-1)2 + (-1) – 6 = -p + q
1 + 4 – 5 – 1 – 6 = -p + q
-8 = -p + q …(ii)
Eliminate equations (i) and (ii), to become:
-32 =2p +q
-8 =-p +q
-24 =3p
p = -8
If we substitute p = –p + q = -8
-(-8) + q = -8
q = -16
So the remainder is = p + q = -8x – 16
Answer: D
Problem 3.
It is known that F(x) = 2x3 – 3x2 + x + 5 ,P(x) = 2x2 – x – 1
Determine the quotient and remainder using the indeterminate method
Discussion of questions:
m = 3, n = 2, k = 1
H(x) is degree 1, let's say H(x) = ax+b
S(x) is of degree 2-1=1 eg S(x) = px+q
Substitute F(x), P(x), H(x), S(x) into the equation
F(x) = P(x). H(x) + S(x), then obtained
2x3 – 3x2 + x + 5 = (2x2 – x – 1)(ax+b) + px+q
2x3 – 3x2 + x + 5 = 2ax3 + 2bx2 – ax2 – bx – ax – b + px + q
(2)x3 +(– 3)x2 + (1)x + (5) = (2a)x3 + (2b– a) x2 + (– b – a + p) x + (– b + q)
Then equate the coefficients of the left and right sides to be
2a = 2
a = 1
2b – a = -3
2b – 1 = -3
2b = -2
b = -1
– b – a + p = 1
1 – 1 + p = 1
p = 1
– b + q = 5
1 + q = 5
q = 4
So,
H(x) = ax + b = x – 1
S(x) = px + q = x + 4
Problem 4.
One of the factors of (2x³ -5x² – px =3) is (x + 1). Another factor of the multitude is…
a. (x – 2) and (x – 3)
b. (x + 2) and (2x – 1)
c. (x + 3) and (x + 2)
d. (2x + 1) and (x – 2)
e. (2x – 1) and (x – 3)
Answer:
Which is a factor is x + 1 -> x = -1
f(-1) = 0
2(-1)³ – 5(-1)³ – p(-1) + 3 = 0
-2 – 5 + p + 3 = 0
p = 4
Then, f (x) = 2x³ -5x³ – 4x =3
= (x + 1)(2×2 – 7x + 3)
= (x + 1)(2x – 1)(x – 3)
So, the other factors are (2x – 1) and also (x – 3).
Answer: E

Problem 5.
There are Two polynomials x³ -4x³ – 5x + m and x2 -3x – 2 ÷ x + 1 will have the same remainder, so 2m + 5 = …
a. 17
b. 18
c. 24
d. 27
e. 30
Answer:
For example f(x) = x³ -4x2 – 5x + m and x2 -3x – 2
If ÷(x + 1 ) –> x = -1 will have the same remainder, then:
f(-1) = g(-1)
(-1)³ – 4(-1)2 + 5(-1) + m = (-1)2 + 3(-1) – 2
-1 -4 – 5 + m = 1 – 3 – 2
-10 + m = -4
m = -4 + 10
m = 6
So, the value of 2m + 5 = 2(6) + 5 = 17
Answer: A
Thus the review from About the knowledge.co.id about Polynomial , hopefully can add to your insight and knowledge. Thank you for visiting and don't forget to read other articles.
List of contents
Recommendation:
- Movement System in Humans: Bones, Joints, Muscles,… Movement System in Humans: Bones, Joints, Muscles, Functions, Abnormalities and Disturbances - What are the systems motion in the human body?, On this occasion, Se regarding the knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about…
- Definition of Operating Systems and their Types (Full Discussion) Understanding Operating Systems and Types (Full Discussion) - On a computer we know the terms software and hardware. What we will discuss is the understanding of the operating system and its types which are…
- Critical Response Text: Definition, Characteristics, Language Rules,… Critical Response Text: Definition, Characteristics, Language Rules, Structure, Functions and Examples - What is Text Critical Response and its function?, On this occasion, Se regarding the knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about matter…
- Uniformly Changing Circular Motion: Definition, Magnitude… Uniformly Changing Circular Motion: Definition, Physical Quantity, Formulas and Examples of Problems - What is Motion Circular Changes Regularly and Examples? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about...
- Historical Text: Definition, Characteristics, Structure, Language Rules… Historical Text: Definition, Characteristics, Structure, Linguistic Rules and Examples - What is meant by Historical Texts? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss what historical texts are and other things other…
- Properties of Integer Operations and Examples Properties of Integer Operations and Examples - After knowing the meaning of integers and their types, Next, aroundknowledge.com returns to discussing related matters, namely the properties of integer operations along with examples. Here's a full discussion.…
- √ Collection of Trigonometry Material Topics (Complete Discussion) Collection of Trigonometry Material Topics (Complete Discussion) - This time we will discuss trigonometry material. Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with the relationships between angles and sides in triangles. Gathering…
- Papers: Definition, Characteristics, Functions, Types, Structures, Methods… Papers: Definition, Characteristics, Functions, Types, Structure, How to Make and Examples - What is meant by Papers and how to write them properly and correctly? On this occasion Seputarknowledge.co.id will…
- Vector: Definition, Material, Formulas and Example Problems Vector: Definition, Material, Formulas and Example Problems - What is meant by Vector in operation mathematics? On this occasion, Around the Knowledge.co.id will discuss vectors and other matters about it.…
- √ History of the Minangkabau Tribe, Origins and Characteristics The History of the Minangkabau Tribe, Its Origins and Characteristics - On this occasion, Around Knowledge will discuss the Minangkabau Tribe. Which in the discussion this time explains the history of the Minangkabau tribe, the origin...
