Vertical Downward Motion: Definition, Characteristics, Physical Quantities, Formulas and Example Problems
Vertical Downward Motion: Definition, Characteristics, Physical Quantities, Formulas and Example Problems – On this occasion About the knowledge.co.id will discuss Vertical Downward Motion, formulas and of course other things that also cover it. Let's look at the discussion together in the article below to better understand it.
Vertical Downward Motion: Definition, Characteristics, Physical Quantities, Formulas and Example Problems
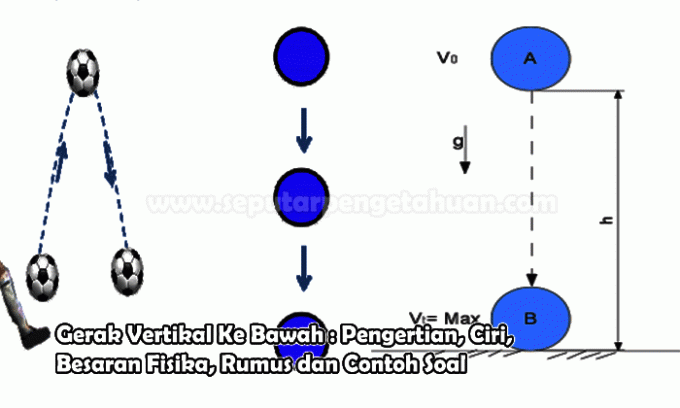
Downward Vertical Motion (GVB) is a form of rectilinear motion which is included in Straight Changing Motion Regular (GLBB), where the movement of objects begins with the initial velocity and the vertical trajectory of the object's movement lower.
In vertical downward motion, the longer the object's velocity will increase, resulting in an acceleration of the object. This acceleration is influenced by the force of gravity so that the value of the acceleration is equal to the value of the acceleration due to gravity (a = g).
Vertical Downward Motion must have an initial velocity, if the object does not have an initial velocity or falls by itself then the movement that occurs is Free Falling Motion (GJB). An example of downward vertical motion is when we throw a rock from a certain height.
Characteristics of Vertical Downward Motion (GVB)
- The trajectory is a vertical straight line
- Move from the highest point to the lowest point
- Has initial speed
- The longer the speed of the object increases before finally stopping on the surface
- Due to the influence of gravity, the acceleration is equal to the acceleration due to gravity which is positive (a=g).
Physical quantity in downward vertical motion (GVB)
-
Speed (v)
Speed is a quantity in physics that shows how fast an object moves from one place to another.
The international unit for speed is meters per second (m/s). However, in Indonesia more often use units of kilometers per hour (km/hour).
Speed is obtained by multiplying the distance traveled by the time traveled. The symbol for speed is v (lowercase).
In the formula for vertical downward motion there are two speeds, namely the initial velocity (vo), which is the speed at which the object moves for the first time, and the velocity at a certain second t (vt).
Distance(s)
Distance is a quantity in physics that shows how far an object changes position in a certain path. The international unit of distance is (m).
The distance is obtained by multiplying the speed by the travel time. The distance in the downward vertical motion is the height of the object from the surface.
Travel Time (t)
Travel time is the time it takes an object to move from one position to another at a certain speed.
The symbol for the past time is t (lowercase) with the international unit second (s). The travel time is obtained by dividing the distance by the speed.
Acceleration (a)
Acceleration is a change in velocity that occurs in an object either due to the influence of a force acting on the object or because of the state of the object.
Because changes to objects in downward vertical motion are affected by the force of gravity, their acceleration is equal to the acceleration of gravity.
The value of the acceleration due to gravity that is used if it is not known in a problem is 9.81m/s² or evens out to 10m/s². The symbol for gravity is g (lowercase).
