The Nitrogen Cycle: Definition, Process, Form and Examples
The Nitrogen Cycle: Definition, Process, Forms and Examples – What is the nitrogen cycle?, On this occasion About the knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things that also cover it. Let's look at the discussion together in the article below to better understand it.
The Nitrogen Cycle: Definition, Process, Form and Examples
Nitrogen or N is one of the most abundant elements in the atmosphere, which is about 78% of the gas in the atmosphere is nitrogen.
But the use of nitrogen in the biological field is minimal. Nitrogen is one of the elements that is not reactive because it is difficult to react with other elements, so the use of this element is like In living things, various processes are needed, these processes include: nitrogen fixation, mineralization, nitrification, denitrification.
Nitrogen is needed by plants in very large quantities, and this is certainly one of the limiting factors in soils that are not fertilized.
The form is in the form of amino acids, namely amides and amines which have a function as a framework or building blocks and intermediate compounds in the form of protein, chlorophyll and acids nucleate. Proteins or enzymes will regulate biochemical reactions.
Nitrogen is a complete part of the chlorophyll structure. The availability of nitrogen elements certainly affects the ecosystem level which includes primary productivity and decomposition processes.
Activities such as fuel combustion and the use of nitrogen fertilizers as well as the discharge of nitrogen into wastewater can change the nitrogen cycle as a whole or globally.
Nitrogen is an essential element for all purposes for the continuity of life on earth. Nitrogen is a basic component of amino acids and proteins, bases derived from nucleic acids consisting of nitrogen, such as DNA and RNA.
Whereas in plants, chlorophyll molecules use nitrogen in large enough quantities in the process of photosynthesis.
The nitrogen cycle is a process of converting compounds containing the element nitrogen which then turns into other chemical forms.
Nitrogen Cycle Process
Nitrogen is spread in various forms, such as organic nitrogen and ammonium, nitrogen oxides and nitrates, nitric oxide and nitrites or inorganic nitrogen gas.
Nitrogen in organic form can be used as living cells or living organisms / humus / in the form of intermediate products in the decomposition of organic matter.
The process of the nitrogen cycle will change nitrogen from one elemental form to another. It should be noted that most of the transformation process is carried out by microorganisms.
Stages The nitrogen cycle has several stages, including:
nitrogen fixation
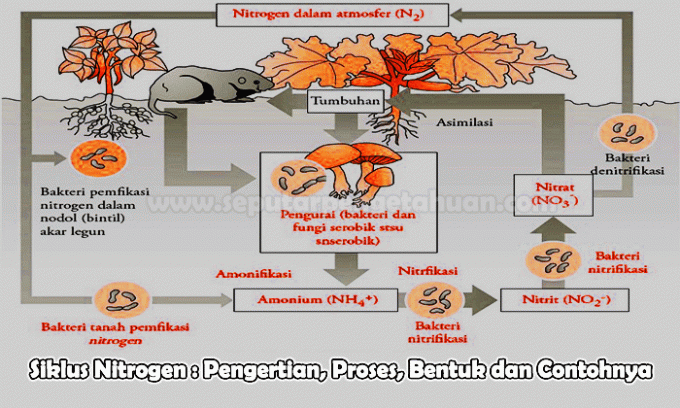
Nitrogen fixation process is a process of converting nitrogen in the atmosphere into ammonia. This process is carried out by bacteria that are in the roots of legume plants.
This process is the conversion of nitrogen gas into ammonia through the stages of biological fixation. Several groups of small bacteria such as rhizobium and cyanobacteria use the enzyme nitrogenase involved to convert the nitrogen gas into ammonia.
Nitrification
Nitrification is the biological oxidation of ammonia with oxygen to ammonium and then to nitrite which is followed by the oxidation of nitrite to this nitrate. The degradation of ammonia to nitrite is known as nitrification.
This is an important step in the soil nutrient cycle. This process is carried out by autotrophic bacterial species with several types of ammonia oxidizing bacteria viz ß-Proteobacteria and gammaproteobacteria and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria of the genera nitrosomonas and also nitrosococcus.
Assimilation
Nitrogen assimilation is the formation of organic nitrogen compounds, for example amino acids from inorganic nitrogen compounds present in the environment.
