Dynamic fluids: types, characteristics, Bernoulli's equation, Toricelli's theorem, formulas and examples of problems
Dynamic Fluids: Types, Features, Bernoulli's Equation, Toricelli's Theorem, Formulas and Examples of Problems – What is a dynamic fluid and its types? On this occasion, Se regarding the knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things that also cover it. Let's look at the discussion together in the article below to better understand it.
Dynamic fluids: types, characteristics, Bernoulli's equation, Toricelli's theorem, formulas and examples of problems
Fluid is a substance that can flow. The word fluid includes car, water and gas because these two substances can flow, whereas rock and hard objects or all solid substances are not classified as fluids because they cannot flow.
All liquids can be grouped into fluids because they can flow from one place to another. Apart from liquids, gases are also fluids. Gases can also flow from one place to another. Blowing wind is an example of air moving from one place to another.
Fluid is one important aspect in everyday life. Every day humans breathe it, drink it, float or sink in it. Every day airplanes fly through it and ships float above it.
Likewise a submarine can float or float in it. The water we drink and the air we breathe also circulates in the human body all the time, although we often don't realize it.
Dynamic fluids are fluids (can be liquids, gases) that move. For convenience in studying, the fluid here is considered steady (has a constant velocity with respect to time), incompressible (not changing volume), not viscous, not turbulent (not experiencing rounds).
Hydrodynamics is the science that studies fluids in motion. Before studying moving fluids, it is necessary to know the ideal fluid and the types of fluid flow.
Ideal Fluid
An ideal fluid is a fluid that is incompressible, moves without experiencing friction, and has a stationary flow:
- The flow is steady, that is, the velocity of each fluid particle at a certain point is constant, both in size and direction. Steady flow occurs in slow flow.
- The flow is irrational, meaning that at every point the fluid particle has no angular momentum with respect to that point. The flow follows the current line (streamline).
- Incompressible (incompressible), meaning that the fluid does not experience a change in volume (density) due to pressure.
- It is not viscous, meaning that it does not experience friction either with the surrounding fluid layers or with the walls through which it passes. Viscosity in fluid flow is related to viscosity.
Fluid Flow Type
There are several types of fluid flow. The path taken by a fluid in motion is called the flow line. Here are some types of fluid flow, namely as follows:
- Straight or laminar flow is smooth fluid flow. The adjacent layers glide smoothly over each other. In this flow the fluid particles follow a smooth path and these paths do not cross each other. Laminar flow is found in water flowing through pipes or hoses.
- Turbulent flow is flow that is characterized by the presence of erratic circles and resembles a vortex. Turbulent flow is often found in rivers and ditches.
Dynamic Fluid Characteristics
The general characteristics of fluid dynamics are as follows:
- fluid is considered incompatible
- fluid is considered to move without friction, even though there is movement of the material (it has no viscosity)
Fluid flow is stationary flow, that is, the speed and direction of motion of the pulid particles passing through a certain point are always fixed - independent of time (steady), meaning that the velocity is constant at a certain point, and forms a laminar (layered) flow
Dynamic Fluid Formulas
-
debit
Debit is the amount of fluid volume flowing in unit time (generally per second)
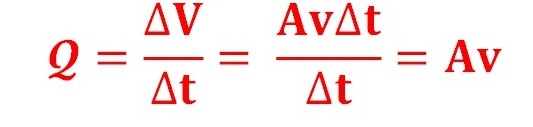
Where :
Q = flow rate (m3/s)
A = cross-sectional area (m2)
V = fluid flow rate (m/s)
Fluid flow is often expressed in terms of flow rate

Where :
Q = flow rate (m3/s)
V = volume (m3)
t = time interval (s)
-
Toricelli's theorem
Toricelli's theorem is a phenomenon of water gushing out of a water tank hole.
The magnitude of the kinetic energy of the water that spurts out of the water tank hole is equal to the magnitude of the potential energy.
Therefore, the speed of the water spraying at the hole is the same as water falling freely from the water level limit.
Because the greater the difference between the height of the hole and the water level limit, the faster the water spray will be.