Downward Vertical Motion Formula (GVB)
Vt = V0 + g.t
h = Vo. t + ½ g. t²
Vt²= V0² + 2. g. h
Information :
- Vt: Speed at time t (m/s)
- V0: Initial speed (m/s)
- g: Acceleration of gravity (m/s2)
- h: Height (m)
- t: Time(s)
In vertical downward motion (GVB) there are a number of basic formulas that can be used to solve physics problems concerned with upward vertical motion. Those formulas are:
Initial Velocity and Final Velocity Formulas
Vertical upward motion (GVA) is the motion of objects from zero elevation (initial position) pointing upwards and will arrive at a point called the highest point. The highest point is the maximum height or greatest exodus that an object can reach.
In order to move up, the object must have an initial velocity, so that the value of the initial velocity of the object is not equal to zero. The initial velocity in the upward vertical motion will affect the maximum elevation that can be reached by the object. The greater the initial velocity, the greater the maximum elevation.
Pay attention to the picture above. Suppose an object is moving vertically upwards with an initial velocity v0. When landing at a certain point its speed decreases to vt due to the influence of the acceleration due to gravity. The object's speed will continue to decrease until finally its speed becomes zero, which is at its highest point.
The velocity at this highest point is called the final acceleration of the object moving vertically upwards.
v = 0
Information:
v0 = initial velocity of the object (m/s)
v = object's final velocity (m/s)
Object Acceleration Formula
As in the two types of vertical motion discussed earlier, namely GJB and GVB, in upward vertical motion (GVA), the acceleration felt by an object is also the acceleration of gravity. However, because the direction of the object's upward motion is against the direction of Earth's gravity, the acceleration due to Earth's gravity acts as a deceleration.
Deceleration is acceleration which has a negative value to the extent that the following negative acceleration causes the object's speed to decrease. The figure above indicates that the value of the acceleration of the object's motion is equal to the magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity, which is negative.
a = -g
Information:
g = 9.8 m/s2 or 10 m/s2
If in the problem the value of g is not known, then we use the value of 10 m/s2 as the value of the acceleration due to gravity in free fall or other types of vertical motion.
Displacement Formulas and Height of Objects
In vertical motion, elevation (h) is measured from the ground or floor leading to the object's position at a certain elevation. Look at the picture above, in the vertical upward motion, the exodus (s) of the object is measured from the initial position of the object (on the floor) towards the position of the object at a certain elevation.
So in vertical upward motion, the object's exodus is equal to its height. That's why, the exodus in vertical motion is symbolized by h. By substituting equations 4 and 6 into equation 2, the exodus or elevation of an object in vertical upward motion can be calculated using the formula:
s |
= |
s0 + v0t ± ½ at2 |
h |
= |
0 + v0t − ½ gt2 |
h |
= |
v0t − ½ g.t2 |
Information :
h = displacement or height (m)
v0 = initial speed (m/s)
g = acceleration due to gravity (m/s2)
t = time (s)
Velocity Formula After t Seconds
Because the direction of motion is against the direction of gravity, the object feels a slowdown or a negative acceleration value. If the initial velocity of the object is v0 and the velocity of the object in t seconds is vt, then by substituting equation 6 into equation 1, the formula for the object's velocity after t seconds in GVA is as follows:
vt |
= |
v0 ± at |
vt |
= |
v0 − gt |
Meanwhile, if you substitute equations 4 and 5 into equation 3, you will get the velocity formula after t seconds as follows:
vt2 |
= |
v02 ± 2as |
vt2 |
= |
v02 − 2gh |
Information:
vt = speed of object after t seconds (m/s)
v0 = initial speed (m/s)
g = acceleration due to gravity (m/s2)
t = time (s)
h = object displacement (m)
Problems example
Problem 1
Ayu throws a ball from a multi-storey building with an initial speed of 40 m/s, the ball reaches the ground in 4 seconds. What is the speed when the ball hits the ground???
Discussion :
Is known :
vo = 40 m/s
t = 4 s
Asked: Vt…. ?
Answer :
vt = vo + g.t
vt = 40 m/s + (10)(4)
vt = 80m/s
Problem 2
A child throws a stone into a well with an initial speed of 5 m/s and it hits the surface of the water after 2 seconds. Calculate the depth of the well?
