Parts of the Skin: Epidermis, Dermis, Structure and Functions
Parts of the Skin: Epidermis, Dermis, Structure and Functions – On this occasion About the knowledge.co.id will discuss the parts of the skin and of course about other things that also cover it. Let's look at the discussion together in the article below to better understand it.
Parts of the Skin: Epidermis, Dermis, Structure and Functions
The skin is the organ that covers the entire outer surface of the body, is the heaviest and largest organ of the body. The whole skin weighs about 16% of body weight, in an adult it is about 2.7 - 3.6 kg and has an area of about 1.5 - 1.9 square meters.
The thickness of the skin varies from 0.5 mm to 6 mm depending on the location, age and sex. Thin skin lies on the eyelids, penis, labium minus and the skin of the medial upper arm. Meanwhile, thick skin is found on the palms, soles of the feet, back, shoulders and buttocks.
Embryologically the skin is derived from two different layers, the outer layer is the epidermis which is the epithelial layer derived from the ectoderm while the inner layer derived from the mesoderm is the dermis or corium which is a layer of tissue tie. (Ganong, 2008).
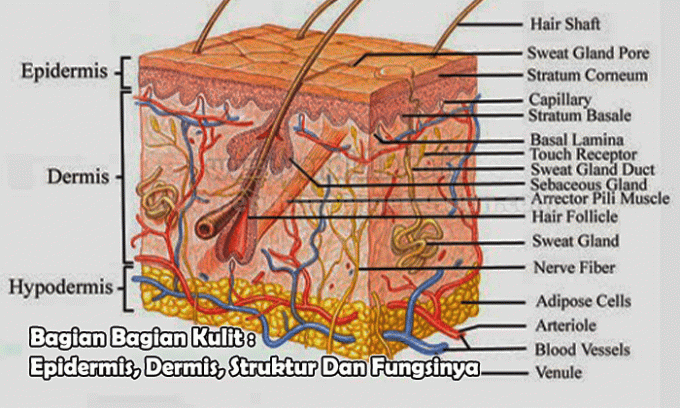
Skin Layer Structure
-
Ari Skin (Epidermis)
The epidermis is the outer layer of skin which is thin and avascular. Consist of horny stratified squamous epithelium, containing melanocytes, Langerhans and Merkel cells. The thickness of the epidermis varies in various places on the body, being thickest on the palms and soles.
The thickness of the epidermis is only about 5% of the total thickness of the skin. Regeneration occurs every 4-6 weeks. The epidermis consists of five layers (from top to deep):
- Stratum Corneum
Consists of keratinocyte cells that can slough off and replace.
- Stratum Lucidum
In the form of translucent lines, usually found on the thick skin of the soles of the feet and palms. Not visible on thin skin.
- Stratum Granulosum
Characterized by 3-5 layers of flattened polygonal cells whose core is in the middle and the cytoplasm is filled with coarse basophilic granules called keratohyalin granules which contain protein rich in histidine. There are Langerhans cells.
- Stratum Spinosum
There are bundles of filaments called tonofibrils, which are thought to play an important role in maintaining cell cohesion and protecting against the effects of abrasion. The epidermis in places that are constantly subjected to friction and pressure has a stratum spinosum with more tonofibrils. The stratum basale and stratum spinosum are known as the Malpighian layers. There are Langerhans cells.
- Stratum Basale (Stratum Germinativum)
There is intense mitotic activity and is responsible for the constant renewal of epidermal cells. The epidermis is renewed every 28 days to migrate to the surface depending on location, age and other factors. Is a single layer of cells that contain melanocytes.
Epidermis Function: Barrier protection, cell organization, synthesis of vitamin D and cytokines, cell division and mobilization, pigmentation (melanocytes) and allergen recognition (Langerhans cells) (Wasitaatmadja, 1997).
The function of the epidermis (epidermis) is
to protect the body from various chemical substances from outside the body,
protect the body from UV rays,
protect the body from bacteria.
-
Skin Hides (Dermis)
Is the most important part of the skin which is often considered as "True Skin". It consists of connective tissue that supports the epidermis and connects it to the subcutaneous tissue. The thickness varies, the thickest on the soles of the feet is about 3 mm.
The dermis consists of two layers:
- papillary layer; thin containing sparse connective tissue.
- reticular layer; thick layer of dense connective tissue.
Collagen fibers thicken and collagen synthesis decreases with age. Elastin fibers continue to increase in number and thicken, the elastin content of human skin increases approximately 5 times from fetus to adulthood.