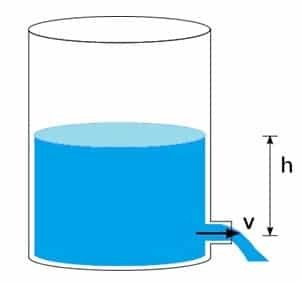
t = √(2H/g)
Information :
v is the velocity of liquid leaving the hole
H is the distance where the liquid (soil) falls to the leak hole
X is the horizontal distance the liquid falls
t is the time it takes for the liquid to touch the ground
h is the distance from the liquid surface to the leak hole
-
Continuity Equation
The continuity equation is an equation that relates the fluid velocity in one place to another.
Before deriving a relationship, it is better to understand some fluid flow terms. The flow line can be interpreted as an ideal fluid flow path (soft flow).
The tangent is at a point on the line that gives the direction of velocity to the fluid flow.
Fluid flow lines do not intersect one another. The water tube is a collection of flow lines.
Q1 = Q2
A1v1 = A2v2
-
Bernoulli's equation
Bernoulli's law is a law that is based on the law of the conservation of energy and is experienced in fluid flow.
This law states that the amount of pressure (p), kinetic energy pressure per unit volume, & potential energy per unit volume, has the same value at every point along a current line.
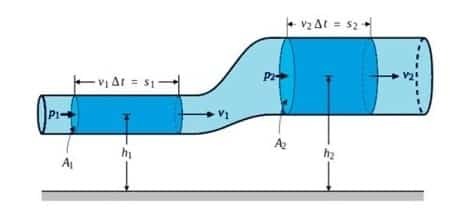
P + 1/2 ρv2 + ρgh = Constant
P1 + 1/2 ρv12 + ρgh1 = P2 + 1/2 ρv22 + ρgh2
Information :
P is pressure (Pascal = Pa = N/m2)
ρ is the density of the fluid; liquid or gas (kg/m3)
g is the acceleration due to gravity (m/s2)
Examples of Dynamic Fluid Problems
Problem 1.
2012/2013 SMA Physics National Examination Questions SA 55 No.15
A large tub filled with water and there is a faucet like the picture. If g = 10 ms-2, then the speed of the water spray from the faucet is...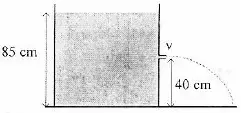
A 3 ms-1
B. 8 ms-1
C. 9 ms-1
D. 30 ms-1
E. 900 ms-1
Discussion
Is known :
Height (h) = 85 cm – 40 cm = 45 cm = 0.45 meters
Acceleration due to gravity (g) = 10 m/s2
Wanted: Speed of water spray from the faucet (v)
Answer :
Torricelli's theorem states that the speed of a jet of water through a hole a distance h from the surface of the water is equal to the speed of free fall of water from a height h.
The speed of the water jet is calculated using the free fall motion formula vt2 = 2 g h
vt2 = 2 g h = 2(10)(0.45) = 9
vt = √9 = 3 m/s
The correct answer is A.
Problem 2.
Pipes for channeling water attached to a wall of the house as shown in the following picture! The ratio of the cross-sectional area of a large pipe and a small pipe is 4: 1.
The position of the large pipe is 5 m above the ground and the small pipe is 1 m above the ground. The velocity of the water flow in the large pipe is 36 km/hour with a pressure of 9.1 x 105 Pa. Define:
a) The velocity of the water in the small pipe
b) Difference in pressure in the two pipes
c) Pressure in small pipe
(ρwater = 1000 kg/m3)
Discussion
Known: h1 = 5 m; h2 = 1m; v1 = 36 km/h = 10 m/s; P1 = 9.1 x 105 Pa; A1: A2 = 4: 1
a) The velocity of the water in the small pipe
Continuity Equation :
A1v1 = A2v2
(4)(10) = (1) (v2)
v2 = 40m/s
b) Difference in pressure in the two pipes
From Bernoulli's Equation:
P1 + 1/2 ρv12 + ρgh1 = P2 + 1/2 ρv22 + ρgh2
P1 − P2 = 1/2 ρ(v22 − v12) + ρg (h2 − h1)
P1 − P2 = 1/2(1000)(402 − 102) + (1000)(10)(1 − 5)
P1 − P2 = (500)(1500) − 40000 = 750000 − 40000
P1 − P2 = 710000 Pa = 7.1 x 105 Pac) Pressure in small pipe
P1 − P2 = 7.1 x 105
9.1 x 105 − P2 = 7.1 x 105
P2 = 2.0 x 105 Pa

Problem 3.