After the nitrification process is carried out by bacteria, plants will absorb nitrogen in the form of nitrate. Then the nitrate proton transporter gradient will absorb nitrate to the plant and then nitrate is transported from roots to shoots via xylem.
Reduction of nitrogen that occurs is carried out in the shoots in two steps, namely nitrate will be reduced to nitrite by reductase nitrate in the cytosol and nitrite in the chloroplast will be reduced to ammonia by reductase nitrite.
Ammonification
Ammonification is a stage in the nitrogen cycle where plant residues and waste products are decomposed by microorganisms to produce ammonia.
Microorganisms in the soil will eat dead organic matter which will then become energy and will later be produce ammonia as well as other basic compounds which will be by-products of yang metabolism happen. This ammonia will be retained in the soil in the form of ammonium ions.
Denitrification
Denitrification is the process of reducing nitrate to inert nitrogen gas which will complete the nitrogen cycle. Denitrification is usually carried out by bacterial species such as Pseudomonas and also Clostridium under anaerobic conditions.
During the respiration process, bacteria will use nitrate as an electron acceptor. Bacteria that can survive in aerobic conditions are facultative anaerobic bacteria.
Forms of the Nitrogen Cycle in Nature
The process of the nitrogen cycle converts nitrogen from one form to another chemical form. Many of the processes carried out by microbes are either to produce energy or to store nitrogen in a form required for growth. The diagram below shows how the processes in the nitrogen cycle.
Nitrogen in the environment exists in various chemical forms including organic nitrogen, ammonium (NH4+), nitrites (NO2-), nitrates (NO3-), and gaseous nitrogen (N2). Organic nitrogen can be in the form of living organisms, or humus, and in the intermediate products of the decomposition of organic matter or built up humus. The process of the nitrogen cycle converts nitrogen from one chemical form to another. Many of the processes carried out by microbes are either to produce energy or to store nitrogen in a form required for growth.
Ammonia
Ammonia and its salts are easily soluble in water. The source of ammonia in the waters is the breakdown of organic nitrogen (protein and urea) and inorganic nitrogen found in soil and water, which originates from the decomposition of organic matter by microbes and fungi (ammonification).
The source of ammonia is the reduction of nitrogen gas originating from the diffusion process of atmospheric air, industrial and domestic waste. Ammonia contained in minerals enters water bodies through soil erosion. Apart from being present as a gas, ammonia forms complex compounds with several metal ions.
Ammonia can also be absorbed into suspended and colloidal materials so that it settles to the bottom of the waters. Ammonia in water can disappear through the volatilization process because the partial pressure of ammonia in solution increases with increasing pH.
Nitrite
Sources of nitrite can be in the form of industrial waste and domestic waste. The level of nitrite in the water is relative because it is immediately oxidized to nitrate. Natural waters contain about 0.001 mg/liter of nitrites. In waters, nitrites are found in very small amounts, less than nitrates, because they are unstable in the presence of oxygen. Nitrite is an intermediate form between ammonia and nitrate (nitrification) and between nitrate and nitrogen gas (denitrification) which is formed under anaerobic conditions.
Nitrate
Nitrate is the main source of nitrogen in waters, but ammonium is preferred by plants. Nitrate levels in unpolluted waters are usually higher than ammonium levels. Nitrate levels of more than 5 mg/liter illustrate the occurrence of anthropogenic pollution originating from human activities and animal feces.
Nitrogen levels that are more than 0.2 mg/liter indicate eutrophication of waters. Nitrate is a form of nitrogen as the main nutrient for plant and algae growth. Nitrate nitrogen is very soluble in water and is stable. This compound is produced from a complete oxidation process in water.
Nirogen Cycle Example
Examples of the nitrogen cycle include:
Plants need nitrogen from the soil by absorbing it through their roots. Nitrogen comes in the form of nitrogen ions. When nitrogen is absorbed by plants, it is reduced to nitrite ions. Then it becomes ammonium ion which can be incorporated into amino or nucleic acids and into chlorophyll.
When plants die or animals die or when a factory or sewage system expels animals, organic nitrogen is then released. Bacteria can convert this organic nitrogen into ammonium. This is done through a process known as mineralization.
