Organelles of Animal Cells and Their Functions and Explanations of Their Structures
Organelles of Animal Cells and Their Functions and Explanations of Their Structures – What are the functions of the organelles in animal cells? On this occasion About the knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course other things that also cover it. Let's look at the discussion together in the article below to better understand it.
Organelles of Animal Cells and Their Functions and Explanations of Their Structures
The cell is a small unit of the whole body of living things. But in this cell, it turns out that there are also several organelles that can still be further classified. Animal cell is the general name for the eukaryotic cells that make up animal tissues.
Animal cells differ from other eukaryotic cells, such as plant cells, in that animal cells do not have a cell wall, and chloroplasts, and they usually have smaller, if not none, vacuoles. Because they do not have a hard cell wall, animal cells vary in shape. The human cell is a type of animal cell.
The body of an animal, generally consists of many different organs. These organs are composed of tissues and each tissue is composed of cells.
Animal cells are eukaryotic cells that do not have a cell wall like that of plant cells. The shape of the animal cell itself is not fixed and varies. This difference also applies to cell size.
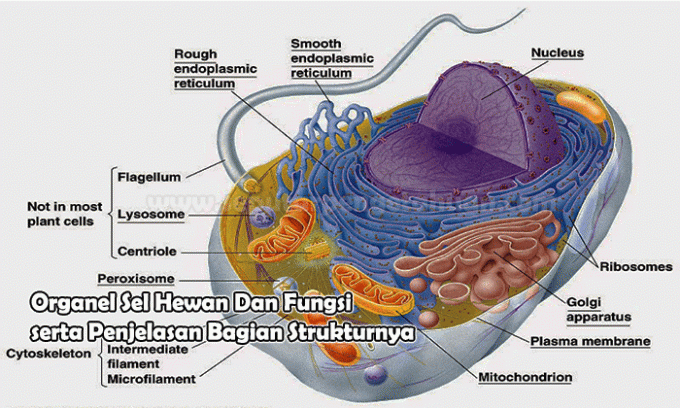
Each of these cells is composed again of the cell organelles that compose it. Here are the organelles that you can find in animal cells, namely the nucleolus, nucleus, rough ER, ER smooth, vesicles, golgi apparatus, mitochondria, vacuoles, cytoplasm, lysosomes, centrosomes and membranes plasma.
Each of these organelles has a varied structure and function. Everything works together to make the animal's body function normally as it should.
Organelle Structure of Animal Cells and Their Functions
Animal cells are a form of eukaryotic cells that form body tissues and then form organs. Smst animal cells are different when compared to plant cells. Plant cells have a cell wall while animal cells do not have a cell wall. This clearly illustrates the difference between animal and plant cells.
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane is the outermost part that wraps the cell composed of fat and protein
The functions of the cell membrane are:
- as a recipient of external stimuli
- Protects cells
- Regulates the entry and exit of substances
-
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is the fluid of the cell and anything dissolved in it, except for the nucleus and organelles, the cytoplasm consists of protein material and also water. The cytoplasm has a non-liquid and non-solid complex colloidal nature that can change depending on the concentration of water, if the concentration When the water concentration is low, the cytoplasm becomes a mushy solid, which is called a gel, if the water concentration is high, the cytoplasm becomes dilute, which is called a gel sol.
The functions of the cytoplasm are:
- Source of cell chemicals
- Where cell metabolism takes place
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum is the part of the cell that has the shape of the threads that are in the cell nucleus. The endoplasmic reticulum is divided into two parts, namely the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (REh) and the rough endoplasmic reticulum (REk). Smooth endoplasmic reticulum is not attached to ribosomes, whereas rough endoplasmic reticulum is attached to ribosomes.
The functions of the Endoplasmic Reticulum are:
- Protein synthesis (REk)
- Synthesizes lipids in cells (REh)
- Means of transport of substances within the cell itself
- Helps detoxify harmful cells in cells (REh)
-
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are the largest organelles in the form of machines in cells. Mitochondria have a shape similar to a cigar which has two layers of indented membranes and are called critas.