Discussion :
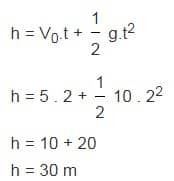
So the depth of the well is 30 meters.
Problem 3
A small box is thrown from a building with a height of 80 meters and an initial speed of 10 m/s. How long does it take the box to reach the ground?
Discussion :
Vt2 = V02 + 2. g. h
Vt2 = 102 + 2. 10. 80
Vt2 = 100 + 1600
Vt2 = 1700 m/s
Enter a V valuet to the following equation:
Vt = V0 + g.t
41 = 10 + 10.t
10t = 31
t = 3.1 seconds
So the time it takes the box to reach the ground is 2.1 seconds.
Thus the review from About the knowledge.co.id about Downward Vertical Move, hopefully can add to your insight and knowledge. Thank you for visiting and don't forget to read other articles.
List of contents
Recommendation:
- Types of Drones, Terms, Parts, Basic Principles And… Types of Drones, Terms, Parts, Basic Principles and Movement - What are the types of drones and function?, On this occasion Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course other things Also…
- 12 Definitions of Motion According to Experts and Its Types (Complete) 12 Definitions of Motion According to Experts and Its Types (Complete) - After we discussed understanding physics, then we will discuss the meaning of motion and the types of motion that are internal matter physics…
- Three Variable Linear Equation System: Features, Components,… System of Three Variable Linear Equations: Features, Components, Solving Methods and Example Problems - What is in what do you mean by a system of three-variable equations? On this occasion, Se regarding the knowledge.co.id will discuss it...
- Microscope Images: Definition, History, Types, Parts, How to… Microscope Images: Definition, History, Types, Parts, How Microscopes Work and Care - How close are they do you recognize the shape and function of a microscope? At this time, about the knowledge Microscope…
- √ Definition of Swimming, Types of Styles, Benefits and Risks… Definition of Swimming, Types of Style, Benefits and Risks (Complete) - The following article explains about swimming. Which explains the meaning of swimming, various swimming styles and the benefits of swimming with a brief discussion...
- DNA and RNA: Definition, Characteristics, Differences and… DNA and RNA: Definition, Characteristics, Differences and Discussion of the Process - What are the meanings and differences of DNA and RNA? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course other things that...
- Baseball: Definition, History, Techniques, Means, How to… Baseball: Definition, History, Techniques, Facilities, How to Play and Game Rules - What's in call it the Kasti Ball Game? Ball…
- Motivational short stories: definition, writing tips and examples Motivational Short Stories: Definition, Writing Tips and Examples - What is a Motivational Short Story?, On On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss whether it is the Short Story of Friendship and other matters about it. Let's see…
- Friendship Short Stories: Definition, Writing Tips and Examples Friendship Short Stories: Definition, Writing Tips and Examples - What are Friendship Short Stories like? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss whether it is the Short Story of Friendship and other things about it. Let's see together…
- Cone formulas, characteristics, properties, elements and examples of problems Cone Formulas, Characteristics, Properties, Elements and Examples Problem - How to calculate the area and volume of a shape cone space?, On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things Which…
- √ Understanding Speed and Agility According to Experts &… Understanding Speed and Agility According to Experts & Kinds - In this world there are lots of living things that can move freely to and fro, up and down, and so on. Understanding Speed…
- Dimensions of Momentum: Definition, Formulas, Fundamentals and… Dimensions of Momentum: Definition, Formulas, Principal Quantity and Example Problems - What do you know about Dimensions of Momentum? On this occasion, about the knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course things which also…
- Computer Hardware: How it Works, Types, Examples and… Computer Hardware: How it Works, Types, Examples and Functions - In today's computerized era, we are definitely familiar with computers and their devices. However, some may not know...