Nitrogen enters the oceans due to runoff from groundwater or when it rains. Nitrogen can also enter the sea through precipitation "rain", nitrogen in the water undergoes fixation which is generally facilitated by bacteria called cynobacteria. After fixation, nitrogen in a biologically available form in the marine phytoplankton can be used.
Plankton secretes both urea and ammonia into the water. Phytoplankton and waste products can sink to the bottom, introducing ammonia at depths into the euophotic zone. Ammonia from this waste product is then excreted from the euphotic zone and bacteria living below the euphotic zone can convert the ammonia to nitrate.
This conversion can only occur under the euphotic zone where there is no light because the bacteria carrying out the conversion are inhibited by light. This conversion process is called ammonification or mineralization.
After the ammonia is converted, nitrification occurs and the ammonia is converted into nitrites and nitrates, and partical mixing upwelling can carry nitrate upwards and then it can be used by photoplankton to continue cycle.
Thus the review from About the knowledge.co.id about The Nitrogen Cycle: Definition, Process, Form and Examples, hopefully can add to your insight and knowledge. Thank you for visiting and don't forget to read other articles.
List of contents
Recommendation:
- Pencak Silat: Definition, History, Characteristics, Purpose, Techniques,… Pencak Silat: Definition, History, Characteristics, Purpose, Techniques, and Levels - Does anyone know what it is Pencak Silat? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss Pencak Silat and other things other…
- Covalent Bonds: Definition, Characteristics, Types, Formulas… Covalent Bonds: Definition, Characteristics, Types, Chemical Formulas and Properties of Compounds - What is a covalent bond? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things as well covered it. Let…
- Types of Official Letters, Characteristics, Functions and Examples Types of Official Letters, Characteristics, Functions and Examples - What are the types of official letters? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things as well covered it. Let…
- Branches of Biology: Functions, Benefits and Explanations Branches of Biology: Functions, Benefits and Explanations - What are the branches of Biology? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it, including functions and of course other things as well covered it. Let…
- Factors Inhibiting Social Mobility: Definition, Factors… Inhibiting Factors of Social Mobility: Definition, Driving Factors and Explanations - What is the meaning of social mobility and What are the inhibiting factors? On this occasion, about the knowledge of Knowledge.co.id will discuss it, including nutritional content and naturally…
- √ Definition of the Solar System, Theory Formed and Its Structure… Definition of the Solar System, Formed Theory and Structure (Complete) - In this discussion we will explain about the solar system. Which includes the understanding of the solar system, the theory of the formation of the solar system, and the arrangement of the solar system...
- Respiratory Plant Plants: Definition, Types, Process… Respiratory Organs of Plants: Definition, Types, Respiration Process and Relationship of Respiration with Photosynthesis – Anything and how does the process of breathing plants? Of course…
- Crude Oil is: Definition, History, Stages of Processing &… Petroleum is: Definition, History, Stages of Processing & Its Use - In this discussion, you will learn about Petroleum. Which includes understanding, history, stages of processing and use of petroleum...
- Preface: Definition, Structure and Examples Preface: Definition, Structure and Examples - How to write a good Preface ?On this occasion, Around the Knowledge.co.id will discuss what is the Preface and other things about it. Let's see…
- Definition of Chemical Elements and Their Grouping (Discussion… Definition of Chemical Elements and Their Grouping (Full Discussion) - Here will be discussed about understanding of chemical elements, grouping or division of chemical elements based on their nature and based on his discovery. Let's look at the discussion below...
- Mangrove Forests Are: Characteristics, Benefits, Causes of Damage And… Mangrove Forests Are: Characteristics, Benefits, Triggers of Damage and Countermeasures - What is meant by forest mangroves and their functions? On this occasion, Se regarding the knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about it other…
- Papers: Definition, Characteristics, Functions, Types, Structures, Methods… Papers: Definition, Characteristics, Functions, Types, Structure, How to Make and Examples - What is meant by Papers and how to write them properly and correctly? On this occasion Seputarknowledge.co.id will…
- Metamorphosis Is: Definition, Phases, Types and Examples Metamorphosis Is: Definition, Phases, Types and Examples - What is Metamorphosis? Metamorphosis is defined as the process of development of living things that was originally an egg to mature perfectly and experience something…
- Islamic Words of Wisdom Islamic Words of Wisdom - On this occasion, SeputihKnowledge.co.id will discuss Islamic Words of Wisdom and examples. Let's look at the discussion together in the article below to get more...