Oxygen and glucose combine to form the energy required for metabolism and cellular activity of organelles. Mitochondria in their stump form are called mitochondrions. Mitochondrion is an organelle that converts chemical energy into other energy
-
Microfilaments
Microfilaments are cell organelles made up of actin and myosin proteins. Microfilaments are similar to microtubules but they are softer and smaller in diameter.
The functions of microfilaments are: Play a role in cell movement, endocytosis and exocytosis
-
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that are used to control intracellular digestion under any circumstances. Lysosomes are present in eukaryotic cells.
The function of the lysosome is:
- Controls intracellular digestion
- Entry of macromolecules from outside into the cell by endocytosis mechanism
- Digests matter using phagocytosis
- destruction of damaged cell organelles
-
Peroxisomes (Micro Bodies)
Peroxisomes are small pouches that contain the enzyme catalase whose function is to decompose peroxide (H2O2) which is the waste of metabolism and has toxic properties to water and oxygen which are harmful cell. Peroxisomes are found in liver and kidney cells.
The functions of peroxisomes are:
- Change of fat to carbohydrates
- Decomposes peroxides from toxic metabolic wastes
-
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are compact and small cell organelles that have a diameter of 20 nm which consist of 65% ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and 35% ribosomal protein. Ribosomes work in translating mRNA to form polypeptide chains (proteins) by using the amino acids below the tRNA in the translation process. In cells ribosomes are attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum or the cell nucleus membrane.
The function of the ribosome is: The place where protein synthesis takes place
-
Centrioles
Centrioles are tubular structures that can be found in eukaryotic cells. Centrioles also play a role in cell division and in the formation of cilia and flagella. A pair of centrioles forms a combined structure called a centrosome.
The function of the Centrioles are:
- Plays a role in forming cilia and flagella
- The process of cell division in forming spindle threads
-
Microtubules
Microtubules are cell organelles in the cytoplasm and are found in eukaryotic cells The shape is a long, hollow cylindrical shape with an inner diameter of approximately 12 nm and an outer diameter 25nm. Microtubules consist of spherical globular protein molecules called tubulin, which spontaneously combine to form long, hollow cylinders under certain conditions. Microtubules are rigid.
The function of Microtubules are:
- Gives the shape of the cell
- Protects cells
- Plays a role in the formation of flagella, cilia and centrioles
-
Golgi bodies
The golgi apparatus or golgi apparatus or golgi complex are organelles associated with the excretory function of the cell. Golgi bodies can be found in all eukaryotic cells and exist in excretory functions, such as the kidneys. The Golgi apparatus has the form of small to large flattened sacs bound by a membrane. Each animal cell has 10-20 golgi bodies.
The functions of the Golgi apparatus are:
- Forms lysosomes
- Forms vesicles (sacs) for excretion
- Processing proteins
- form the plasma membrane
-
nucleus
The nucleus is the cell nucleus that regulates and controls cell activity. both metabolism to cell division. The nucleus is present in eukaryotic cells and contains most of the genetic material in the form of long linear DNA and forms chromosomes with proteins. The nucleus consists of parts such as the nuclear membrane, nucleoplasm (karyolymph), chromatin/chromosome, nucleolus.
The functions of the Nucleus are:
- Stores genetic information
- maintain gene integrity
- Controls cell activity by managing gene expression
- Replication site
- Controls metabolic processes in cells
-
Nucleolus
The nucleolus is the area in the cell nucleus that is responsible for the formation of proteins using RNA (ribonucleic acid).
The function of the Nucleolus is: Responsible for the formation of proteins
-
Nucleoplasm
Nucleoplasm, which is a solid and adad fluid in the cell nucleus (nucleus) contains chromatin fibers, which densely form chromosomes and genes that carry genetic information.