A reservoir filled with water and in the wall there is a hole (see picture). The speed of the water as it exits the hole is… (g = 10 ms-2)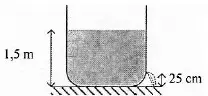
A 12 ms-1
B. 10ms-1
C. 6 ms-1
D. 5 ms-1
E. 2 ms-1
Discussion
Is known :
Height (h) = 1.5 m – 0.25 m = 1.25 meters
Acceleration due to gravity (g) = 10 m/s2
Wanted: Speed of water as it leaves the hole (v)
Answer :
vt2 = 2 g h = 2(10)(1,25) = 25
vt = √25 = 5 m/s
The correct answer is D.
Problem 4.
A tank filled with water 1 meter high (g = 10 ms-2) and on the wall there is a leak hole (see picture). The speed of the water coming out of the hole is...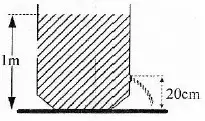 A 1 ms-1
A 1 ms-1
B. 2 ms-1
C. 4 ms-1
D. 8 ms-1
E. 10ms-1
Discussion
Is known :
Height (h) = 1 m – 0.20 m = 0.8 meters
Acceleration due to gravity (g) = 10 m/s2
Wanted: Speed of water as it leaves the hole (v)
Answer :
vt2 = 2 g h = 2(10)(0.8) = 16
vt = √16 = 4 m/s
The correct answer is D.
Problem 5.
A pipe carries water with a discharge of 1M3 every second, and will be used to fill a dam measuring (100 X 100 X 10) M. Then calculate the time required to fill the Dam to the brim!.
Answer :

So the answer is the time needed for the dam to be full, namely 100,000 seconds.
Thus the review from Seputarknowledge.co.id about Dynamic Fluids,hopefully can add to your insight and knowledge. Thank you for visiting and don't forget to read other articles.
List of contents
Recommendation:
- Meaning of Yaumul Milad: Explanation and Replies to His Speech The Meaning of Yaumul Milad: Explanation and Replies to His Sayings - What are the words or sayings of Yaumul Milad? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course things that also…
- Acid-Base Solutions: Definition, Acid-Base Theory, Properties and… Acid-Base Solutions: Definition, Acid-Base Theory, Properties and Types - Acid and base solutions are two groups of chemical compounds that are widely found and used in everyday life.
- Definition of Floor Gymnastics: History, Types, Elements and… Definition of Floor Gymnastics: History, Types, Elements and Benefits of Floor Gymnastics - What is Floor Gymnastics and examples? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss Floor Gymnastics...
- Covalent Bonds: Definition, Characteristics, Types, Formulas… Covalent Bonds: Definition, Characteristics, Types, Chemical Formulas and Properties of Compounds - What is a covalent bond? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things as well covered it. Let…
- Motivational short stories: definition, writing tips and examples Motivational Short Stories: Definition, Writing Tips and Examples - What is a Motivational Short Story?, On On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss whether it is the Short Story of Friendship and other things about it. Let's see…
- Characteristics of Planets: Types of Planets and Their Characteristics Characteristics of Planets: Types of Planets and Their Characteristics - What are the characteristics that a planet must have Planet?, On this occasion, Around the Knowledge.co.id will discuss it, including objectives, examples and naturally…
- Types of Energy: Understanding According to Experts, Properties and… Types of Energy: Understanding According to Experts, Properties and Examples of Energy Changes - What are they what kind of energy is there? naturally…
- √ 14 Examples of Renewable Natural Resources 14 Examples of Renewable Natural Resources - On this occasion, Around Knowledge explains about Natural Resources. Which in this discussion discusses several types and examples…
- Megalithic: Definition, Characteristics, Belief Systems and… Megalithic: Definition, Characteristics, Belief Systems and Legacy - What is meant by Megalithic and when did it occur? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss what is Megalithic and other things...
- Archimedes' Law: Definition, Sound, Formula, Application,… Archimedes' Law: Definition, Sounds, Formulas, Application, Example Problems - In this discussion we will explain about Archimedes' law. Which includes the understanding of Archimedes' law, the sound of Archimedes' law, the formula of Archimedes' law,…
- Class 6 Farewell Speech Text: Main Contents, Characteristics,… Farewell Speech Text for Class 6: Main Contents, Characteristics, Purpose and Examples of Speeches - What is the composition of the text of farewell speech for class 6 which is good and true and touching?