In old age collagen crosses over to each other in large quantities and elastin fibers decrease causing the skin to lose its elasticity and appear to have many wrinkles. The dermis has a rich network of blood vessels.
The dermis also contains several epidermal derivatives, namely hair follicles, sebaceous glands and sweat glands. The quality of the skin depends on the number of epidermal derivatives in the dermis. Functions of the Dermis: supporting structure, mechanical strength, supply of nutrients, resisting shearing forces and inflammatory responses (Wasitaatmadja, 1997).
The skin or also the dermis is a second layer of skin. The boundary with the epidermis is lined with a basement membrane. The dermis or the hide layer is thicker than the epidermis. The dermis has elastic fibers that allow the skin to stretch when the person is getting fatter, and the skin can sag when the person is thin.
In the inner layer of the dermis there are also various kinds of layers. The layers of the dermis include the following...
- The capillary vessels function to be able to deliver nutrients or nutrients to the hair roots and skin cells
- The sweat glands (glandula sudorifera) are scattered throughout the skin and also function to produce sweat which is released through the pores of the skin.
- The oil glands (grandula sebaceae) function to produce oil so that the skin and hair are not dry and wrinkled
- Hair glands, have roots as well as the hair shaft and hair oil glands. when it's cold and also fear, the hair on our body will stand up. This is because near the hair root there is smooth muscle which has a function in pulling hair down.
-
Connective Tissue Under the Skin (Hypodermis)
The connective tissue under the skin is under the dermis. This tissue does not have a clear boundary with the dermis, that is, as a rule, within its boundaries, there is a fat cell. there is a lot of fat in this layer of skin. The function of the layer of fat is to be able to protect the body from collisions, namely as a source of reserve energy and also retain body heat.
Subcutis Is the layer below the dermis or hypodermis which consists of a layer of fat. This layer contains connective tissue that connects the skin loosely with the underlying tissue. The number and size vary according to the area of the body and the nutritional state of the individual.
Serves to support the blood supply to the dermis for regeneration. Subcutis / hypodermis functions: attached to the base structure, heat insulation, calorie reserve, shape control and mechanical shock absorber. (Wasitaatmadja, 1997).
Receptors that quickly adapt in the skin are tactile (touch) receptors in the skin that tell about changes in pressure on the surface of the skin. Because these receptors adapt quickly, a person does not realize he is wearing a watch, ring and so on.
When wearing something, you will get used to it because of the fast adaptation of the receptors. When uninstalling it, you will notice it because of an off response (Sherwood, 2001).
The adaptation mechanism for the Pacinian corpuscle, a skin receptor that detects pressure and vibration, is known from its physical properties. The Pacinian corpuscle is a specialized receptor terminal consisting of concentric layers of onion skin-like connective tissue covering the peripheral end of an afferent neuron (Sherwood, 2001).
Each sensory neuron responds to sensory information in only a limited area on the surface of the surrounding skin, this area is known as the receptive field. The size of the receptive field varies inversely with the density of receptors in that area.
The closer the placement of certain types of receptors, the smaller the skin area that is monitored by these receptors. The smaller the receptive field in an area, the greater the acuity or discriminatory ability (Sherwood, 2001).
The arteries that nourish the skin form a plexus located between the papillary and reticular layers of the dermis and additionally between the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. Small branches leaving this plexus supply the papillary dermis, each papilla having one ascending artery and one venous branch.
The hypodermis consists of 4 main elements, namely:
Tissue or layer of fat that varies in thickness and depth. The thickest layer is in the buttocks area, while the thinnest layer is in the eyelid area.
Connective tissue under the skin that functions to support the inner body from collisions, forms body contours, and serves as a food reserve.
Fibroblasts are responsible for producing collagen which is then distributed to the dermis layer to strengthen the skin.
Blood and lymph vessels which are nerves that run parallel to the surface of the skin.
Skin Function
In general, the skin has a function. The functions of the skin include the following:
- Protection Function.
The skin functions in protecting the inside of the body against physical disturbances outside the body. For example, friction, pressure, pull and so forth - Absorption Function.
It is easier for the skin to absorb what evaporates from liquid or solid objects, as well as those that dissolve like fat. - Excretion Function.
The glands in the skin will secrete substances that are not useful as a result of metabolism in the body. - Perception Function.
The skin contains sensory nerve endings in the dermis as well as the subcutis. Against a hot stimulus played by the subcutis bodies as well as ruffini dermis - Body temperature regulation function
- Pigment Formation Function.