- Short Story Text: Definition, Characteristics, Structure, Elements and Examples Short Story Text: Definition, Characteristics, Structure, Elements and Examples - What is a Short Story Text? Let us…
- The Collapse of the Kediri Kingdom: History and Legacy The Fall of the Kediri Kingdom: History and Legacy - The Kediri Kingdom or the Kadiri Kingdom or the Panjalu Kingdom was a kingdom that existed in East Java between 1042-1222. The kingdom is in the city…
- Ionic Bonds: Definition, Characteristics, Properties and Examples of Compounds Ionic Bonds: Definition, Characteristics, Properties, and Examples of Their Compounds - On this occasion, Around the Knowledge.co.id will discuss about ionic bonds and of course about other things that also cover it. Let's see together…
- Standard Deviation Formula: Definition and Example Problems Standard Deviation Formula: Definition and Example Questions - What is meant by standard deviation and how calculate using the formula? On this occasion, SeputihKnowledge.co.id will discuss the standard deviation along with…
- Pre-literate Age: Definition, Age Division, Types… Pre-literate Age: Definition, Age Division, Types of Humans, and Their Legacy - What is meant by The Age of Pre-literacy? On this occasion, Around the Knowledge.co.id will discuss what is the Age of Pre-literacy and other things Which…
- Factors Inhibiting Social Mobility: Definition, Factors… Inhibiting Factors of Social Mobility: Definition, Driving Factors and Explanations - What is the meaning of social mobility and What are the inhibiting factors? On this occasion, about the knowledge. co.id will discuss it, including nutritional content and naturally…
- Number Patterns: Definition and Types of Number Patterns Number Patterns: Definition and Types of Number Patterns - What is a Number Pattern? On this occasion, we want to review what is the meaning of number patterns and their types and...
- Punctuation Marks: Definition, Functions, Types and Examples Punctuation Marks: Definition, Functions, Types and Examples - In this discussion we will explain about Punctuation. Which includes the meaning, function, types and examples of using punctuation with…
- Derived Algebraic Functions: Formulas, Applications, Notation, Multiplication… Derivative of Algebraic Functions: Formulas, Applications, Notation, Multiplication of Division by Two Functions and Example Problems - Do you understand what is meant by Derivative of an Algebraic Function? On occasion…
- Ijarah Law: Definition, Legal Basis, Requirements, Pillars, Types of… Ijarah Law: Definition, Legal Basis, Terms, Pillars, Types and Terms - What is Ijarah law and basically?, On this occasion Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about it other…
- √ Definition of One Variable Linear Equation (PLSV) & Examples… Definition of One Variable Linear Equation (PLSV) & Example Problems - In this discussion we will explain about one variable linear equation. Which includes the understanding of the notion of a linear equation one variable and…
- Microscope Images: Definition, History, Types, Parts, How to… Microscope Images: Definition, History, Types, Parts, How Microscopes Work and Care - How close are they do you recognize the shape and function of a microscope? At this time, about the knowledge Microscope…
- Kinds of Numbers: Definition and Examples Kinds of Numbers: Definition and Examples - What are numbers? A number is a collection of numbers that occupy a sequence. On this occasion we will discuss the various types and examples. Let's see for more…
- Types of Color Types: Definition, Characters and Explanations Types of Color Types: Definition, Characters and Explanations - What are the types of colors and their explanations? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course the things that also cover it.…
- Operations to Count Integers & Examples (Discussion… Operations to count integers and complete examples - We need to know that integers has several arithmetic operations, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and rank. Operations to Count Integer &…
- Example of historical story text in Indonesia Examples of historical story texts in Indonesia – What are examples of historical stories like? This time around the knowledge.co.id will discuss examples of historical stories and their structure. Let's take a look at the discussion in the article on…
- 5 Recommended Best Mathematics Learning Applications for 2023 aroundknowledge.co.id - Math learning apps help children improve their understanding of math concepts without solving problems or looking for answers. The Math app introduces all the major math topics in a fun way…
- Roman Numerals: History, Basic Numbers, How to Write, Formulas… Roman Numerals: History, Basic Numbers, How to Write, Formulas and Disadvantages - Do you know what they are Roman numerals and how to read them? covers…
- Definition of Learning Methods: Characteristics, Purpose, Types and… Definition of Learning Methods: Characteristics, Purpose, Types and Discussion - What is meant by Method Learning?, On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things Also…
- Preface: Definition, Structure and Examples Preface: Definition, Structure and Examples - How to write a good Preface ?On this occasion, Around the Knowledge.co.id will discuss what is the Preface and other things about it. Let's see…