The function of Nucleoplasm is to form chromosomes and genes
-
Core Membrane
The nuclear membrane is the main structural element of the nucleus which encloses all organelles and separates the cytoplasm and the nuclear region. The nuclear membrane is impermeable, with most of the molecules that make up the nucleus need a nuclear pore so that the nucleus can cross the membrane.
The functions of the nuclear membrane are:
- Place of exchange of substances between the nuclear material and the cytoplasm
- Protection of the cell nucleus (Nucleus)
Thus the review from About the knowledge.co.id about Animal Cell Organelles And Functions, hopefully can add to your insight and knowledge. Thank you for visiting and don't forget to read other articles.
List of contents
Recommendation:
- Moss Life Cycle: Definition, Structure and Benefits of Moss Moss Life Cycle: Definition, Structure and Benefits of Moss - How is the life cycle of a moss plant?, On this occasion, about the knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course other things too covered it. Let…
- The Collapse of the Kediri Kingdom: History and Legacy The Fall of the Kediri Kingdom: History and Legacy - The Kediri Kingdom or the Kadiri Kingdom or the Panjalu Kingdom was a kingdom that existed in East Java between 1042-1222. The kingdom is in the city…
- LHO Text: Definition, Characteristics, Characteristics, Purpose, Functions,… LHO Text: Definition, Characteristics, Characteristics, Purpose, Function, Structure, Linguistic Rules and Examples - What is what do you mean by LHO Text or Observation Report Text? On this occasion About knowledge.co.id…
- Definition of Cambium: Characteristics, Functions, Types and Structures Definition of Cambium: Characteristics, Functions, Types and Structure - What is Cambium in plants and its functions? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things as well covered it. Let…
- Classification of Living Things: Definition, Purpose, Taxon and… Classification of Living Things: Definition, Purpose, Taxon and Classification System - To more easily recognize the grouping of living things, a classification is needed. On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss the classification of…
- Lymph Circulatory System Functions: Constituent Components And… Functions of the Lymph Circulatory System: Composing Components and Their Anatomy - What is the Function of the Lymph Circulatory System Bening?, On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things that also…
- Understanding Reptiles, Structure, Body Functions and Characteristics Definition of Reptiles, Structure, Body Functions and Characteristics - Living things that live on this earth have various types and their habitats. Some are in the water, in the air, on land, as for those who are...
- Branches of Biology: Functions, Benefits and Explanations Branches of Biology: Functions, Benefits and Explanations - What are the branches of Biology? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it, including functions and of course other things as well covered it. Let…
- Karate: Definition, History, Basic Techniques and Flow Karate: Definition, History, Basic Techniques and Trends - What is Karate? On this occasion, AboutKnowledge.co.id will discuss what Karate is and other things about it. Let's take a look at the discussion on...
- √ Definition of Plant Tissue, Structure, Characteristics, Functions &… Definition of Plant Tissue, Structure, Characteristics, Functions & Types - On this occasion Around Knowledge will discuss Plant Tissues. Which in the discussion this time is one of the materials for…
- Example of Cultural Arts Questions for Class 10 (X) SMA/MA/SMK Semester 1… Examples of Class 10 (X) Cultural Arts Questions for SMA/MA/SMK Semesters 1 and 2 (2019 and 2020) - On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss Multiple Choice Class 10 Cultural Arts Questions and Essay…
- Swimming Material: History, Understanding According to Experts, Style,… Swimming Materials: History, Expert Definition, Styles, Benefits, Basic Principles and Techniques - Anything what needs to be learned in swimming material? discuss…
- Parts of the Skin: Epidermis, Dermis, Structure And… Parts of the Skin: Epidermis, Dermis, Structure and Functions - On this occasion, Se regarding the knowledge.co.id will discuss the parts of the skin and of course about other things that also cover it. Let's see together…
- Mangrove Forests Are: Characteristics, Benefits, Causes of Damage And… Mangrove Forests Are: Characteristics, Benefits, Triggers of Damage and Countermeasures - What is meant by forest mangroves and their functions? On this occasion, Se regarding the knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about it other…
- Types of Roots in Plants, Properties, Functions and… Types of Roots in Plants, Properties, Functions and Structures - What are the different types of roots in plants ?On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course other things too covers it.…
- Cell Structure and Its Functions in Plants and Animals Cell Structure and Its Functions in Plants and Animals - The cell is the smallest unit of living things. Inside the cell there is a protoplasm composed of carbohydrates, fats, proteins and nucleic acids. Structure…
- Definition of Computer Networks, Complete Types and Benefits Complete Understanding of Computer Networks, Types and Benefits - On the last occasion we have discussed the meaning of computers, the meaning of intranets and the internet. This time we will discuss the understanding of computer networks and their benefits.