Pigment-forming cells (melanocytes in the basal layer as well as cells derived from the neural ridges). - Keratinization Function.
There are three layers of the mature epidermis, namely the melanocytes, keratinocytes, and Langerhans cells
Formation of Color on the Skin
The color of the skin is influenced by two factors, namely the pigmentation of the epidermis and the capillary circulation in the dermis layer. Epidermal pigmentation is influenced by two pigments, namely carotene and melanin.
Carotene is a red-orange pigment that accumulates in the epidermis. Most abundant in the stratum corneum in light-skinned people, also in the adipose tissue in the dermis and subcutis.
The discoloration caused by carotene is most noticeable in people with pale skin, whereas it is difficult to see in people with dark skin. Carotene can be converted into vitamin A which is necessary for epithelial maintenance and photoreceptor synthesis in the eye.
Melanin is a yellow-brown, or black pigment produced by melanocytes. Melanocytes themselves are located between the basal cells and have projections to the cells above them. The ratio of the number of melanocytes to basal cells varies from 1:20 to 1:4.
The Golgi apparatus of melanocytes forms melanin from tyrosine with the help of Cu and oxygen, then packages it into melanosome vesicles. These melanosomes will be delivered through the projections of the melanocytes and stain the keratin cells above them until they are degraded by lysosomes.
The number of melanocytes in both blacks and whites is the same, what is different is the activity and production of pigment (melanocytes). In people with pale skin, the transfer of melanosomes is only limited to the stratum spinosum, whereas in people with dark skin, melanosomes can be delivered up to the stratum granulosum.
Blood circulation in the capillaries in the dermis also plays a role in determining skin color. Hemoglobin whose function is to transport oxygen is a pigment. When bound with oxygen, hemoglobin is bright red, giving the capillaries a red coloring.
Thus the review from About the knowledge.co.id about Skin Parts, hopefully can add to your insight and knowledge. Thank you for visiting and don't forget to read other articles.
List of contents
Recommendation:
- Purpose of Explanatory Text: Definition, Structure, Characteristics, Rules,… Purpose of Explanatory Text: Definition, Structure, Characteristics, Rules, Examples - In this discussion we will explain about explanatory text. Which includes the understanding of explanatory text, the purpose of explanatory text, the structure of the text...
- √ Definition of Typography, Functions, Elements & Their Classification… Definition of Typography, Functions, Elements & Classification (Complete) – On this occasion, About Knowledge will discuss Typography. Which in this discussion explains the meaning of typography, functions, elements and their classification with…
- Prayer and Dhikr After Prayer Prayer and Dhikr After Prayer - How are the readings of Prayer and Dhikr after prayer? Let's look at the discussion together...
- Types of Color Types: Definition, Characters and Explanations Types of Color Types: Definition, Characters and Explanations - What are the types of colors and their explanations? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course the things that also cover it.…
- Nutrition: Definition, Types, Kinds and Benefits Nutrition: Definition, Types, Kinds and Benefits - In the body of living things there are lots of organs in it that work continuously with one another. And when someone…
- News Text: Definition, Characteristics, Elements, Structure, Terms,… News Text: Definition, Characteristics, Elements, Structure, Terms, Language Rules, Writing Guidelines and Examples - What is meant by News Text? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss about...
- Physical Fitness: Definition, Components, Concepts, Elements,… Physical Fitness: Definition, Components, Concepts, Elements, Purpose, Benefits and Forms of Exercise - What's in What do you mean by physical fitness? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss fitness Physical and…
- √ Ocean: Definition, Formation Process and… Ocean: Definition, Formation Process and Its Characteristics - On this occasion, Around Knowledge will discuss Oceans. Which in this discussion explains the meaning of oceans, the process of forming oceans, the names…
- Class 6 Farewell Speech Text: Main Contents, Characteristics,… Farewell Speech Text for Class 6: Main Contents, Characteristics, Purpose and Examples of Speeches - What is the composition of the text of farewell speech for class 6 which is good and true and touching?
- Big Ball Game: Definition, Types, and Explanations Big Ball Game: Definition, Types, and Explanations - What is meant by big ball game? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course other things that also cover it.…
- DNA and RNA: Definition, Characteristics, Differences and… DNA and RNA: Definition, Characteristics, Differences and Discussion of the Process - What are the meanings and differences of DNA and RNA? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course other things that...