- Dynamic Fluids: Types, Features, Bernoulli Equation, Theorems… Dynamic Fluids: Types, Properties, Bernoulli's Equation, Toricelli's Theorem, Formulas And Examples of Problems - What is it dynamic fluids and their types? about…
- Characteristics of Planets: Types of Planets and Their Characteristics Characteristics of Planets: Types of Planets and Their Characteristics - What are the characteristics that a planet must have Planet?, On this occasion, Around the Knowledge.co.id will discuss it, including objectives, examples and naturally…
- Derived Algebraic Functions: Formulas, Applications, Notation, Multiplication… Derivative of Algebraic Functions: Formulas, Applications, Notation, Multiplication of Division by Two Functions and Example Problems - Do you understand what is meant by Derivative of an Algebraic Function? On occasion…
- Specific Gravity: Definition, Formula, Use and Difference… Specific Gravity: Definition, Formula, Use and Difference with Density - What is meant by Specific Gravity and What is the Unit Formula? discuss it...
- The Watt Formula: Definition, Units, Symbols and Relationships… The Watt Formula: Definition, Unit, Symbol and Relationship with Amperes and Volts - What is the watt formula and how to implement it? things…
- Adsorption: Definition, Working Principle, Types, Factors That… Adsorption: Definition, Working Principle, Types, Influencing Factors and Examples - What is Adsorption?, On this occasion, about the knowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course other things as well covered it. Let's see…
- The Collapse of the Kediri Kingdom: History and Legacy The Fall of the Kediri Kingdom: History and Legacy - The Kediri Kingdom or the Kadiri Kingdom or the Panjalu Kingdom was a kingdom that existed in East Java between 1042-1222. The kingdom is in the city…
- Ribosomes: Definition, Types, Functions, Forms, and Structures Ribosomes: Definition, Types, Functions, Shapes, and Structures - Ever heard of the term ribosome? On this occasion, we will discuss what is meant by ribosomes? Let's see the explanation...
- Scapula: Definition, Function, Movement, Muscles That… Scapula: Definition, Function, Movement, Attached Muscles and Diseases - What is a bone scapula and its function?, On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about it other…
- Table Tennis: Definition, History, Techniques, Equipment,… Table Tennis: Definition, History, Techniques, Equipment, Rules, Types of Strokes and Scoring Systems - What do you know about Table Tennis? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss whether...
- Example of historical story text in Indonesia Examples of historical story texts in Indonesia – What are examples of historical stories like? This time around the knowledge.co.id will discuss examples of historical stories and their structure. Let's take a look at the discussion in the article on…
- √ Definition of Energy, Its Forms and Benefits for Life… Definition of Energy, Forms and Benefits for Complete Life - In this discussion we will explain about energy. Which includes the meaning of energy, forms of energy and the benefits of energy for life discussed...
- Properties of Exponential Number Operations With Example Problems And… Properties of Raised Number Operations With Examples of Problems and Their Solutions - What are the mathematical operations on numbers rank?, On this occasion Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss it and of course about other things as well covered it. Let…
- Nouns Are: Characteristics, Types, Uses and Examples Nouns Are: Characteristics, Types, Uses and Examples - On this occasion, Around Knowledge will explain about Nouns. In this case the noun is a noun that functions as a subject or...
- √ Understanding Particle Dynamics, Types of Forces and Relationships… Definition of Particle Dynamics, Types of Forces and Mass Relations - In this discussion we will explain about particle dynamics. Which includes the understanding of particle dynamics, the types of particle dynamics forces and the relationship...
- Hexagonal Prism: Definition, Types, Elements and Construct Formulas… Hexagonal Prism: Definition, Types, Elements and Formulas for Building a Prism Space - Hello guys, do you know what a hexagonal prism is? On this occasion, Seputarknowledge.co.id will discuss what a hexagonal prism is...
- Sprint Running: Definition, History, Benefits of Sprint Running Sprint Running: Definition, History, Benefits of Sprint Running - On this occasion, Around Knowledge will discuss Sprint Running. Which in this discussion explains Sprint Running: Understanding,…