- 74 Definition of Education According to Experts 74 Definition of Education According to Experts – Humans have been educated since they were born into the world until they enter school. The word education is no longer foreign to our ears, because all...
- Cone formulas, characteristics, properties, elements and examples of problems Cone Formulas, Characteristics, Properties, Elements and Examples Problem - How to calculate the area and volume of a shape cone space?, On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things Which…
- Three Variable Linear Equation System: Features, Components,… System of Three Variable Linear Equations: Features, Components, Solving Methods and Example Problems - What is in what do you mean by a system of three-variable equations? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it...
- Computer Hardware: How it Works, Types, Examples and… Computer Hardware: How it Works, Types, Examples and Functions - In today's computerized era, we are definitely familiar with computers and their devices. However, some may not know...
- Standby Scout Material: Ranks, Honor Codes and Requirements… Standby Scout Materials: Ranks, Honor Codes and General Proficiency Requirements - What are the materials for alert level scouts? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it, including the level of alert scouts,…
- Pencak Silat: Definition, History, Characteristics, Purpose, Techniques,… Pencak Silat: Definition, History, Characteristics, Purpose, Techniques, and Levels - Does anyone know what it is Pencak Silat? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss Pencak Silat and other things other…
- Boyle's Law: Definition, Formulas, Applications and Examples… Boyle's Law: Definition, Formulas, Applications and Examples of Problems - In this discussion we will explain about Boyle's law. Which includes the meaning of Boyle's law, the Boyle's law formula, the application of…
- Types of Drones, Terms, Parts, Basic Principles And… Types of Drones, Terms, Parts, Basic Principles and Movement - What are the types of drones and function?, On this occasion Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course other things Also…
- Inclined Plane: Definition, Formulas, Mechanical Advantage And… Oblique Plane: Definition, Formulas, Mechanical Advantages and Examples of Problems - What is meant by plane oblique and how to calculate the physics? naturally…
- Example of historical story text in Indonesia Examples of historical story texts in Indonesia – What are examples of historical stories like? This time around the knowledge.co.id will discuss examples of historical stories and their structure. Let's take a look at the discussion in the article on…
- Mental Verbs: Definition, Characteristics, Types, and Examples Mental Verbs: Definition, Characteristics and Examples - What is a mental verb?, On occasion This time around the knowledge.co.id will discuss it, including features, examples and of course other things as well covered it. Let…
- Preface: Definition, Structure and Examples Preface: Definition, Structure and Examples - How to write a good Preface ?On this occasion, Around the Knowledge.co.id will discuss what is the Preface and other things about it. Let's see…
- Rain Occurrence Process: Types and Forms of Rain The Process of Rain: Types and Forms of Rain - How does the process of rain take place?, On On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss this and of course other things as well covered it. Let's see together…
- Alternative Energy: Understanding According to Experts, Characteristics,… Alternative Energy: Understanding According to Experts, Characteristics, Benefits, Terms and Types - What is energy alternative?, On this occasion Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things Also…
- Friendship Short Stories: Definition, Writing Tips and Examples Friendship Short Stories: Definition, Writing Tips and Examples - What are Friendship Short Stories like? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss whether it is the Short Story of Friendship and other things about it. Let's see together…
- √ Natural Gas: Definition, Composition, Types, Benefits and… Natural Gas: Definition, Composition, Types, Benefits and Properties - On this occasion, Around Knowledge will discuss Natural Gas. Which in this discussion explains the meaning of natural gas,…
- Types of Color Types: Definition, Characters and Explanations Types of Color Types: Definition, Characters and Explanations - What are the types of colors and their explanations? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course the things that also cover it.…
- Vacuoles Are: Characteristics, Functions, Structures and… Vacuoles Are: Characteristics, Functions, Structures and Types - Is that what is called a vacuole plants and animals?, On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about matter…
- LHO Text: Definition, Characteristics, Characteristics, Purpose, Functions,… LHO Text: Definition, Characteristics, Characteristics, Purpose, Function, Structure, Linguistic Rules and Examples - What is what do you mean by LHO Text or Observation Report Text? On this occasion About knowledge.co.id…