- High Jump: Definition, History, Style, Technique, Rules… High Jump: Definition, History, Style, Technique, Rules, Stages and Forms of Course - Is it a sport High Jump? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss High Jump and other things Which…
- Soccer Material: Definition, Benefits, Goals, Techniques,… Football Material: Definition, Benefits, Goals, Techniques, Football Rules - Of course we all know what football is, right? Football is a sport that is very popular and very…
- Understanding the Position of Indonesian Astronomy and Its Influence… Understanding Indonesian Astronomical Positions and Their Influences (Complete) - Astronomical positions have existed since time immemorial. It's been a long time since sailors, drivers, pilots or jobs related to the location of their area determine it by…
- Long Jump: Definition, History, Technique, Style and… Long Jump: Definition, History, Technique, Style and Rules - What is called the Long Jump ?On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss what the Long Jump is and other things about it. Let…
- Definition of Plastids: Function, Structure, Characteristics, Types,… Definition of Plastids: Function, Structure, Characteristics, Types, Classification and Differences with Mitochondria - What is what do you mean by plastids?, On this occasion Se regarding the knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about matters other…
- Examples of Scientific Work: Functions and Rules of Language Examples of Scientific Papers: Functions and Rules of Language - What are examples of good and correct forms of writing scientific papers? Previously, Seputar the knowledge.co.id has discussed Scientific Work: Definition, Characteristics, Benefits,…
- Unit of Weight: Definition, Conversion Ladder and Examples… Unit of Weight: Definition, Conversion Ladder and Example Problem - What is a Unit of Weight?, On this occasion About the knowledge.co.id will discuss it, including understanding and of course other things as well covered it. Let…
- Cartesian Coordinates: Definition, System, Diagram and Examples… Cartesian Coordinates: Definition, Systems, Diagrams and Example Problems - What do you mean by Cartesian coordinates ?On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss Cartesian coordinates and other things covers it.…
- Branches of Biology: Functions, Benefits and Explanations Branches of Biology: Functions, Benefits and Explanations - What are the branches of Biology? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it, including functions and of course other things as well covered it. Let…
- Reading the Dead Prayer Reading the Dead Prayer - How is the reading in the Dead Prayer or the Body and the Procedure?, At On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss this and of course other things as well covered it. Let's see together…
- Unit Conversion: Definition, Factor, Length, Mass, Time,… Unit Conversion: Definition, Factor, Length, Mass, Time, Volume and Pressure - What is unit conversion?, On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it, including factors, types and of course other things Which…
- Kutai Kingdom: Founder, Lineage, Heyday and… Kutai Kingdom: Founder, Lineage, Heyday and Fall and Legacy - What is the history of the kingdom Kutai, which is located in Kalimantan? On this occasion, Se regarding the knowledge.co.id will discuss the kingdom of Kutai And…
- Optical Instruments: Definition, Functions, Types and Parts Optical Instruments: Definition, Functions, Types and Parts - What are optical devices and what are their types? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course other things that...
- Examples of Ovoviviparous Animals: Definition, Characteristics and Explanations Examples of Ovoviviparous Animals: Definition, Characteristics and Explanations - What are examples of ovoviviparous animals? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss Ovoviviparous animals and things about them. Let's take a look at the discussion on…
- Female Reproductive Organs1 and Their Functions Female Reproductive Organs1 and Their Functions – Living things that live on earth have the ability to reproduce in order to be able to continue to maintain their species. Every day even every time there are living things...
- Scapula: Definition, Function, Movement, Muscles That… Scapula: Definition, Function, Movement, Attached Muscles and Diseases - What is a bone scapula and its function?, On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about it other…
- Crafts from Hard Materials: Definition, Types, Techniques,… Crafts from Hard Materials: Definition, Types, Techniques, Stages of How to Make and Examples - What is it handicrafts made of hard materials? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course things…
- Characteristics of Planets: Types of Planets and Their Characteristics Characteristics of Planets: Types of Planets and Their Characteristics - What are the characteristics that a planet must have Planet?, On this occasion, Around the Knowledge.co.id will discuss it, including objectives, examples and naturally…
- Sample Physical Education Questions for Class 11 (XI) SMA/MA/SMK Semester 1 and 2 Examples of Physical Education Questions for Class 11 (XI) for SMA/MA/SMK Semester 1 and 2 (2019 and 2020) - On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss examples of Physical Education Questions for Class 11 Multiple Choice and Essay...