- Belief in the Last Days: Definition, Proof, Signs of the Last Hour,… Belief in the Last Days: Definition, Propositions, Signs of the Last Days, Events at the End of Days, Their Functions and Lessons - What is the Meaning of Faith in the Last Day and Its Benefits?
- Linguistic Elements of Explanatory Text: Characteristics, Structure, Types,… Linguistic Elements of Explanatory Text: Definition, Characteristics, Structure, Types and Examples - What is explanatory text with its linguistic elements? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss what is explanatory text and element…
- Example of historical story text in Indonesia Examples of historical story texts in Indonesia – What are examples of historical stories like? This time around the knowledge.co.id will discuss examples of historical stories and their structure. Let's take a look at the discussion in the article on…
- Scope of Psychology: Definition, Kinds, Tasks and… Scope of Psychology: Definition, Kinds, Tasks and Methodology of Psychological Research - What is the scope psychology? On this occasion, Around the Knowledge.co.id will discuss what psychology is and what it is covered it. Let us…
- Example of Cultural Arts Questions for Class 10 (X) SMA/MA/SMK Semester 1… Examples of Class 10 (X) Cultural Arts Questions for SMA/MA/SMK Semesters 1 and 2 (2019 and 2020) - On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss Multiple Choice Class 10 Cultural Arts Questions and Essay…
- Understanding the Atmosphere, Layers and Its Utilization (Complete) Understanding the Atmosphere, Layers and Its Utilization (Complete) – Of course we all have often heard the word atmosphere, but in fact many of us still don't know the definition of the atmosphere And…
- Qiyas: Definition, Pillars, Propositions, Elements, Conditions and… Qiyas: Definition, Pillars, Postulates, Elements, Terms and Distribution - What is meant by Qiyas? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course other things that also cover it. Let…
- Humans As Individual Beings and Social Beings Humans As Individual Beings and Social Beings - Why is that, humans are the most perfect creatures in this universe, because they have reason to think. The word Human comes from…
- DNA and RNA: Definition, Characteristics, Differences and… DNA and RNA: Definition, Characteristics, Differences and Discussion of the Process - What are the meanings and differences of DNA and RNA? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course other things that...
- Microscope Images: Definition, History, Types, Parts, How to… Microscope Images: Definition, History, Types, Parts, How Microscopes Work and Care - How close are they do you recognize the shape and function of a microscope? At this time, about the knowledge Microscope…
- The Political Life of the Majapahit Empire: Early History and… The Political Life of the Majapahit Kingdom: Early History and Legacy - How was the Political Life of the Kingdom Majapahit? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss the Majapahit Kingdom and other things covered it. Let's look at the discussion together...
- Movement System in Humans: Bones, Joints, Muscles,… Movement System in Humans: Bones, Joints, Muscles, Functions, Abnormalities and Disturbances - What are the systems motion in the human body?, On this occasion, Se regarding the knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about…
- LHO Text: Definition, Characteristics, Characteristics, Purpose, Functions,… LHO Text: Definition, Characteristics, Characteristics, Purpose, Function, Structure, Linguistic Rules and Examples - What is what do you mean by LHO Text or Observation Report Text? On this occasion About knowledge.co.id…
- Branches of Biology and Explanation Branches of Biology and Explanations - Branches of biology are various sciences developed from the field of biology. Biology is a science which studies the ins and outs of living things. Where…
- √ Definition of Living in Harmony, Benefits, Values, Forms and… Understanding Living in Harmony, Benefits, Values, Forms and Examples - On this occasion, Around Knowledge will discuss Living in Harmony. Which in this discussion explains the meaning of living in harmony, benefits,…
- 2 Dimensional Art Works: Definition, Techniques, Elements, Media… 2 Dimensional Art Works: Definition, Techniques, Elements, Media and Examples - What is meant by 2 Dimensional Art Works?