- Definition of the Cytoskeleton, Function and Structure (Complete) Definition of the Cytoskeleton, Function and Structure (Complete) - Meeting again with Around Knowledge, now we will discuss the cytoskeleton. What is the cytoskeleton? So for those who don't know and who want to know, let's...
- Pre-literate Age: Definition, Age Division, Types… Pre-literate Age: Definition, Age Division, Types of Humans, and Their Legacy - What is meant by The Age of Pre-literacy? On this occasion, Around the Knowledge.co.id will discuss what is the Age of Pre-literacy and other things Which…
- Bacteria and Their Role: Types, Beneficial and… Bacteria and Their Role: Types, Beneficial and Harmful Roles - What are bacteria? Bacteria are single-celled or unicellular organisms, prokaryotes or prokaryotes, microscopic or very small in size. Bacteria contribute...
- Physical Fitness: Definition, Components, Concepts, Elements,… Physical Fitness: Definition, Components, Concepts, Elements, Purpose, Benefits and Forms of Exercise - What's in What do you mean by physical fitness? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss fitness Physical and…
- 2 Dimensional Art Works: Definition, Techniques, Elements, Media… 2 Dimensional Art Works: Definition, Techniques, Elements, Media and Examples - What is meant by 2 Dimensional Art Works?
- Understanding Fossils According to Experts (Full Discussion) Understanding Fossils According to Experts (Full Discussion) - Every living thing that lives in this world will definitely experience death. Not only humans but animals and plants will all encounter…
- Short Story Text: Definition, Characteristics, Structure, Elements and Examples Short Story Text: Definition, Characteristics, Structure, Elements and Examples - What is a Short Story Text? Let us…
- 6 Functions of Roots in Plants and Their Types 6 Functions of Roots in Plants and Their Types - Friends, all of you must already know the shape of the roots that we will discuss on this occasion. Where the root is an important part apart from...
- Animal Cells: Definition, Parts and Functions Animal Cells: Definition, Parts and Functions - In this explanation, you will learn about Animal Cells. Which includes understanding, the parts of animal cells and their functions with complete and easy discussion...
- Motivational short stories: definition, writing tips and examples Motivational Short Stories: Definition, Writing Tips and Examples - What is a Motivational Short Story?, On On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss whether it is the Short Story of Friendship and other matters about it. Let's see…
- Megalithic: Definition, Characteristics, Belief Systems and… Megalithic: Definition, Characteristics, Belief Systems and Legacy - What is meant by Megalithic and when did it occur? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss what is Megalithic and other things...
- Movement System in Humans: Bones, Joints, Muscles,… Movement System in Humans: Bones, Joints, Muscles, Functions, Abnormalities and Disturbances - What are the systems motion in the human body?, On this occasion, Se regarding the knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about…
- Business Entity: Definition, Form, Type and Comparison Business Entity: Definition, Form, Type and Comparison - What is meant by a Business Entity? This time around the knowledge.co.id will discuss the Business Entity and the things that surround it. Let's see together…
